The Earth in the Solar System Chapter 1
सौरमंडल में पृथ्वी अध्याय 1
Solar System (सौर प्रणाली)
The sun, nine planets, satellites, asteroids and meteoroids form the solar system.
सूर्य, नौ ग्रह, उपग्रह, क्षुद्रग्रह और उल्कापिंड मिलकर सौरमंडल का निर्माण करते हैं।
The Sun (सूरज)
- The sun is in the center of the solar system. (सूर्य सौरमंडल के केंद्र में है।)
- It is made up of extremely hot gases. (यह अत्यधिक गर्म गैसों से बना होता है।)
- The sun is about 150 million km away from the earth. (सूर्य पृथ्वी से लगभग 150 मिलियन किमी दूर है।)

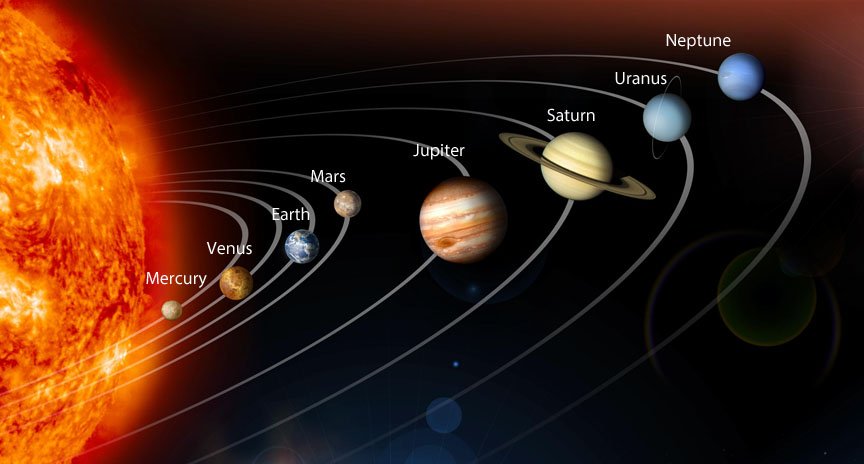
Planets (ग्रहों)
- There are nine planets in our solar system. (हमारे सौरमंडल में नौ ग्रह हैं।)
- The nine planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn , Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. (नौ ग्रह बुध, शुक्र, पृथ्वी, मंगल, बृहस्पति, शनि ग्रह, यूरेनस, नेपच्यून और प्लूटो हैं।)
- Planets move around the sun in a fixed orbit. (ग्रह एक निश्चित कक्षा में सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं।)
- Mercury is the nearest planet. (बुध निकटतम ग्रह है।)
- Pluto is the farthest planet. (प्लूटो सबसे दूर का ग्रह है।)
- A new planet 2003 UB313 has been discovered. It is bigger than Pluto and is farthest from the sun. (एक नया ग्रह 2003 UB313 खोजा गया है। यह प्लूटो से बड़ा है और सूर्य से सबसे दूर है।)
Earth (धरती)
- It is the third nearest planet to the sun and fifth largest planet of our solar system. (यह सूर्य का तीसरा निकटतम ग्रह है और हमारे सौर मंडल का पांचवां सबसे बड़ा ग्रह है।)
- The earth is a unique planet because it supports life. (पृथ्वी एक अनूठा ग्रह है क्योंकि यह जीवन का समर्थन करती है।)
- It is also called the blue planet. (इसे नीला ग्रह भी कहा जाता है।)
- Its shape is Geoid. (इसका आकार जियोइड है।)

The Moon (चांद)
- It is the only satellite of the earth. (यह पृथ्वी का एकमात्र उपग्रह है।)
- Its diameter is one-quarter of the earth. ‘(इसका व्यास पृथ्वी का एक चौथाई है।)
- It is about 3.84,400 km away from us. (यह हमसे लगभग 3,84,400 किमी दूर है।)
- It moves around the earth in about 27 days. (यह लगभग 27 दिनों में पृथ्वी का चक्कर लगाता है।)
- Only one side of the moon is visible to us on the earth. (पृथ्वी पर हमें चन्द्रमा का केवल एक ही भाग दिखाई देता है।)
- No life exists on moon as it has neither water nor air. (चंद्रमा पर कोई जीवन मौजूद नहीं है क्योंकि इसमें न तो पानी है और न ही हवा।)

Asteroids (क्षुद्र ग्रह)
- They are numerous tiny bodies which move around the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. (वे असंख्य छोटे पिंड हैं जो मंगल और बृहस्पति की कक्षाओं के बीच सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं।)
- The largest asteroid is the Ceres. (सबसे बड़ा क्षुद्रग्रह सेरेस है।)

Meteoroids (उल्कापिंड)
- The small pieces of rocks which move around the sun are called meteoroids. (चट्टानों के छोटे-छोटे टुकड़े जो सूर्य के चारों ओर चक्कर लगाते हैं, उल्कापिंड कहलाते हैं।)
- Our solar system is a part of the Milky Way galaxy. (हमारा सौर मंडल मिल्की वे आकाशगंगा का एक हिस्सा है।)
- Milky Way galaxy was named Akash Ganga. (मिल्की वे आकाशगंगा का नाम आकाश गंगा रखा गया।)
- There are millions of galaxies that make the Universe. (ब्रह्मांड बनाने वाली लाखों आकाशगंगाएँ हैं।)

The Stars and the MOON are celestial bodies which are visible only at night in the sky. During daytime, the power of the sun’s light renders them invisible. (तारे और चंद्रमा आकाशीय पिंड हैं जो केवल रात में आकाश में दिखाई देते हैं। दिन के समय, सूर्य के प्रकाश की शक्ति उन्हें अदृश्य बना देती है।)
The moon appears differently on different nights—like the Full Moon only once a month, on the poornima night whereas on the fifteenth night after that, there is no moon in the sky (amavasya). (चंद्रमा अलग-अलग रातों में अलग-अलग दिखाई देता है – जैसे पूर्णिमा की रात को महीने में केवल एक बार पूर्णिमा की रात जबकि उसके बाद पंद्रहवीं रात को आकाश में चंद्रमा (अमावस्या) नहीं होता है।)
Some celestial bodies are big and hot since they are made of gases. They are called Stars. The sun is also a star. We do not feel the heat and light of the stars other than the sun since they are very far away from us. (कुछ खगोलीय पिंड बड़े और गर्म होते हैं क्योंकि वे गैसों से बने होते हैं। उन्हें सितारे कहा जाता है। सूर्य भी एक तारा है। सूर्य के अलावा अन्य तारों का ताप और प्रकाश हमें महसूस नहीं होता क्योंकि वे हमसे बहुत दूर हैं।)
Groups of stars that are visible in definite patterns are called Constellations. Ursa Major (the Big Bear), The Small Bear (Saptarishi), etc are some well-known constellations. (निश्चित पैटर्न में दिखाई देने वाले तारों के समूह को तारामंडल कहते हैं। उरसा मेजर (बड़ा भालू), छोटा भालू (सप्तऋषि), आदि कुछ प्रसिद्ध नक्षत्र हैं।)
The Pole Star is known to retain the same position every night in the sky. It is also called the North Star since it helps in knowing the North direction. (ध्रुव तारा हर रात आकाश में एक ही स्थिति बनाए रखने के लिए जाना जाता है। इसे उत्तर सितारा भी कहा जाता है क्योंकि यह उत्तर दिशा को जानने में मदद करता है।)
There are celestial bodies that do not have their own heat and light. They reflect the light they get from stars. Such bodies are the Planets. We live on the earth, a planet. Most planets have Satellites, which are celestial bodies that revolve around a particular planet. The moon is the only satellite of the earth. (ऐसे खगोलीय पिंड हैं जिनकी अपनी ऊष्मा और प्रकाश नहीं है। वे तारों से प्राप्त प्रकाश को परावर्तित करते हैं। ऐसे पिंड ग्रह हैं। हम पृथ्वी पर रहते हैं, एक ग्रह। अधिकांश ग्रहों में उपग्रह होते हैं, जो आकाशीय पिंड होते हैं जो किसी विशेष ग्रह की परिक्रमा करते हैं। चन्द्रमा पृथ्वी का एक मात्र उपग्रह है।)
The earth and moon are part of a bigger system (or family) of celestial-bodies, called the Solar System. The sun is the “head” of this system and is present at its centre. The planets revolve around the sun, while the satellite revolves around the placets. The planets, in addition to revolving around the sun, also rotate about their own axis. (पृथ्वी और चंद्रमा खगोलीय पिंडों की एक बड़ी प्रणाली (या परिवार) का हिस्सा हैं, जिसे सौर मंडल कहा जाता है। सूर्य इस प्रणाली का “प्रमुख” है और इसके केंद्र में मौजूद है। ग्रह सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं, जबकि उपग्रह ग्रहों के चारों ओर घूमते हैं। ग्रह, सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमने के अलावा, अपनी धुरी पर भी घूमते हैं।)
The sun is made of extremely hot gases, and it provides heat and light to the rest of the solar system. It is about 150 million kilometres away from the earth. (सूर्य अत्यधिक गर्म गैसों से बना है, और यह शेष सौर मंडल को गर्मी और प्रकाश प्रदान करता है। यह पृथ्वी से लगभग 150 मिलियन किलोमीटर दूर है।)
All the planets of the solar system are listed below: (in the order of their distance from sun) (सौरमंडल के सभी ग्रह नीचे सूचीबद्ध हैं: (सूर्य से उनकी दूरी के क्रम में)
- Mercury (planet nearest to the Sun) (बुध (सूर्य के निकटतम ग्रह))
- Venus (शुक्र)
- Earth (धरती)
- Mars (मंगल)
- Jupiter (बृहस्पति)
- Saturn (शनि ग्रह)
- Uranus (अरुण ग्रह)
- Neptune (नेप्च्यून)
Mnemonic: (स्मरणीय)
To memorise the names of the eight planets in the order of their distance from the sun (सूर्य से दूरी के क्रम में आठ ग्रहों के नाम याद करना)
My Very Efficient Mother Just Served Us Nuts
Where the beginning of each word is the same as the first letter of the planet existing at that position in the order (check the list above) (जहां प्रत्येक शब्द की शुरुआत क्रम में उस स्थिति में मौजूद ग्रह के पहले अक्षर के समान हो (उपरोक्त सूची की जांच करें)
Till August 2006, Pluto was also a planet. But it is now recognised as a “dwarf planet”. (अगस्त 2006 तक प्लूटो भी एक ग्रह था। लेकिन अब इसे “बौने ग्रह” के रूप में मान्यता प्राप्त है।)
The shape of the earth is called a Geoid. This means it is not perfectly spherical, since it is flattened at the poles. The earth is probably the only planet that can support life. This is because its temperature, resources like water and oxygen, etc are present in the proportions appropriate for life. The earth, with its 2/3 rd of surface covered with water, appears blue from space and is called Blue Planet. (पृथ्वी के आकार को जियोइड कहा जाता है। इसका मतलब यह है कि यह पूरी तरह गोलाकार नहीं है, क्योंकि यह ध्रुवों पर चपटा है। पृथ्वी शायद एकमात्र ऐसा ग्रह है जो जीवन का समर्थन कर सकता है। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि इसका तापमान, संसाधन जैसे पानी और ऑक्सीजन आदि जीवन के लिए उपयुक्त अनुपात में मौजूद हैं। पृथ्वी, जिसकी सतह का 2/3 भाग पानी से ढका हुआ है, अंतरिक्ष से नीले रंग की दिखाई देती है और इसे नीला ग्रह कहा जाता है।)
The Moon’s diameter is 1/4TH of that of the earth. It is 3,84,400 km away from earth. It completes a revolution around the earth in about 27 days. Incidentally, it also takes around the same time for a rotation about its own axis. It does not support life. (चंद्रमा का व्यास पृथ्वी के व्यास का एक चौथाई है। यह पृथ्वी से 3,84,400 किमी दूर है। यह लगभग 27 दिनों में पृथ्वी के चारों ओर एक चक्कर पूरा करता है। संयोग से, यह अपनी धुरी के चारों ओर एक चक्कर लगाने में भी लगभग इतना ही समय लेता है। यह जीवन का समर्थन नहीं करता है।)
There are several other tiny bodies in space (the Asteroids) that move around the sun. There is a “belt” of such objects, called the Asteroid Belt, between Mars and Jupiter. (अंतरिक्ष में कई अन्य छोटे पिंड (क्षुद्रग्रह) हैं जो सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं। मंगल और बृहस्पति के बीच ऐसी वस्तुओं का एक “बेल्ट” है, जिसे क्षुद्रग्रह बेल्ट कहा जाता है।)
There exist small pieces of rocks (Meteroids) which also move around the sun. (चट्टानों के छोटे-छोटे टुकड़े (Meteroids) मौजूद हैं जो सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं।)
The Milky Way is the galaxy (a huge system of billions of stars) we live in. The Milky Way is further a part of a bigger collection of galaxies, called the Universe, (refer Flow¬Learning) (मिल्की वे वह आकाशगंगा है (अरबों सितारों की एक विशाल प्रणाली) जिसमें हम रहते हैं। मिल्की वे आकाशगंगाओं के एक बड़े संग्रह का एक हिस्सा है, जिसे ब्रह्मांड कहा जाता है, (फ्लो¬लर्निंग देखें)
Celestial Body: An object in the universe (but not on the earth) is said to be a celestial body. Examples are sun, earth, moon, stars, etc.
आकाशीय पिंड: ब्रह्मांड में एक वस्तु (लेकिन पृथ्वी पर नहीं) को आकाशीय पिंड कहा जाता है। उदाहरण सूर्य, पृथ्वी, चंद्रमा, तारे आदि हैं।)
Star: A celestial body that is characterized by being very hot and big, and made of gases is a star. A star typically has its own heat and light.
तारा: एक खगोलीय पिंड जो बहुत गर्म और बड़ा होने की विशेषता है, और गैसों से बना है, एक तारा है। आमतौर पर एक तारे की अपनी ऊष्मा और प्रकाश होता है।)
Full Moon Night: A night when the moon is visible from the earth as a full sphere is called the Full Moon night, and it occurs once a month.
पूर्णिमा की रात: एक रात जब चंद्रमा पृथ्वी से एक पूर्ण क्षेत्र के रूप में दिखाई देता है, पूर्णिमा की रात कहलाती है, और यह महीने में एक बार होती है।)
New Moon Night: The fifteenth night after the Full Moon night, when the moon is not visible at all in the sky, is called the New Moon night.
अमावस्या की रात: पूर्णिमा की पंद्रहवीं रात, जब चंद्रमा आकाश में बिल्कुल भी दिखाई नहीं देता है, उसे अमावस्या की रात कहा जाता है।)
Constellation: A group of several stars which can usually be recognized by a definite pattern is called a constellation. An example is Ursa Major.
तारामंडल (Constellation): कई तारों का समूह जिसे आमतौर पर एक निश्चित पैटर्न द्वारा पहचाना जा सकता है, एक तारामंडल कहलाता है। एक उदाहरण उरसा मेजर है।)
Planets: A celestial body which revolves around a particular star in an orbit, and gets all its light from that star, is called a planet. Earth is a planet.
ग्रह: एक खगोलीय पिंड जो एक कक्षा में किसी विशेष तारे की परिक्रमा करता है, और अपना सारा प्रकाश उसी तारे से प्राप्त करता है, ग्रह कहलाता है। पृथ्वी एक ग्रह है।)
Satellites: A celestial body which revolves around a planet in a particular orbit is called a satellite. The moon is a satellite of the Earth.
उपग्रह: वह आकाशीय पिंड जो किसी ग्रह के चारों ओर एक विशेष कक्षा में परिक्रमा करता है, उपग्रह कहलाता है। चंद्रमा पृथ्वी का एक उपग्रह है।)
Orbit: The particular and definite elliptical path in which a planet (or satellite) always remains, is called the orbit of that planet (or satellite).
कक्षा (Orbit): कोई ग्रह (या उपग्रह) सदैव जिस विशिष्ट एवं निश्चित अण्डाकार पथ में रहता है, उस ग्रह (या उपग्रह) की कक्षा कहलाती है।)
Sun: The Sun is a star that acts as the “head” of the solar system and around which all planets revolve: Note that the sun is not at the center of the orbit, instead it is like in the figure above.
सूर्य: सूर्य एक तारा है जो सौर मंडल के “सिर” के रूप में कार्य करता है और जिसके चारों ओर सभी ग्रह घूमते हैं: ध्यान दें कि सूर्य कक्षा के केंद्र में नहीं है, बल्कि यह ऊपर की आकृति की तरह है।
Inner Planets: The Inner Planets are the planets that orbit around the sun between the suns and the asteroid belt that is, are close to the sun. These are: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
आंतरिक ग्रह: आंतरिक ग्रह वे ग्रह हैं जो सूर्य के चारों ओर सूर्य के चारों ओर परिक्रमा करते हैं और क्षुद्रग्रह बेल्ट अर्थात सूर्य के करीब हैं। ये हैं: बुध, शुक्र, पृथ्वी और मंगल।)
Outer Planets: The Outer Planets are the planets that orbit the sun beyond the asteroid belt, that is, are very far away from the sun. These are: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
बाहरी ग्रह: बाहरी ग्रह वे ग्रह हैं जो क्षुद्रग्रह बेल्ट से परे सूर्य की परिक्रमा करते हैं, अर्थात सूर्य से बहुत दूर हैं। ये हैं: बृहस्पति, शनि, यूरेनस और नेपच्यून।)
Geoid: The shape of the earth is called a geoid. A geoid is spherical except for the flattening at two places diametrically opposite to each other.
भूआभ: पृथ्वी के आकार को भूआभ कहते हैं। जियॉएड गोलाकार होता है सिवाय दो स्थानों पर चपटे होने के अलावा एक दूसरे के विपरीत।)
Poles: The two places diametrically opposite to each other and which lie on the axis about which a spherical body rotates are called poles.
ध्रुव: वे दो स्थान जो एक दूसरे के बिल्कुल विपरीत होते हैं और जो उस अक्ष पर स्थित होते हैं जिसके चारों ओर एक गोलाकार पिंड घूमता है, ध्रुव कहलाते हैं।)
Asteroids: A large number of tiny celestial bodies which move around the sun, and are mainly present in a belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, are called Asteroids.
क्षुद्रग्रह: बड़ी संख्या में छोटे आकाशीय पिंड जो सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमते हैं, और मुख्य रूप से मंगल और बृहस्पति की कक्षाओं के बीच एक बेल्ट में मौजूद होते हैं, क्षुद्रग्रह कहलाते हैं।)
Meteoroid: Small pieces of rocks which move around the sun are called meteoroids.
उल्कापिंड: चट्टानों के छोटे-छोटे टुकड़े जो सूर्य के चारों ओर चक्कर लगाते हैं, उल्कापिंड कहलाते हैं।)
Galaxy: A galaxy is a collection of innumerable stars. Most stars have their own families like the solar system. The Milky Way is the galaxy in which we live.
आकाशगंगा: एक आकाशगंगा असंख्य तारों का संग्रह है। सौरमंडल की तरह अधिकांश तारों का अपना परिवार होता है। मिल्की वे वह आकाशगंगा है जिसमें हम रहते हैं।)
Universe: The Universe is the largest unit in which we live. It is a collection of galaxies. There is only one Universe and everything that exists in this Universe itself.
ब्रह्मांड: ब्रह्मांड सबसे बड़ी इकाई है जिसमें हम रहते हैं। यह आकाशगंगाओं का संग्रह है। केवल एक ही ब्रह्माण्ड है और सब कुछ जो इस ब्रह्माण्ड में ही विद्यमान है।)
Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Chapter 2
ग्लोब अक्षांश और देशांतर अध्याय 2
Globe is a true model of the Earth. (ग्लोब पृथ्वी का एक सच्चा मॉडल है।)
A needle is fixed through the globe in a tilted manner, which is called its axis. (ग्लोब के माध्यम से एक सुई झुकी हुई तरीके से तय की जाती है, जिसे इसकी धुरी कहा जाता है।)
The imaginary line running on the globe divides it into equal parts. This line is known as the Equator. (ग्लोब पर चलने वाली काल्पनिक रेखा इसे बराबर भागों में विभाजित करती है। इस रेखा को भूमध्य रेखा के नाम से जाना जाता है।)
All parallel circles from the Equator up to the poles are called parallels of latitude. Latitude is measured in degrees. (भूमध्य रेखा से ध्रुवों तक के सभी समानांतर वृत्तों को अक्षांश के समानांतर कहा जाता है। अक्षांश को डिग्री में मापा जाता है।)
As we move away from the Equator, the size of the parallels of latitude decreases. (जैसे-जैसे हम भूमध्य रेखा से दूर जाते हैं, अक्षांशों के समानांतरों का आकार घटता जाता है।)
The four important parallels of latitude are: (अक्षांश के चार महत्वपूर्ण समानांतर हैं)
- Tropic of Cancer ( (कर्क रेखा ( °N))
- Tropic of Capricorn ( (मकर रेखा ( )
- Arctic of Circle ( (वृत्त का आर्कटिक ( °N)
- Antarctic Circle ( (अंटार्कटिक सर्कल
Heat Zones of the Earth (पृथ्वी के ताप क्षेत्र)
- Torrid Zone receives the maximum heat. (उष्ण कटिबंध में अधिकतम ताप प्राप्त होता है।)
- The temperate zone has a moderate temperature. (समशीतोष्ण क्षेत्र में मध्यम तापमान होता है।)
- The Frigid Zone has a cold climate as the sun rays are always slanting. (शीत क्षेत्र में ठंडी जलवायु होती है क्योंकि सूर्य की किरणें हमेशा तिरछी होती हैं।)

Longitudes (देशांतर)
- The line of reference running from the North Pole to the South Pole is called Meridians of Longitude. (उत्तरी ध्रुव से दक्षिणी ध्रुव तक जाने वाली संदर्भ रेखा को देशांतर रेखा कहा जाता है।)
- The distance between them is measured in ‘degrees of longitude’. (उनके बीच की दूरी को ‘देशांतर की डिग्री’ में मापा जाता है।)
- All meridians are of equal length. (सभी देशांतर रेखाएँ समान लंबाई की होती हैं।)
- The meridian which passes through Greenwich, where the British Royal Observatory is located, is called the Prime Meridian. (जो मध्याह्न रेखा ग्रीनविच से होकर गुजरती है, जहां ब्रिटिश रॉयल वेधशाला स्थित है, प्रधान मध्याह्न रेखा कहलाती है।)
- The value of Prime Meridian is 0° longitude and from it, we count 180° Eastward as well as 180° westward. (प्रधान याम्योत्तर का मान 0° देशांतर होता है और इससे हम 180° पूर्व और 180° पश्चिम की ओर गिनते हैं।)
- Prime Meridian divides the earth into two equal halves, the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere. (प्रधान मध्याह्न रेखा पृथ्वी को दो बराबर हिस्सों में बांटती है, पूर्वी गोलार्ध और पश्चिमी गोलार्ध।)
- 180° East and 180° West meridians are on the same line. (180° पूर्व और 180° पश्चिम याम्योत्तर एक ही रेखा पर होते हैं।)
- We can locate any point on the globe if we know its latitude and longitude. (हम ग्लोब पर किसी भी बिंदु का पता लगा सकते हैं यदि हमें उसका अक्षांश और देशांतर पता हो।)

Longitude and Time (देशांतर और समय)
- As the earth rotates from West to East, those places East of Greenwich will be ahead of Greenwich Time and those to the West will be behind it. (जब पृथ्वी पश्चिम से पूर्व की ओर घूमती है, तो ग्रीनविच के पूर्व के स्थान ग्रीनविच समय से आगे होंगे और पश्चिम के स्थान इसके पीछे होंगे।)
- The earth rotates 360° in about 24 hours. (पृथ्वी लगभग 24 घंटे में 360° घूम जाती है।)
- At any place, a watch can be adjusted to read at 12 o’clock when the Sun is at the highest point in the sky. (किसी भी स्थान पर, घड़ी को 12 बजे पढ़ने के लिए समायोजित किया जा सकता है जब सूर्य आकाश में उच्चतम बिंदु पर होता है।)
Standard Time (मानक समय)
- The local time various places are different, so it is necessary to adopt the local time of some central meridian of a country as the Standard Time. (विभिन्न स्थानों का स्थानीय समय अलग-अलग होता है, इसलिए किसी देश की किसी मध्य याम्योत्तर के स्थानीय समय को मानक समय के रूप में अपनाना आवश्यक है।)
- Is treated as the Standard Meridian of India. The local time at this meridian is known as the Indian Standard Time (IST). ( को भारत की मानक याम्योत्तर माना जाता है। इस याम्योत्तर पर स्थानीय समय को भारतीय मानक समय (आईएसटी) के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
- India located East of Greenwich at 82° 30’E, is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT. (ग्रीनविच के पूर्व में 82° 30’E पर स्थित भारत, GMT से 5 घंटे 30 मिनट आगे है)
- Some countries have a great longitudinal extent and so they have adopted more than one standard time. (कुछ देशों का देशांतरीय विस्तार बहुत अधिक है और इसलिए उन्होंने एक से अधिक मानक समय को अपनाया है।)

The Globe is a true model of the earth, in a small form. A needle, called the Axis is fixed through the globe in a tilted manner. (ग्लोब एक छोटे रूप में, पृथ्वी का एक सच्चा मॉडल है। एक सुई, जिसे एक्सिस कहा जाता है, ग्लोब के माध्यम से झुके हुए तरीके से तय की जाती है।)
The axis of the globe passes through two extreme points: known as the Poles (the North Pole and the South Pole). This axis is shown in the form of a needle on the globe. The real earth has no such axis. (ग्लोब की धुरी दो चरम बिंदुओं से होकर गुजरती है: ध्रुवों (उत्तरी ध्रुव और दक्षिणी ध्रुव) के रूप में जाना जाता है। इस अक्ष को ग्लोब पर सुई के रूप में दिखाया जाता है। वास्तविक पृथ्वी की ऐसी कोई धुरी नहीं है।)
The circle passing through the centre of the earth, and perpendicular to the axis, is called the Equator. It divides the earth into two Hemispheres, the Northern and the Southern. We can imagine a number of more circles parallel to the equator, having their centres on the axis and having different radii. These circles are called Parallels of Latitudes. (पृथ्वी के केंद्र से होकर गुजरने वाला वृत्त, और अक्ष के लम्बवत्, भूमध्य रेखा कहलाता है। यह पृथ्वी को दो गोलार्धों, उत्तरी और दक्षिणी में विभाजित करता है। हम भूमध्य रेखा के समानांतर कई और वृत्तों की कल्पना कर सकते हैं, जिनके केंद्र अक्ष पर हैं और जिनकी त्रिज्याएँ भिन्न हैं। इन वृत्तों को अक्षांश रेखाएँ कहते हैं।)
The parallels are identified with the help of degrees. The equator represents the zero degrees latitude. The latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere are designated as degrees north (°N), e.g. 10°N, 20°N, and so on till 90°N (which is the North Pole). Similarly the latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere are designated as degrees south (°S), and 90°S is the South Pole. (अंशों की सहायता से समानताओं की पहचान की जाती है। भूमध्य रेखा शून्य डिग्री अक्षांश का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है। उत्तरी गोलार्ध में अक्षांशों को डिग्री उत्तर (°N) के रूप में निर्दिष्ट किया जाता है, उदा। 10°N, 20°N, और इसी तरह 90°N तक (जो उत्तरी ध्रुव है) । इसी प्रकार दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में अक्षांशों को डिग्री दक्षिण (°S) के रूप में नामित किया गया है, और 90°S दक्षिणी ध्रुव है।)
The circle passing through Greenwich in Britain, and perpendicular to the equator, and parallel to the axis, is called the Prime Meridian. It divides the earth into two Hemispheres, the Eastern and the Western. Together, the Equator and the Prime Meridian divide the earth into four equal parts. We can imagine a number of more circles parallel to the Prime Meridian, having their centre at the centre of the earth, and having equal radii. These circles are called Degrees of Longitudes. (ब्रिटेन में ग्रीनविच से गुजरने वाला और विषुवत रेखा के लम्बवत् तथा अक्ष के समांतर वृत्त को प्रधान याम्योत्तर कहते हैं। यह पृथ्वी को दो गोलार्धों, पूर्वी और पश्चिमी में विभाजित करता है। भूमध्य रेखा और प्रधान मध्याह्न मिलकर पृथ्वी को चार बराबर भागों में विभाजित करते हैं। हम मुख्य मध्याह्न रेखा के समानांतर कई और वृत्तों की कल्पना कर सकते हैं, जिनका केंद्र पृथ्वी के केंद्र में है, और जिनकी त्रिज्याएँ समान हैं। इन वृत्तों को देशांतर की डिग्री कहा जाता है।)
The longitudes are identified with the help of degrees. The Prime Meridian represents
The zero degrees longitude. The longitudes in the Eastern Hemisphere are designated as degrees east (°E), e.g. 10°E, 20°E, and so on till 180°. Similar is the case with the Western Hemisphere. (देशांतरों की पहचान अंशों की सहायता से की जाती है। प्राइम मेरिडियन प्रतिनिधित्व करता है
शून्य डिग्री देशांतर। पूर्वी गोलार्ध में देशांतरों को डिग्री पूर्व (°E) के रूप में निर्दिष्ट किया जाता है, उदा। 10°E, 20°E, और इसी तरह 180° तक। पश्चिमी गोलार्ध की भी यही स्थिति है।)
Degrees are further divided into minutes and minutes into seconds. Note that the symbol
For a minute is an apostrophe (‘) and that for a second is a double apostrophe (“). 60′ (60 minutes) make up a degree and 60″ (60 seconds) make up a minute. So 30’ means half a degree and 40” means two-thirds of a minute. (डिग्रियों को आगे मिनटों में और मिनटों को सेकंड में विभाजित किया गया है। ध्यान दें कि प्रतीक एक मिनट के लिए एक apostrophe (‘) है और एक सेकंड के लिए एक डबल apostrophe (“) है। 60′ (60 मिनट) से एक डिग्री बनती है और 60″ (60 सेकंड) से एक मिनट बनता है। तो 30′ का अर्थ है आधा डिग्री और 40’ का अर्थ है एक मिनट का दो-तिहाई।)
Two points on earth can lie on the same latitude but still be far away from each other. Also, two distant points may lie on the same longitude. But only one point lief on a particular pair of latitude and longitude. So latitudes and longitudes are helpful in locating a point on earth. (पृथ्वी पर दो बिंदु एक ही अक्षांश पर स्थित हो सकते हैं लेकिन फिर भी एक दूसरे से बहुत दूर हो सकते हैं। साथ ही, दो दूरस्थ बिंदु एक ही देशांतर पर स्थित हो सकते हैं। लेकिन अक्षांश और देशांतर की एक विशेष जोड़ी पर केवल एक बिंदु झूठ बोलता है। अतः अक्षांश और देशांतर पृथ्वी पर किसी बिंदु का पता लगाने में सहायक होते हैं।)
The Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle are studied as special latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere. They are at 23 1/2° N and 6612° N respectively. (उत्तरी गोलार्द्ध में कर्क रेखा और आर्कटिक वृत्त का विशेष अक्षांश के रूप में अध्ययन किया जाता है। वे क्रमशः 23 1/2° उत्तर और 6612° उत्तर पर हैं।)
The Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle are studied as special latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere. They are at 23 12° S and 66 12° S respectively. (मकर रेखा और अंटार्कटिक वृत्त का अध्ययन दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में विशेष अक्षांशों के रूप में किया जाता है। वे क्रमशः 23 12° दक्षिण और 66 12° दक्षिण पर हैं।)
The area between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn receive maximum heat from the Sun and this region is called the Torrid Zone. (कर्क रेखा और मकर रेखा के बीच का क्षेत्र सूर्य से अधिकतम ऊष्मा प्राप्त करता है और इस क्षेत्र को उष्ण कटिबंध कहा जाता है।)
The area between the Artie Circle and the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere, and that between the Antarctic Circle and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern, have moderate temperatures. These regions are the Temperate Zones. (उत्तरी गोलार्ध में आर्टी सर्कल और कर्क रेखा के बीच का क्षेत्र, और दक्षिणी में अंटार्कटिक सर्कल और मकर रेखा के बीच का तापमान मध्यम है। ये क्षेत्र समशीतोष्ण क्षेत्र हैं।)
The area north to the Arctic Circle and that south to the Antarctic Circle is close to the Poles and receive the sunlight of very low intensity. So it is very cold here. These regions are called the Frigid Zones. (आर्कटिक सर्कल के उत्तर का क्षेत्र और अंटार्कटिक सर्कल के दक्षिण का क्षेत्र ध्रुवों के करीब है और बहुत कम तीव्रता की धूप प्राप्त करता है। इसलिए यहां बहुत ठंड है। इन क्षेत्रों को शीत कटिबंध कहते हैं।)
The Frigid Zones, the Temperate Zones, and the Torrid Zone are called the Heat Zones. (शीत कटिबंध, शीतोष्ण कटिबंध और उष्ण कटिबंध को उष्मा कटिबंध कहते हैं।)
The sun does not shine equally on all longitudes at a time. When it is 12 noon at a time, it means that the sun is not at all visible at the place on the other side of the earth. ‘So it must be midnight there. In fact, we can say that the time difference is 24 hours at 360 degrees longitudes apart. So every longitude brings a difference of 4 minutes. This gives us the concept of Time Zones. Two consecutive time zones differ by an hour. The time at a particular place is said to be the local time. (सूर्य एक समय में सभी देशांतरों पर समान रूप से नहीं चमकता है। जब एक समय में दोपहर के 12 बजते हैं, तो इसका अर्थ है कि सूर्य पृथ्वी के दूसरी ओर के स्थान पर बिल्कुल भी दिखाई नहीं देता है। ‘तो वहाँ आधी रात होनी चाहिए। वास्तव में, हम कह सकते हैं कि 360 डिग्री देशांतर पर समय का अंतर 24 घंटे का है। अतः प्रत्येक देशांतर 4 मिनट का अंतर लाता है। यह हमें समय क्षेत्र की अवधारणा देता है। लगातार दो समय क्षेत्र एक घंटे से भिन्न होते हैं। किसी स्थान विशेष के समय को स्थानीय समय कहा जाता है।)
It may happen that a certain country extends over a long range of longitudes, thus giving a large amount of time difference. E.g. Russia extends over eleven time zones. India actually extends over a range of a 2-hour time difference. But this is not too much, so for convenience and for uniformity, we have a standard meridian set at Allahabad (82° 30’), which gives the time for all over India. This time is called the Indian Standard Time (IST). (ऐसा हो सकता है कि एक निश्चित देश देशांतरों की एक लंबी श्रृंखला में फैला हुआ है, इस प्रकार बड़ी मात्रा में समय का अंतर देता है। उदा. रूस ग्यारह समय क्षेत्रों में फैला हुआ है। भारत वास्तव में 2 घंटे के समय के अंतर की सीमा तक फैला हुआ है। लेकिन यह बहुत अधिक नहीं है, इसलिए सुविधा और एकरूपता के लिए, हमारे पास इलाहाबाद (82° 30′) पर एक मानक याम्योत्तर सेट है, जो पूरे भारत के लिए समय देता है। इस समय को भारतीय मानक समय (आईएसटी) कहा जाता है।)
Globe: The globe is a model of the earth, as it is, but in a very small and convenient form. It shows all continents, countries, and oceans, labeled.
ग्लोब: ग्लोब पृथ्वी का एक मॉडल है, जैसा कि यह है, लेकिन बहुत छोटे और सुविधाजनक रूप में। यह लेबल वाले सभी महाद्वीपों, देशों और महासागरों को दिखाता है।)
Axis: The imaginary line about which the earth rotates once in 24 hours is called its axis.
अक्ष (Axis): पृथ्वी जिस काल्पनिक रेखा के चारों ओर 24 घंटे में एक बार परिक्रमा करती है, उसे उसका अक्ष कहते हैं।)
Poles: The two extreme points of the axis are called the Poles. One of them is the North Pole and the other is the South Pole.
ध्रुव: अक्ष के दो चरम बिंदुओं को ध्रुव कहा जाता है। इनमें से एक उत्तरी ध्रुव और दूसरा दक्षिणी ध्रुव है।)
Equator: The circle passing through the center of the earth, and perpendicular to the axis, is called the equator.
विषुवत रेखा (Equator): पृथ्वी के केंद्र से होकर गुजरने वाले तथा अक्ष के लम्बवत् वृत्त को भूमध्य रेखा कहते हैं।)
Prime Meridian: The circle passing through Greenwich in Britain, and perpendicular to the equator, and parallel to the axis, is called the Prime Meridian.
प्रधान याम्योत्तर: ब्रिटेन में ग्रीनविच से होकर भूमध्य रेखा के लम्बवत् तथा अक्ष के समानांतर गुजरने वाले वृत्त को प्रधान याम्योत्तर कहते हैं।)
Latitude: One of the imaginary circles parallel to the Equator is called latitude. The latitudes have their centers on one common line and they have different radii.
अक्षांश: भूमध्य रेखा के समानांतर काल्पनिक वृत्तों में से एक को अक्षांश कहा जाता है। अक्षांशों के केंद्र एक सामान्य रेखा पर होते हैं और उनकी अलग-अलग त्रिज्याएँ होती हैं।)
Longitude: One of the imaginary circles parallel to the Prime Meridian is called longitude. The longitudes have their centers at the center of the earth and have the same radius as the Earth.
देशांतर: प्रमुख भूमध्य रेखा के समानांतर काल्पनिक वृत्तों में से एक को देशांतर कहा जाता है। देशांतरों के केंद्र पृथ्वी के केंद्र में होते हैं और पृथ्वी के समान त्रिज्या होती है।)
Hemisphere: One of the two equal halves of the earth’s spherical shape is called a hemisphere. If the earth is halved along the equator, we get the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres. If we halve it perpendicular to the equator, we get the Eastern and the Western Hemispheres.
गोलार्द्ध: पृथ्वी के गोलाकार आकार के दो बराबर हिस्सों में से एक को गोलार्ध कहा जाता है। यदि पृथ्वी को भूमध्य रेखा के साथ आधा कर दिया जाए, तो हमें उत्तरी और दक्षिणी गोलार्ध मिलते हैं। यदि हम इसे भूमध्य रेखा के लंबवत आधा कर दें, तो हमें पूर्वी और पश्चिमी गोलार्ध मिलते हैं।)
Heat Zones: Heat zones are the different zones of the earth, where the sun’s rays fall differently, thus causing different climate patterns. These zones are called the Torrid Zone, the two Temperate Zones, and the two Frigid Zones.
हीट जोन: हीट जोन पृथ्वी के विभिन्न क्षेत्र हैं, जहां सूर्य की किरणें अलग-अलग तरह से पड़ती हैं, जिससे अलग-अलग जलवायु पैटर्न बनते हैं। इन क्षेत्रों को उष्ण कटिबंध, दो शीतोष्ण कटिबंध और दो शीत कटिबंध कहा जाता है।)
Greenwich: Greenwich is a place in the United Kingdom, near London, whose time is used as a standard all over the world. The Prime Meridian passes through this place, and so it is the place which divides the earth into the Eastern and the Western Hemispheres.
ग्रीनविच: ग्रीनविच लंदन के पास यूनाइटेड किंगडम में एक जगह है, जिसका समय पूरे विश्व में एक मानक के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है। प्रमुख मध्याह्न रेखा इस स्थान से होकर गुजरती है, और इसलिए यह वह स्थान है जो पृथ्वी को पूर्वी और पश्चिमी गोलार्ध में विभाजित करता है।)
Standard Time: Standard time of a country or region is the time regarded as a standard for that place, despite the fact that there exists time difference geographically across that region. It is used only for convenience.
मानक समय: किसी देश या क्षेत्र का मानक समय उस स्थान के लिए एक मानक के रूप में माना जाने वाला समय है, इस तथ्य के बावजूद कि उस क्षेत्र में भौगोलिक रूप से समय का अंतर मौजूद है। इसका उपयोग केवल सुविधा के लिए किया जाता है।)
Motions of the Earth Chapter 3
पृथ्वी की गति अध्याय 3
Rotation (चक्कर)
- Rotation is the movement of the Earth, on its axis. (घूर्णन पृथ्वी की अपनी धुरी पर गति है।)
- The axis of the Earth, which is an imaginary line, makes an angle of 66/2° with its orbital plane. (पृथ्वी की धुरी, जो एक काल्पनिक रेखा है, अपने कक्षीय तल के साथ 66/2° का कोण बनाती है।)
- The portion facing the Sun experiences day, while the other half away from the Sun experiences night. (सूर्य के सामने वाला भाग दिन का अनुभव करता है, जबकि सूर्य से दूर दूसरा भाग रात का अनुभव करता है।)
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination. (ग्लोब पर दिन को रात से अलग करने वाले वृत्त को प्रदीप्ति वृत्त कहते हैं।)
- The Earth takes about 24 hrs to complete one rotation around its axis, it is known as earthday. (पृथ्वी को अपनी धुरी के चारों ओर एक चक्कर पूरा करने में लगभग 24 घंटे लगते हैं, इसे पृथ्वी दिवस के रूप में जाना जाता है।)

Revolution (परिक्रमण)
- The movement of the Earth around the Sun in a fixed path or orbit is called revolution. (सूर्य के चारों ओर एक निश्चित पथ या कक्षा में पृथ्वी की गति को परिक्रमण कहा जाता है।)
- Earth takes 365)4 days to revolve around the Sun. (पृथ्वी को सूर्य की परिक्रमा करने में 365)4 दिन लगते हैं।)
- Every fourth year, February is of 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year. (प्रत्येक चौथे वर्ष फरवरी 28 दिनों के स्थान पर 29 दिनों की होती है। ऐसा वर्ष जिसमें 366 दिन होते हैं, लीप वर्ष कहलाता है।)
- Earth is going around the Sun in an elliptical-orbit. (पृथ्वी एक अण्डाकार-कक्षा में सूर्य के चारों ओर चक्कर लगा रही है।)
- Seasons change due to change in the position of the Earth around the Sun. (सूर्य के चारों ओर पृथ्वी की स्थिति में परिवर्तन के कारण ऋतुओं में परिवर्तन होता है।)
- Summer solstice is the position of the Earth when the Northern Hemisphere has the longest day and the shortest night. (ग्रीष्म संक्रांति पृथ्वी की वह स्थिति है जब उत्तरी गोलार्ध में सबसे लंबा दिन और सबसे छोटी रात होती है।)
- It occurs on 21st June. (यह 21 जून को होता है।)
- In the Southern Hemisphere, it is winter season at this time. The days are short and the nights are long. (दक्षिणी गोलार्द्ध में इस समय शीत ऋतु होती है। दिन छोटे और रातें लंबी होती हैं।)
- Winter Solstice is the position of the earth when Southern Hemisphere has long days and shorter nights. In the Northern (शीतकालीन अयनांत पृथ्वी की वह स्थिति है जब दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में दिन लंबे और रातें छोटी होती हैं। उत्तरी में)
- Hemisphere, the days are short and the nights are long. It occurs on 22nd December. (गोलार्द्ध में दिन छोटे और रातें लंबी होती हैं। यह 22 दिसंबर को होता है।)
- On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator and the whole earth experiences equal days (21 मार्च और 23 सितंबर को सूर्य की सीधी किरणें भूमध्य रेखा पर पड़ती हैं और पूरी पृथ्वी पर समान दिन होते हैं)
- And equal nights. This is called an equinox. (और बराबर रातें। इसे विषुव कहते हैं)
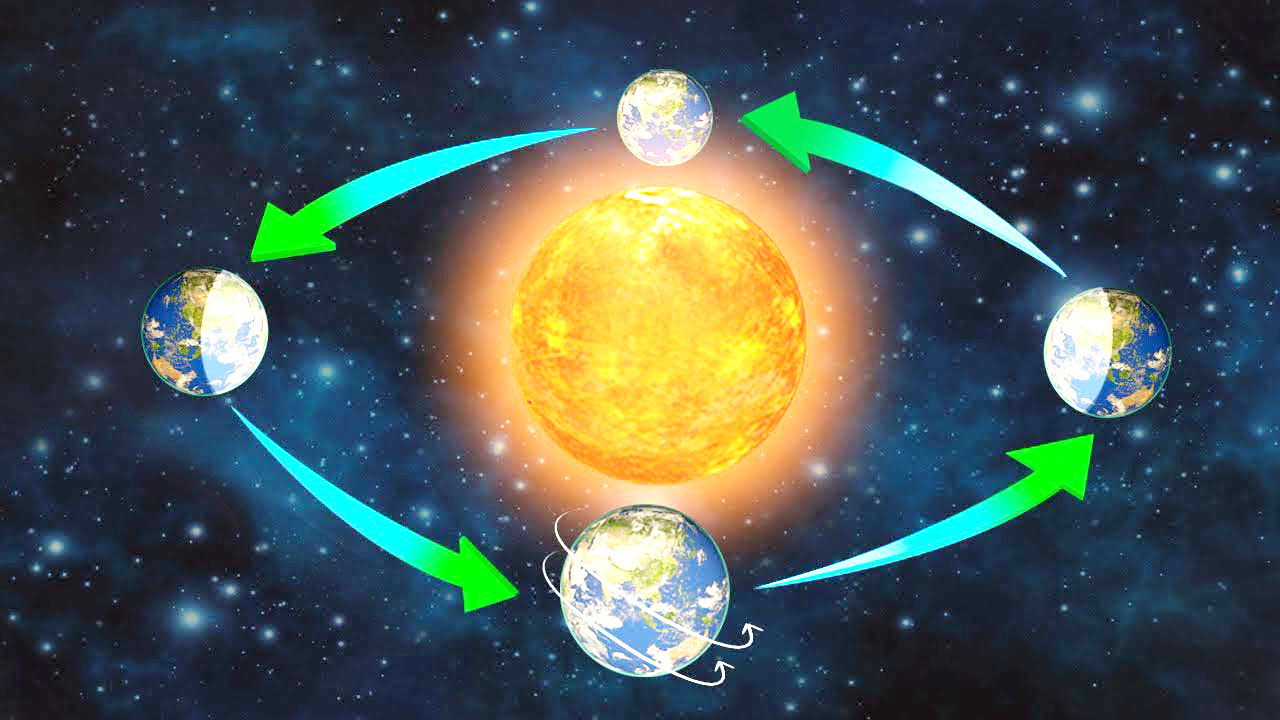
The earth has two types of motions—rotation and revolution. (पृथ्वी की गति दो प्रकार की होती है-घूर्णन और परिक्रमण।)
Rotation is the movement of the earth on its axis. In revolution the earth moves around the sun in a fixed path or orbit. (घूर्णन पृथ्वी की अपनी धुरी पर गति है। परिक्रमण में पृथ्वी एक निश्चित पथ या कक्षा में सूर्य के चारों ओर घूमती है।)
The axis of the earth is an imaginary line. (पृथ्वी की धुरी एक काल्पनिक रेखा है।)
The earth receives light from the sun. As the shape of the earth is spherical, only half of it gets light from the sun at a time. The other half remains dark. In this way day and night are caused. (पृथ्वी सूर्य से प्रकाश प्राप्त करती है। पृथ्वी का आकार गोलाकार होने के कारण एक समय में इसका आधा भाग ही सूर्य से प्रकाश प्राप्त कर पाता है। दूसरे आधे हिस्से में अंधेरा रहता है। इस प्रकार दिन और रात होते हैं।)
The earth completes one rotation around its axis in about 24 hours. This rotation is the daily motion of the earth. (पृथ्वी अपनी धुरी पर एक चक्कर लगभग 24 घंटे में पूरा करती है। यह घूर्णन पृथ्वी की दैनिक गति है।)
The earth takes 365 14 days or one year to complete one revolution around the sun. (पृथ्वी को सूर्य के चारों ओर एक चक्कर पूरा करने में 365 14 दिन या एक वर्ष का समय लगता है।)
There are four seasons in a year—summer, winter, spring and autumn. Seasons change due to the change in the position of the earth around the sun. (एक वर्ष में चार ऋतुएँ होती हैं- ग्रीष्म, शीत, बसंत और शरद ऋतु। सूर्य के चारों ओर पृथ्वी की स्थिति में परिवर्तन के कारण ऋतुओं में परिवर्तन होता है।)
The rays of sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. Hence, these areas are hot. (सूर्य की किरणें कर्क रेखा पर सीधी पड़ती हैं। इसलिए, ये क्षेत्र गर्म हैं।)
The areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting. (ध्रुवों के निकट के क्षेत्रों में कम ऊष्मा प्राप्त होती है क्योंकि सूर्य की किरणें तिरछी होती हैं।)
In the Northern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on 21st June. In the Southern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is known as the summer solstice. (उत्तरी गोलार्द्ध में 21 जून को सबसे बड़ा दिन और सबसे छोटी रात होती है। दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में इस दिन सबसे छोटा दिन और सबसे लंबी रात होती है। पृथ्वी की इस स्थिति को ग्रीष्म संक्रांति के नाम से जाना जाता है।)
When there is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere enjoys winter season and vice-versa. (जब उत्तरी गोलार्ध में गर्मी होती है, तो दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में सर्दी का मौसम होता है और इसके विपरीत।)
In the Northern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on 22nd December. In the Southern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is known as the winter solstice. (उत्तरी गोलार्द्ध में 22 दिसंबर को सबसे छोटा दिन और सबसे लंबी रात होती है। दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में इस दिन सबसे लंबा दिन और सबसे छोटी रात होती है। पृथ्वी की इस स्थिति को शीतकालीन संक्रांति के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
On 21st March and September 23rd the whole earth experiences equal’days and equal nights. This is phenomenon is known as equinox. (21 मार्च और 23 सितंबर को पूरी पृथ्वी समान दिनों और समान रातों का अनुभव करती है। यह घटना विषुव के रूप में जानी जाती है।)
On 23rd September, it is autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Sourthern Hemisphere. (23 सितंबर को उत्तरी गोलार्ध में शरद ऋतु और दक्षिणी गोलार्ध में वसंत ऋतु होती है।)
On 21st March, it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Sourthern Hemisphere. (21 मार्च को उत्तरी गोलार्द्ध में बसंत और दक्षिणी गोलार्द्ध में शरद ऋतु होती है।)
Days and nights occur due to rotation while changes in seasons occur due to revolution. (दिन और रात परिक्रमण के कारण होते हैं जबकि ऋतुओं में परिवर्तन परिक्रमण के कारण होता है।)
Rotation: The movement of the earth on its axis is known as rotation.
चक्कर: पृथ्वी की अपने अक्ष पर गति को चक्कर कहते हैं।)
Revolution: The movement of the earth around the sun in a fixed path or orbit is known as revolution.
परिक्रमण: सूर्य के चारों ओर पृथ्वी की एक निश्चित पथ या कक्षा में गति को परिक्रमण के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Orbital plane: The plane formed by the orbit is known as the orbital plane.
कक्षीय तल: कक्षा द्वारा निर्मित तल को कक्षीय तल के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Circle of illumination: The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
प्रदीप्ति वृत्त: ग्लोब पर दिन को रात्रि से विभाजित करने वाले वृत्त को प्रदीप्ति वृत्त कहते हैं।)
Leap year: The year in which February is of 29 days instead of 28 days is called a leap year.
लीप वर्ष (Leap Year): जिस वर्ष फरवरी में 28 दिनों के स्थान पर 29 दिन हो जाते हैं, उसे लीप वर्ष कहते हैं।)
Summer solstice: In the Northern Hemisphere the longest day and the shortest night occur on 21st June. In the Southern Hemisphere, the shortest day and the longest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is called summer solstice.
ग्रीष्म संक्रांति: उत्तरी गोलार्ध में सबसे लंबा दिन और सबसे छोटी रात 21 जून को होती है। दक्षिणी गोलार्द्ध में इस दिन सबसे छोटा दिन और सबसे लंबी रात होती है। पृथ्वी की इस स्थिति को ग्रीष्म संक्रांति कहते हैं।)
Winter solstice: In the Northern Hemisphere the shortest day and the longest night occur on 22nd December. In the Southern Hemisphere, the longest day and the shortest night occur on this day. This position of the earth is called winter solstice.
शीतकालीन संक्रांति: उत्तरी गोलार्ध में 22 दिसंबर को सबसे छोटा दिन और सबसे लंबी रात होती है। दक्षिणी गोलार्द्ध में इस दिन सबसे लंबा दिन और सबसे छोटी रात होती है। पृथ्वी की इस स्थिति को शीतकालीन संक्रांति कहते हैं।)
Equinox: On 21st March and September 23rd the entire earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is known as the equinox.
विषुव: 21 मार्च और 23 सितंबर को पूरी पृथ्वी समान दिनों और समान रातों का अनुभव करती है। इसे विषुव के नाम से जाना जाता है।)
Maps Chapter 4
मानचित्र अध्याय 4
A globe can be useful when we want to study the Earth as a whole. (एक ग्लोब तब उपयोगी हो सकता है जब हम पूरी पृथ्वी का अध्ययन करना चाहते हैं।)
A map is a representation or a drawing of the Earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale. (मानचित्र पृथ्वी की सतह या उसके किसी भाग का एक पैमाने के अनुसार समतल सतह पर खींचा गया प्रतिनिधित्व या चित्र है।)
When many maps are put together we, get an Atlas. (जब अनेक मानचित्रों को एक साथ रखा जाता है तो हमें एक एटलस प्राप्त होता है।)
Physical maps show natural features of the Earth. (भौतिक मानचित्र पृथ्वी की प्राकृतिक विशेषताओं को दिखाते हैं।)
Political maps show different boundaries of different countries and states. (राजनीतिक मानचित्र विभिन्न देशों और राज्यों की विभिन्न सीमाओं को दर्शाते हैं।)
Thematic maps focus on specific information. (विषयगत मानचित्र विशिष्ट जानकारी पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं।)
There are three components of maps—distance, direction and symbol. (मानचित्रों के तीन घटक होते हैं- दूरी, दिशा और प्रतीक।)
Distance (दूरी)
- The scale is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map. (पैमाना जमीन पर वास्तविक दूरी और मानचित्र पर दिखाई गई दूरी के बीच का अनुपात है।)
- If you know the scale, you will be able to calculate the distance between any two places on a map. (यदि आप पैमाना जानते हैं, तो आप मानचित्र पर किन्हीं दो स्थानों के बीच की दूरी की गणना करने में सक्षम होंगे।)
- When large areas like continents or countries are to be shown on paper, then we use a small scale map. (जब महाद्वीपों या देशों जैसे बड़े क्षेत्रों को कागज पर दिखाना होता है तो हम एक छोटे पैमाने के मानचित्र का उपयोग करते हैं।)
- When a small area like your village or town is to be shown on paper, then we use a large scale map. Direction (जब अपने गाँव या कस्बे जैसे किसी छोटे क्षेत्र को कागज पर दिखाना होता है तो हम बड़े पैमाने के मानचित्र का प्रयोग करते हैं। दिशा)
- There are four major directions, North, South, East and West. They are called cardinal points. (चार प्रमुख दिशाएं हैं, उत्तर, दक्षिण, पूर्व और पश्चिम। उन्हें कार्डिनल पॉइंट कहा जाता है।)
- We can find out the direction of a place with the help of a magnetic compass. (चुंबकीय दिक्सूचक की सहायता से हम किसी स्थान की दिशा का पता लगा सकते हैं।)
Symbols (प्रतीक)
- The conventional symbols give a lot of information in a limited space. (पारंपरिक प्रतीक सीमित स्थान में बहुत सारी जानकारी देते हैं।)
- The blue colour is used for showing water bodies, brown for mountains, yellow for plateau and green is used for plains. (नीले रंग का उपयोग जल निकायों को दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है, भूरा रंग पहाड़ों के लिए, पीला रंग पठार के लिए और हरा रंग मैदानों के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।)
Sketch (स्केच)
- A sketch is a drawing mainly based on memory and spot observation and not to scale. (एक रेखाचित्र मुख्य रूप से स्मृति और स्थान अवलोकन पर आधारित आरेखण है न कि पैमाने पर।)
- A rough drawing is drawn without scale is called a sketch map. (बिना पैमाने के एक कच्चा चित्र बनाया जाता है जिसे रेखाचित्र मानचित्र कहा जाता है।)
Plan (योजना)
- A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale. (एक योजना बड़े पैमाने पर एक छोटे से क्षेत्र का आरेखण है।)
- There are certain things which we may sometimes want to know, for example, the length and breadth of a room. (कुछ ऐसी चीजें हैं जो हम कभी-कभी जानना चाहते हैं, उदाहरण के लिए, एक कमरे की लंबाई और चौड़ाई।)
A map is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale. (मानचित्र पृथ्वी की सतह या उसके किसी भाग का एक पैमाने के अनुसार समतल सतह पर खींचा गया प्रतिनिधित्व या चित्र है।)
Maps are of different types—physical maps, political maps and thematic maps. (मानचित्र विभिन्न प्रकार के होते हैं-भौतिक मानचित्र, राजनीतिक मानचित्र और विषयगत मानचित्र।)
Physical maps show natural features of the earth, political maps show cities, towns, countries etc. with their boundaries and thematic maps focus on some particular information such as maps showing distribution of population. (भौतिक मानचित्र पृथ्वी की प्राकृतिक विशेषताओं को दिखाते हैं, राजनीतिक मानचित्र शहरों, कस्बों, देशों आदि को उनकी सीमाओं के साथ दिखाते हैं और विषयगत मानचित्र कुछ विशेष सूचनाओं पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं जैसे जनसंख्या के वितरण को दर्शाने वाले मानचित्र।)
The three components of maps are distance, direction and symbol. (मानचित्र के तीन घटक दूरी, दिशा और प्रतीक हैं।)
A scale is needed to represent a small distance on paper for a large distance on the ground. Thus, scale is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map. (जमीन पर बड़ी दूरी के लिए कागज पर एक छोटी दूरी का प्रतिनिधित्व करने के लिए एक पैमाने की जरूरत होती है। इस प्रकार, पैमाना जमीन पर वास्तविक दूरी और मानचित्र पर दिखाई गई दूरी के बीच का अनुपात है।)
A small scale map is used to show large areas like continents or countries on a paper. (एक छोटे पैमाने के मानचित्र का उपयोग बड़े क्षेत्रों जैसे महाद्वीपों या देशों को एक कागज पर दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है।)
A large scale map is used to show a small area like a village or town on a paper. (एक बड़े पैमाने के नक्शे का उपयोग एक छोटे से क्षेत्र जैसे गाँव या कस्बे को एक कागज पर दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है।)
There are four major directions—North, South, East and West, known as cardinal points. (चार प्रमुख दिशाएँ हैं- उत्तर, दक्षिण, पूर्व और पश्चिम, जिन्हें कार्डिनल पॉइंट के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
There are four intermediate directions—north-east (NE), south-east (SE), south-west (SW) and north-west (NW). (चार मध्यवर्ती दिशाएँ हैं- उत्तर-पूर्व (NE), दक्षिण-पूर्व (SE), दक्षिण-पश्चिम (SW) और उत्तर-पश्चिम (NW)
Symbols are used to show features like buildings, roads, bridges, etc. on the map. By using symbols we make the map very informative. (प्रतीकों का उपयोग मानचित्र पर इमारतों, सड़कों, पुलों आदि जैसी विशेषताओं को दर्शाने के लिए किया जाता है। प्रतीकों के प्रयोग से हम मानचित्र को बहुत सूचनात्मक बनाते हैं।)
Maps have a universal language. There is an international agreement regarding the use of these symbols. These are called conventional symbols. (मानचित्रों की एक सार्वभौमिक भाषा होती है। इन प्रतीकों के उपयोग के संबंध में एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय समझौता है। इन्हें पारंपरिक प्रतीक कहा जाता है।)
A sketch map is a rough drawing without scale. (स्केच मैप बिना स्केल के रफ ड्रॉइंग होता है।)
A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale. (एक योजना बड़े पैमाने पर एक छोटे से क्षेत्र का चित्र है।)
Map: It is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale.
मानचित्र: यह पृथ्वी की सतह या उसके किसी भाग का एक पैमाने के अनुसार समतल सतह पर खींचा गया प्रतिनिधित्व या आरेखण है।)
Scale: It is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map.
पैमाना: यह जमीन पर वास्तविक दूरी और मानचित्र पर दिखाई गई दूरी के बीच का अनुपात है।
Cardinal points: The four directions—North, South, East and West—are called cardinal points.
कार्डिनल पॉइंट्स: चार दिशाओं- उत्तर, दक्षिण, पूर्व और पश्चिम- को कार्डिनल पॉइंट कहा जाता है।
Symbols: To represent buildings, roads, bridges, etc. on the map we use symbols. These symbols are of universal significance.
प्रतीकः भवनों, सड़कों, पुलों आदि को मानचित्र पर दर्शाने के लिए हम प्रतीकों का प्रयोग करते हैं। ये प्रतीक सार्वभौमिक महत्व के हैं।
Sketch: A sketch is a drawing mainly based on memory and spot observation and not to scale.
स्केच: एक स्केच मुख्य रूप से मेमोरी और स्पॉट ऑब्जर्वेशन पर आधारित ड्राइंग है न कि स्केल करने के लिए।
Plan: A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale.
योजना: एक बड़े पैमाने पर एक छोटे से क्षेत्र का चित्र बनाना एक योजना है।
Major Domains of the Earth Chapter 5
पृथ्वी के प्रमुख क्षेत्र अध्याय 5
There are three main components of the environment – Lithosphere, Atmosphere and Hydrosphere. (पर्यावरण के तीन मुख्य घटक हैं – स्थलमंडल, वायुमंडल और जलमंडल।)
The solid portion of the Earth on which we live is called the Lithosphere. (पृथ्वी का वह ठोस भाग जिस पर हम रहते हैं स्थलमंडल कहलाता है।)
The gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth is the Atmosphere. (पृथ्वी को चारों ओर से घेरने वाली गैसीय परत वायुमंडल है।)
The area covered by water is called Hydrosphere. (जल से आच्छादित क्षेत्र को जलमंडल कहते हैं।)
The zone which contains all forms of life is called Biosphere. (जीवन के सभी रूपों को समाहित करने वाले क्षेत्र को बायोस्फीयर कहा जाता है।)
Lithosphere (स्थलमंडल)
- It comprises the rocks of the earth’s crust and the thin layers of soil. (इसमें पृथ्वी की पपड़ी की चट्टानें और मिट्टी की पतली परतें शामिल हैं।)
- There are two main divisions of the earth’s surface. (पृथ्वी की सतह के दो मुख्य भाग हैं।)
- The large landmasses are known as the continents. (बड़े भूभाग को महाद्वीप कहा जाता है।)
- The huge water bodies are called the ocean basins. (विशाल जलराशियों को महासागरीय द्रोणी कहते हैं।

Continents (महाद्वीपों)
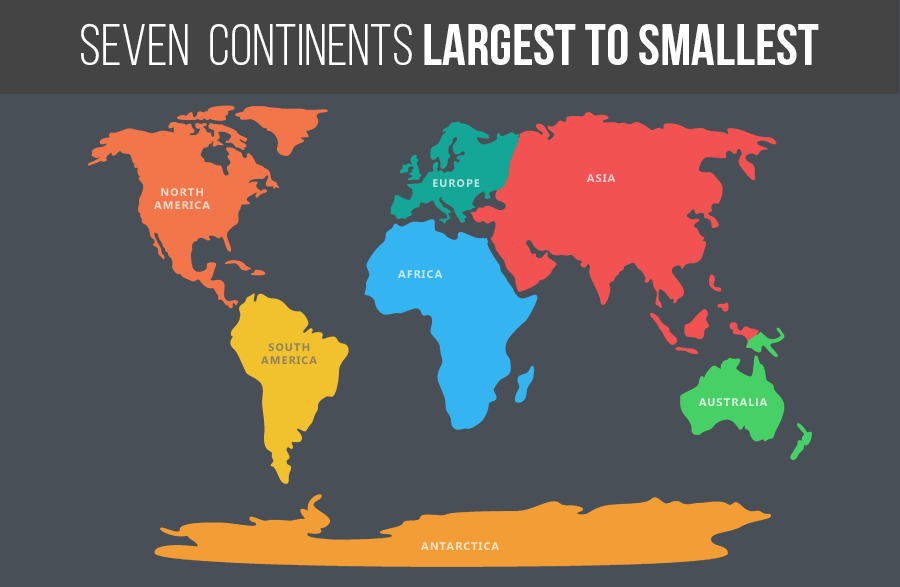
- There are seven major continents. (सात प्रमुख महाद्वीप हैं।)
- The greater part of the land mass lies in the Northern Hemisphere. (भूभाग का बड़ा हिस्सा उत्तरी गोलार्ध में स्थित है।)
- Asia is the largest continent. (एशिया सबसे बड़ा महाद्वीप है।)
- The combined landmass of Europe and Asia is called Eurasia. (यूरोप और एशिया के संयुक्त भूभाग को यूरेशिया कहा जाता है)
- Africa is the second largest continent. It is the only continent through which the Tropic of Cancer, the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn pass. (अफ्रीका दूसरा सबसे बड़ा महाद्वीप है। यह एकमात्र महाद्वीप है जिससे होकर कर्क रेखा, भूमध्य रेखा और मकर रेखा गुजरती है।)
- North America is the third largest continent of the world. (उत्तरी अमेरिका विश्व का तीसरा सबसे बड़ा महाद्वीप है।)
- South America and North America are linked by a very narrow strip of land called the Isthmus of Panama. (दक्षिण अमेरिका और उत्तरी अमेरिका भूमि की एक बहुत ही संकरी पट्टी से जुड़े हुए हैं जिसे पनामा का स्थलडमरूमध्य कहा जाता है।)
- Australia is the smallest continent. It is also called an island continent. (ऑस्ट्रेलिया सबसे छोटा महाद्वीप है। इसे द्वीपीय महाद्वीप भी कहते हैं।)
- Antarctica is permanently covered with thick ice sheets. (अंटार्कटिका स्थायी रूप से बर्फ की मोटी चादर से ढका हुआ है।)
- India has a research station named as Maitri and Dakshin Gangotri at Antarctica. (भारत का अंटार्कटिका में मैत्री और दक्षिण गंगोत्री नामक एक अनुसंधान केंद्र है।)
Hydrosphere (उद्मंडल)
- More than 71 % per cent of the Earth is covered with water, therefore, the Earth is called the blue planet. (पृथ्वी का 71% प्रतिशत से अधिक भाग जल से ढका हुआ है, इसलिए पृथ्वी को नीला ग्रह कहा जाता है।)
- More than 97% of the Earth’s water is found in the oceans. (पृथ्वी का 97% से अधिक जल महासागरों में पाया जाता है।)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1435323-the-four-spheres-of-the-earth-5b69b46a46e0fb002556a079.png)
Oceans (महासागर के)
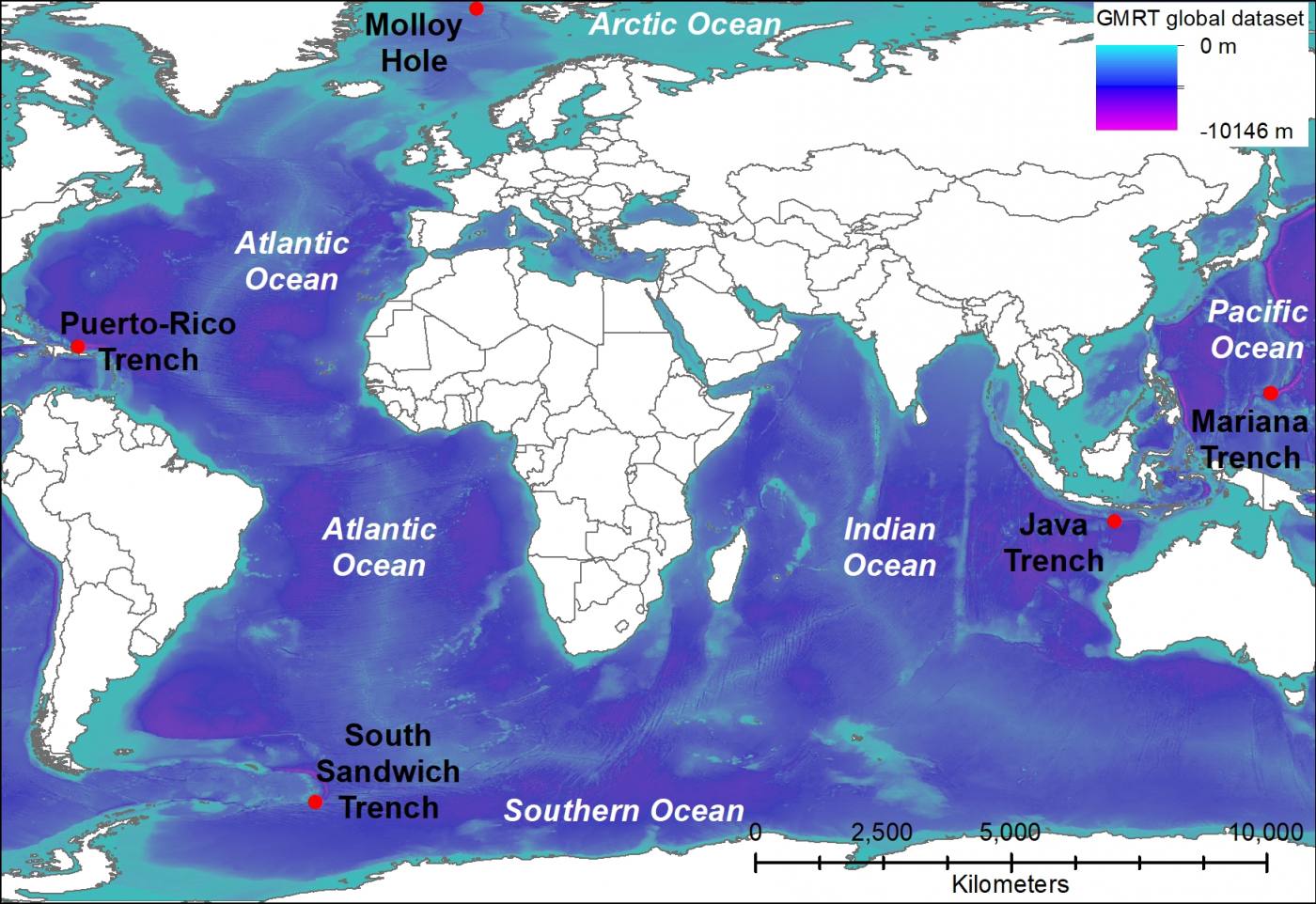
- The four major oceans are the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean and the Arctic Ocean. (चार प्रमुख महासागर प्रशांत महासागर, अटलांटिक महासागर, हिंद महासागर और आर्कटिक महासागर हैं।)
- The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean. (प्रशांत महासागर सबसे बड़ा महासागर है।)
- The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest ocean. (अटलांटिक महासागर दूसरा सबसे बड़ा महासागर है।)
- The Indian Ocean is the only ocean named after a country, that is, India. (हिंद महासागर एक ऐसा महासागर है जिसका नाम किसी देश, यानी भारत के नाम पर रखा गया है।)
- The Arctic Ocean is located within the Arctic Circle. (आर्कटिक महासागर आर्कटिक सर्कल के भीतर स्थित है।)
Atmosphere (वायुमंडल)
- The atmosphere protects us from the harmful effects of the sun’s rays. (वायुमण्डल हमें सूर्य की किरणों के हानिकारक प्रभावों से बचाता है।)
- The atmosphere extends up to a height of about 1,600 kilometres. (वायुमंडल का विस्तार लगभग 1,600 किलोमीटर की ऊँचाई तक है।)
- The atmosphere is divided into five layers—the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere and the exosphere. (वायुमंडल को पांच परतों में बांटा गया है- क्षोभमंडल, समताप मंडल, मध्यमंडल, तापमंडल और बहिर्मंडल।)
- The atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen. (वायुमंडल मुख्य रूप से नाइट्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन से बना है।)

Biosphere – The Domain of Life (जीवमंडल – जीवन का क्षेत्र)
- The biosphere is the narrow zone of contact between the land, water and air. (जीवमंडल भूमि, जल और वायु के बीच संपर्क का संकीर्ण क्षेत्र है।)
- All the living organisms including humans are linked to each other and to the biosphere for survival. (मनुष्य सहित सभी जीवित जीव जीवित रहने के लिए एक दूसरे से और जीवमंडल से जुड़े हुए हैं।)
- The organisms in the biosphere may broadly be divided into the plant kingdom and the animal kingdom. (जीवमंडल में जीवों को मोटे तौर पर पादप जगत और जंतु जगत में विभाजित किया जा सकता है।)
- Increase in the amount of C02 leads to an increase in global temperature. This is termed as global warming. (CO2 की मात्रा में वृद्धि से वैश्विक तापमान में वृद्धि होती है। इसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग कहा जाता है।)

The earth is the only planet where human beings find three life sustaining elements—
Land, water and air. (पृथ्वी ही एकमात्र ऐसा ग्रह है जहां मनुष्य को तीन जीवनदायी तत्व मिलते हैं-भूमि, जल और वायु।)
The surface of the earth is a complex zone. Here three main components of the environment—lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere meet, overlap and interact. (पृथ्वी की सतह एक जटिल क्षेत्र है। यहां पर्यावरण के तीन मुख्य घटक- स्थलमंडल, वायुमंडल और जलमंडल मिलते हैं, ओवरलैप करते हैं और परस्पर क्रिया करते हैं।)
The lithosphere refers to the solid portion of the earth where we live. (लिथोस्फीयर पृथ्वी के उस ठोस भाग को संदर्भित करता है जहाँ हम रहते हैं।)
The atmosphere refers to the gaseous layers which surrounding the earth. (वायुमंडल गैसीय परतों को संदर्भित करता है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए हैं।)
The hydrosphere refers to the water bodies that exist on the earth’s surface. (जलमंडल पृथ्वी की सतह पर मौजूद जल निकायों को संदर्भित करता है।)
The biosphere is the narrow zone where we find land, water and air together. Life exists here. (जीवमंडल वह संकरा क्षेत्र है जहां हम भूमि, जल और वायु को एक साथ पाते हैं। जीवन यहाँ मौजूद है।)
The earth’s surface is divided into continents and ocean basins. (पृथ्वी की सतह महाद्वीपों और महासागर घाटियों में विभाजित है।)
Continents are large landmasses of the earth while ocean basins are huge water bodies. (महाद्वीप पृथ्वी के बड़े भूभाग हैं जबकि महासागर बेसिन विशाल जल निकाय हैं।)
Mount Everest is the highest mountain peak. Its height is 8,848 metres above the sea level. (माउंट एवरेस्ट सबसे ऊंची पर्वत चोटी है। समुद्र तल से इसकी ऊंचाई 8,848 मीटर है।)
The greatest depth of 11,022 metres is recorded at Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean. (प्रशांत महासागर में मारियाना ट्रेंच में 11,022 मीटर की सबसे बड़ी गहराई दर्ज की गई है।)
There are seven continents—Asia, Europe, Africa, North America, South America, Australia and Antarctica. (सात महाद्वीप हैं – एशिया, यूरोप, अफ्रीका, उत्तरी अमेरिका, दक्षिण अमेरिका, ऑस्ट्रेलिया और अंटार्कटिका।)
Asia is the largest continent while Australia is the smallest continent. (एशिया सबसे बड़ा महाद्वीप है जबकि ऑस्ट्रेलिया सबसे छोटा महाद्वीप है।)
Antarctica is permanently covered with thick ice sheets. Hence, it is not suitable for human settlement. (अंटार्कटिका स्थायी रूप से बर्फ की मोटी चादर से ढका रहता है। इसलिए, यह मानव बस्ती के लिए उपयुक्त नहीं है।)
More than 71% of the earth is covered with water and 29% is with land. (पृथ्वी का 71% से अधिक भाग जल से आच्छादित है और 29% भाग भूमि से आच्छादित है।)
More than 97% of the earth’s water is found in the oceans. Ocean water is salty. It is of no human use. A large proportion of the rest of the water is in the form of ice sheets and glaciers or under the ground. Only 0.03% of water is available as fresh water which is usable by human beings. (पृथ्वी का 97% से अधिक जल महासागरों में पाया जाता है। महासागर का पानी खारा होता है। इसका कोई मानव उपयोग नहीं है। बाकी पानी का एक बड़ा हिस्सा बर्फ की चादरों और ग्लेशियरों के रूप में या जमीन के नीचे है। केवल 0.03% पानी ही ताजे पानी के रूप में उपलब्ध है जो मनुष्य के उपयोग योग्य है।)
There are four major oceans—the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean and the Arctic Ocean in order of their size. (आकार के क्रम में चार प्रमुख महासागर हैं-प्रशांत महासागर, अटलांटिक महासागर, हिंद महासागर और आर्कटिक महासागर।)
The Indian Ocean is the only ocean named after a country, i.e. India. (हिंद महासागर एक ऐसा महासागर है जिसका नाम किसी देश, यानी भारत के नाम पर रखा गया है।)
The atmosphere is divided into five layers. These layer starting from earth’s surface Are—the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere and the exosphere? (वायुमंडल को पांच परतों में बांटा गया है। ये परत पृथ्वी की सतह से शुरू होती है हैं- क्षोभमंडल, समतापमंडल, मध्यमंडल, तापमंडल और बहिर्मंडल
The atmosphere is composed of several gases—Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), other gases like carbondioxide, argon and others comprise 1%. (वायुमंडल कई गैसों से बना है- नाइट्रोजन (78%), ऑक्सीजन (21%), अन्य गैसें जैसे कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, आर्गन और अन्य में 1% शामिल हैं।)
Oxygen is essential for our life. We can not live without it. Nitrogen is essential for the growth of living organisms. Carbon dioxide absorbs heat radiated by the earth and in this way it keeps the earth warm. It is also essential for plants. (ऑक्सीजन हमारे जीवन के लिए आवश्यक है। हम इसके बिना नहीं रह सकते। जीवित जीवों के विकास के लिए नाइट्रोजन आवश्यक है। कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड पृथ्वी द्वारा विकिरित ऊष्मा को अवशोषित करती है और इस प्रकार यह पृथ्वी को गर्म रखती है। यह पौधों के लिए भी जरूरी है।)
The biosphere is the zone where life exists. From tiny microbes and bacteria to huge mammals are found in the biosphere. There is a close link between all these organisms including humans. (जीवमंडल वह क्षेत्र है जहां जीवन मौजूद है। जीवमंडल में छोटे रोगाणुओं और जीवाणुओं से लेकर विशाल स्तनधारी पाए जाते हैं। मनुष्य सहित इन सभी जीवों के बीच घनिष्ठ संबंध है।)
The organisms in the biosphere are divided into plant kingdom and the animal kingdom. (जैवमंडल में जीवों को पादप जगत और जंतु जगत में विभाजित किया गया है।)
The three domains of the earth interact with each other and affect each other. For example emission from industries pollute the air. (पृथ्वी के तीन डोमेन एक दूसरे के साथ बातचीत करते हैं और एक दूसरे को प्रभावित करते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए उद्योगों से निकलने वाला उत्सर्जन वायु को प्रदूषित करता है।)
Increase in the amount of CO2 leads to an increase in global temperatures which is known as global warming. (CO2 की मात्रा में वृद्धि से वैश्विक तापमान में वृद्धि होती है जिसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Lithosphere: The solid portion of the earth on which we live is termed as the lithosphere.
स्थलमंडल: पृथ्वी का वह ठोस भाग जिस पर हम रहते हैं, स्थलमंडल कहलाता है।)
Atmosphere: The gaseous layers that surround the earth is known as the atmosphere.
वायुमंडल: पृथ्वी को चारों ओर से घेरने वाली गैसीय परतों को वायुमंडल के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Hydrosphere: The water bodies on the earth’s surface is known as hydrosphere.
उद्मंडल: पृथ्वी की सतह पर मौजूद जलराशियों को जलमंडल कहते हैं।)
Biosphere: It is the narrow zone where land, water and air together are found. All forms of life exists here.
जीवमंडल: यह संकीर्ण क्षेत्र है जहाँ भूमि, जल और वायु एक साथ पाए जाते हैं। जीवन के सभी रूप यहां मौजूद हैं।)
Continents: The large landmasses are called continents.
महाद्वीप: बड़े भूभाग को महाद्वीप कहते हैं।)
Ocean basins: The huge water bodies are called the ocean basins.
महासागरीय घाटियाँ: विशाल जलराशियों को महासागरीय घाटियाँ कहा जाता है।)
Strait: It is a narrow passage of water connecting two large water bodies like seas and oceans.
जलडमरूमध्य: यह समुद्र और महासागरों जैसे दो बड़े जल निकायों को जोड़ने वाला पानी का एक संकीर्ण मार्ग है।)
Isthmus: It is a narrow strip of land joining two landmasses.
स्थलडमरूमध्य (Isthmus): यह दो भूभागों को मिलाने वाली भूमि की संकरी पट्टी होती है।)
Plant Kingdom: The part of biosphere consisting of plants and trees.
संयंत्र साम्राज्य: जीवमंडल का हिस्सा जिसमें पौधे और पेड़ होते हैं।)
Animal Kingdom: The part of biosphere consisting of an animal.
जानवरों का साम्राज्य: बायोस्फीयर का वह हिस्सा जिसमें एक जानवर होता है।)
Global warming: Increase in the amount of carbon dioxide leads to an increase in the global temperatures. This is known as global warming.
भूमंडलीय ऊष्मीकरण: कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड की मात्रा में वृद्धि से वैश्विक तापमान में वृद्धि होती है। इसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Major Landforms of the Earth Chapter 6
पृथ्वी के प्रमुख स्थलरूप अध्याय 6
Mountains (पहाड़ों)
- A mountain is any natural elevation of the earth surface. (पहाड़ पृथ्वी की सतह का कोई भी प्राकृतिक उत्थान है।)
- There are permanently frozen rivers of ice. They are called glaciers. (बर्फ की स्थायी रूप से जमी हुई नदियाँ हैं। उन्हें ग्लेशियर कहा जाता है।)
- Mountains may be arranged in a line known as the range. (पर्वतों को एक रेखा में व्यवस्थित किया जा सकता है जिसे श्रेणी कहते हैं।)
- The Himalaya, the Alps and the Andes are mountain ranges. (हिमालय, आल्प्स और एंडीज पर्वत श्रृंखलाएं हैं।)
- There are three types of mountains—Fold Mountains, Block Mountains and Volcanic Mountains. (पर्वत तीन प्रकार के होते हैं- वलित पर्वत, ब्लॉक पर्वत और ज्वालामुखी पर्वत।)
- The Himalayan Mountains and the Alps are young fold mountains. (हिमालय पर्वत और आल्प्स नवीन वलित पर्वत हैं।)
- The Aravalli range in India is one of the oldest fold mountain systems. (भारत में अरावली श्रेणी सबसे पुरानी वलित पर्वत प्रणालियों में से एक है।)
- Block Mountains are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically. (ब्लॉक पर्वत तब बनते हैं जब बड़े क्षेत्रों को तोड़कर लंबवत विस्थापित किया जाता है।)
- Volcanic mountains are formed due to volcanic activity, e.g. Mt. Kilimanjaro in Africa. (ज्वालामुखी पर्वतों का निर्माण ज्वालामुखी क्रिया के कारण होता है, उदा. अफ्रीका में माउंट किलिमंजारो।)

Plateaus (पठारों)
- A plateau is an elevated flat land. (पठार एक ऊँची समतल भूमि है।)
- The Deccan plateau in India is one of the oldest plateaus. (भारत में दक्कन का पठार सबसे पुराने पठारों में से एक है।)
- The Tibet plateau is the highest plateau in the world. (भारत में दक्कन का पठार सबसे पुराने पठारों में से एक है।)
- The African plateau is famous for gold and diamond mining. (अफ्रीकी पठार सोने और हीरे के खनन के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।)
- The lava plateaus are rich in black soil that are fertile and good for cultivation. (लावा पठार काली मिट्टी से समृद्ध हैं जो उपजाऊ और खेती के लिए अच्छी हैं।)

Plains (मैदानों)
- Plains are large stretches of flat land. (मैदान समतल भूमि के बड़े भाग होते हैं।)
- Most of the plains are formed by rivers and their tributaries. (अधिकांश मैदान नदियों और उनकी सहायक नदियों द्वारा निर्मित हैं।)
- In India, the Indo-Gangetic plains are the most densely populated region of the country. (भारत में सिन्धु-गंगा का मैदान देश का सबसे घनी आबादी वाला क्षेत्र है।)

Landforms and the People (भू-आकृति और लोग)
- Humans have been living in different kinds of landforms in different ways. (मानव भिन्न-भिन्न प्रकार की भू-आकृतियों में भिन्न-भिन्न प्रकार से निवास करता आया है।)
- Sometimes, natural calamities such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, storms and floods cause widespread destruction. (कभी-कभी भूकंप, ज्वालामुखी विस्फोट, तूफान और बाढ़ जैसी प्राकृतिक आपदाएँ व्यापक विनाश का कारण बनती हैं।)

The surface of the earth is not the same everywhere. (पृथ्वी की सतह हर जगह एक जैसी नहीं होती है।)
Mountains, plateaus and plains are different landforms of the earth. (पर्वत, पठार और मैदान पृथ्वी के विभिन्न स्थलरूप हैं।)
A mountain is a natural elevation of the earth surface. There are three types of mountains—Fold mountains, Block mountains and Volcanic mountains. (एक पर्वत पृथ्वी की सतह का एक प्राकृतिक उत्थान है। पर्वत तीन प्रकार के होते हैं- वलित पर्वत, खंड पर्वत और ज्वालामुखी पर्वत।)
A plateau is an elevated flat land. It is a flat-topped table land standing above the surrounding area. A plateau may have one or more sides with steep slopes. (पठार एक ऊँची समतल भूमि है। यह आसपास के क्षेत्र के ऊपर खड़ी एक सपाट-चोटी वाली टेबल भूमि है। एक पठार में खड़ी ढलानों वाली एक या एक से अधिक भुजाएँ हो सकती हैं।)
The Deccan plateau is one of the oldest plateaus. (दक्कन का पठार सबसे पुराने पठारों में से एक है।)
The Tibet plateau is the highest plateau in the world. (तिब्बत का पठार विश्व का सबसे ऊँचा पठार है।)
Plains are large stretches of flat land. Some plains are extremely level while others may be slightly rolling and undulating. (मैदान समतल भूमि के बड़े भाग होते हैं। कुछ मैदान अत्यधिक स्तर के होते हैं जबकि अन्य थोड़े से लुढ़कते और लहरदार हो सकते हैं।)
Plains are generally thickly populated regions of the world. (मैदान आमतौर पर दुनिया के घनी आबादी वाले क्षेत्र हैं।)
Human habitation is found on different kinds of landforms. But population varies on these landforms. Mountains are generally not thickly populated. But plains are the regions where the thick population is found. (मानव निवास विभिन्न प्रकार की भू-आकृतियों पर पाया जाता है। लेकिन इन भू-आकृतियों पर जनसंख्या भिन्न-भिन्न होती है। पहाड़ आमतौर पर घनी आबादी वाले नहीं होते हैं। लेकिन मैदानी क्षेत्र ऐसे क्षेत्र हैं जहाँ सघन जनसंख्या पाई जाती है।)
The land is precious. We must not use it in a wasteful manner. Construction work of any type should not be carried on fertile land. Also, we should not throw garbage on land. It is our duty to take care of the land or any other natural gift. If we do this we will be conscious citizens. (जमीन बेशकीमती है। हमें इसका व्यर्थ उपयोग नहीं करना चाहिए। उपजाऊ भूमि पर किसी भी प्रकार का निर्माण कार्य नहीं किया जाना चाहिए। साथ ही हमें कूड़ा करकट जमीन पर नहीं फेंकना चाहिए। भूमि या किसी अन्य प्राकृतिक उपहार की देखभाल करना हमारा कर्तव्य है। यदि हम ऐसा करते हैं तो हम जागरूक नागरिक होंगे।)
Erosion: The wearing away of the earth’s surface is known as erosion.
अपरदन: पृथ्वी की सतह के घिस जाने को अपरदन कहते हैं।)
Mountain: A mountain is a natural elevation of the earth surface.
पर्वत: एक पर्वत पृथ्वी की सतह का एक प्राकृतिक उत्थान है।)
Glacier: Some mountains have permanently frozen river of ice. They are called glaciers.
हिमनद: कुछ पर्वतों में स्थायी रूप से जमी हुई बर्फ की नदियाँ होती हैं। उन्हें ग्लेशियर कहा जाता है।)
Range: When mountains are in an arranged line, it is called a range.
श्रेणी: जब पर्वत एक व्यवस्थित रेखा में होते हैं तो उसे श्रेणी कहते हैं।)
Horsts and graben: The uplifted blocks are known as horsts and the lowered blocks are known as graben.
होर्स्ट्स और ग्रैबेन: ऊपर उठे हुए ब्लॉकों को हॉर्स्ट्स के रूप में जाना जाता है और निचले ब्लॉकों को ग्रैबेन के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Storehouse: A building where things are stored or kept.
भण्डारगृह: वह भवन जहाँ कोई वस्तु रखी या रखी जाती है।)
Terraces: One of the series of flat areas of ground which are cut into the side of a hill like steps in order to grow crops there.
छतें: जमीन के समतल क्षेत्रों की श्रृंखला में से एक जो वहां फसल उगाने के लिए एक पहाड़ी की तरह कट जाती है।)
Flora: The plants of a particular area.
वनस्पति: एक विशेष क्षेत्र के पौधे।)
Fauna: The animals living in an area.
जीव: एक क्षेत्र में रहने वाले जानवर।)
Plateau: A plateau is an elevated flat land. It is a flat-topped table land standing above the surrounding area.
पठार: पठार एक ऊँची समतल भूमि है। यह आसपास के क्षेत्र के ऊपर खड़ी एक सपाट-चोटी वाली टेबल भूमि है।)
Plain: A plain is a vast stretch of flat land where the thick population is found.
मैदान: मैदान समतल भूमि का एक विशाल खंड है जहाँ सघन आबादी पाई जाती है।)
Our Country India Chapter 7
हमारा देश भारत अध्याय 7
India in the North is bounded by the Himalayas, the Arabian Sea in the West, and the Bay of Bengal in the East and the Indian Ocean in the South. (उत्तर में भारत हिमालय, पश्चिम में अरब सागर, पूर्व में बंगाल की खाड़ी और दक्षिण में हिंद महासागर से घिरा है।)
India has an area of about 3.28 million sq. km. (भारत का क्षेत्रफल लगभग 3.28 मिलियन वर्ग किमी है।)
The North-South extent from Kashmir to Kanyakumari is about 3,200 km. Thus, the west extent from Arunachal Pradesh to Kuchchh is about 2900 km. (कश्मीर से कन्याकुमारी तक उत्तर-दक्षिण की सीमा लगभग 3,200 किलोमीटर है। इस प्रकार अरुणाचल प्रदेश से कच्छ तक पश्चिम का विस्तार लगभग 2900 किमी.)
Locational Setting (स्थान सेटिंग)
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ N) passes almost halfway through the country. (कर्क रेखा (23°30′ N) देश के लगभग आधे रास्ते से होकर गुजरती है।)
- From South to North. India extends between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N latitudes. (दक्षिण से उत्तर की ओर। भारत का विस्तार 8°4′ उत्तर और 37°6′ उत्तर अक्षांशों के बीच है।)
- From West to East, India extends between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E longitudes. (भारत का विस्तार पश्चिम से पूर्व की ओर 68°7′ E और 97°25′ E देशांतरों के बीच है।)
- The local time changes by four minutes for every one degree of longitude. (हर एक डिग्री देशांतर के लिए स्थानीय समय में चार मिनट का परिवर्तन होता है।)
- The local time of longitude of 82°30′ E has been taken as the Indian Standard Time. (82°30′ E देशांतर के स्थानीय समय को भारतीय मानक समय के रूप में लिया गया है।)
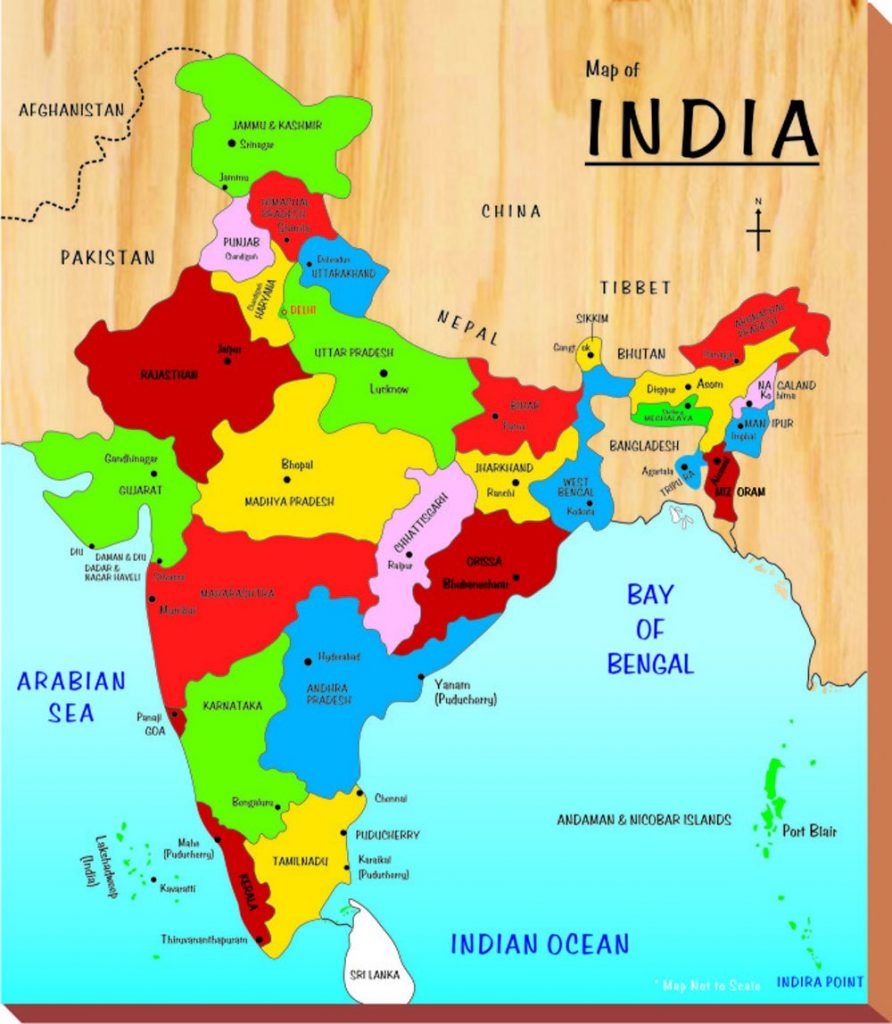
India’s Neighbours (भारत के पडोसी)
- There are seven countries that share land boundaries with India. (भारत के साथ भूमि सीमा साझा करने वाले सात देश हैं।)
- The seven countries are Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, Nepal, and Bhutan. Myanmar and Bangladesh. (सात देश अफगानिस्तान, पाकिस्तान, चीन, नेपाल और भूटान हैं। म्यांमार और बांग्लादेश।)
- Island neighbours are Sri Lanka and the Maldives. (श्रीलंका और मालदीव द्वीपीय पड़ोसी देश हैं।)
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Palk Strait. (श्रीलंका पाक जलडमरूमध्य द्वारा भारत से अलग होता है।)

Political and Administrative Divisions (राजनीतिक और प्रशासनिक प्रभाग)
- India is divided into 29 states and 7 union territories. (भारत 29 राज्यों और 7 केंद्र शासित प्रदेशों में विभाजित है।)
- Delhi is the national capital. (दिल्ली राष्ट्रीय राजधानी है।)
- Rajasthan is the largest state and Goa is the smallest state in terms of area. (क्षेत्रफल की दृष्टि से राजस्थान सबसे बड़ा राज्य है और गोवा सबसे छोटा राज्य है।)
Physical Divisions (भौतिक विभाग)
- The Himalayas in the North are divided into three main parallel ranges. (उत्तर में हिमालय को तीन मुख्य समानांतर श्रेणियों में विभाजित किया गया है।)
- The three main parallel ranges are Great Himalaya or Himadri, Middle Himalaya or Himachal and Shiwalik. (तीन मुख्य समानांतर पर्वतमालाएँ महान हिमालय या हिमाद्री, मध्य हिमालय या हिमाचल और शिवालिक हैं।)
- The Northern Indian plains lie to the South of the Himalayas. (उत्तरी भारतीय मैदान हिमालय के दक्षिण में स्थित है।)
- In the Western part of India lies the Great Indian Desert. (भारत के पश्चिमी भाग में विशाल भारतीय मरुस्थल स्थित है।)
- To the South of Northern plains lies the peninsular plateau. (उत्तरी मैदानों के दक्षिण में प्रायद्वीपीय पठार स्थित है।)
- Aravali Hills is one of the oldest ranges of the world. (अरावली की पहाड़ियाँ विश्व की सबसे पुरानी श्रेणियों में से एक हैं।)
- The Western Ghats or Sahyadris border the plateau in the West and the Eastern Ghats provide the Eastern boundary. (पश्चिमी घाट या सह्याद्री पश्चिम में पठार की सीमा बनाते हैं और पूर्वी घाट पूर्वी सीमा प्रदान करते हैं।)
- To the West of the Western Ghats and the East of Eastern Ghats lie the coastal plains. (पश्चिमी घाट के पश्चिम में और पूर्वी घाट के पूर्व में तटीय मैदान हैं।)
- The rivers Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri drain into the Bay of Bengal. (महानदी, गोदावरी, कृष्णा और कावेरी नदियाँ बंगाल की खाड़ी में गिरती हैं।)
- The Sunderban delta is formed where the Ganga and Brahmaputra flow into the Bay of Bengal. (जहां गंगा और ब्रह्मपुत्र नदियां बंगाल की खाड़ी में गिरती हैं वहां सुंदरबन डेल्टा बनता है।)
- Lakshadweep Islands are located in the Arabian Sea. (लक्षद्वीप द्वीपसमूह अरब सागर में स्थित है।)
- The Andaman and the Nicobar Islands lie to the South-East of the Indian mainland. (अंडमान और निकोबार द्वीप समूह भारतीय मुख्य भूमि के दक्षिण-पूर्व में स्थित हैं।)
Our country, India is vast. It has an area of about 3.28 million sq. km. In the north, it is surrounded by the Himalayas; in the west; there is the Arabian Sea; in the east; the Bay of Bengal and in the south; the Indian Ocean. (हमारा भारत देश विशाल है। इसका क्षेत्रफल लगभग 3.28 मिलियन वर्ग किमी है। उत्तर में, यह हिमालय से घिरा हुआ है; पश्चिम में; अरब सागर है; पूर्व में; बंगाल की खाड़ी और दक्षिण में; हिंद महासागर।)
India has diverse landforms—the lofty mountains, the Great Indian Desert, the Northern plains, the uneven plateau, and the coasts and islands. (भारत में विविध भू-आकृतियाँ हैं- ऊँचे पहाड़, महान भारतीय रेगिस्तान, उत्तरी मैदान, असमान पठार, और समुद्र तट और द्वीप।)
The climate of India also varies from region to region. (भारत की जलवायु भी एक क्षेत्र से दूसरे क्षेत्र में भिन्न होती है।)
We also find diversity in flora and fauna as well as in language and culture. (हम वनस्पतियों और जीवों के साथ-साथ भाषा और संस्कृति में भी विविधता पाते हैं।)
India is the second most populous country of the world after China. (चीन के बाद भारत दुनिया का दूसरा सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला देश है।)
India is located in the Northern hemisphere. The Tropic of Cancer passes through it. (भारत उत्तरी गोलार्ध में स्थित है। कर्क रेखा इससे होकर गुजरती है)
The sun rises two hours earlier in the east, i.e. Arunachal Pradesh than in the west Gujarat. (सूरज पश्चिम गुजरात की तुलना में पूर्व में, यानी अरुणाचल प्रदेश में दो घंटे पहले उगता है
India’s seven neighbouring countries are—Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Afganistan. (भारत के सात पड़ोसी देश हैं- पाकिस्तान, चीन, नेपाल, भूटान, बांग्लादेश, श्रीलंका और अफगानिस्तान।)
Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Palk Strait. (पाक जलडमरूमध्य श्रीलंका को भारत से अलग करता है।)
India is divided into 28 states and 7 Union Territories. Delhi is the national capital. (भारत 28 राज्यों और 7 केंद्र शासित प्रदेशों में विभाजित है। दिल्ली राष्ट्रीय राजधानी है।)
Rajasthan is the largest state while Goa is the smallest state in terms of area. (क्षेत्रफल की दृष्टि से राजस्थान सबसे बड़ा राज्य है जबकि गोवा सबसे छोटा राज्य है।)
India has diverse physical features—mountains, plateaus, plains, coasts and islands. (भारत में विविध भौतिक विशेषताएं हैं-पहाड़, पठार, मैदान, तट और द्वीप।)
The Himalayas Mountains are divided into three main parallel ranges—the Great Himalaya or Himadri, Middle Himalaya or Himachal and the Shiwalik. (हिमालय पर्वत को तीन मुख्य समानांतर श्रेणियों में विभाजित किया गया है- महान हिमालय या हिमाद्री, मध्य हिमालय या हिमाचल और शिवालिक।)
To the south of the Himalayas lie the Northern Indian plains. (हिमालय के दक्षिण में उत्तरी भारतीय मैदान हैं।)
In the western part of India lies the Great Indian Desert with little vegetation. (भारत के पश्चिमी भाग में बहुत कम वनस्पति के साथ महान भारतीय रेगिस्तान स्थित है।)
To the south of northern plains lies the peninsular plateau. It is triangular in shape. This is a region with numerous hill ranges and valleys. The Aravali hills, the Vindhyas, the Satpuras are the important ranges. (उत्तरी मैदानों के दक्षिण में प्रायद्वीपीय पठार स्थित है। यह आकार में त्रिभुजाकार होता है। यह कई पहाड़ी श्रृंखलाओं और घाटियों वाला क्षेत्र है। अरावली पहाड़ियाँ, विंध्य, सतपुड़ा प्रमुख श्रेणियाँ हैं।)
The Western Ghats border the plateau in the west and the Eastern Ghats provide the Eastern boundary. (पश्चिमी घाट पश्चिम में पठार की सीमा बनाते हैं और पूर्वी घाट प्रदान करते हैं पूर्वी सीमा।)
To the west of the Western Ghats and the East of Eastern Ghats lie the Coastal plains. (पश्चिमी घाट के पश्चिम में और पूर्वी घाट के पूर्व में तटीय मैदान हैं।)
Lakshadweep islands are located in the Arabian Sea while Andaman and Nicobar Islands group lie to the south-east of the Indian mainland in the Bay of Bengal. (लक्षद्वीप द्वीप अरब सागर में स्थित हैं जबकि अंडमान और निकोबार द्वीप समूह बंगाल की खाड़ी में भारतीय मुख्य भूमि के दक्षिण-पूर्व में स्थित हैं।)
Peninsula: A piece of land that is surrounded by water on three sides.
प्रायद्वीप: स्थल का वह भाग जो तीन ओर से जल से घिरा हो।)
Island: A piece of land that is surrounded by water on all sides.
द्वीप: भूमि का वह भाग जो चारों ओर से जल से घिरा हो।)
Desert: A vast sandy stretch of land.
रेगिस्तान: भूमि का एक विशाल रेतीला खंड।)
Alluvial deposits: Fine soil brought by rivers and deposited in the river basins.
जलोढ़ निक्षेप: नदियों द्वारा लाई गई और नदी घाटियों में जमा की गई महीन मिट्टी)
Tributary: A small river or stream that contributes its water to the main river by discharging it into the main river from either side.
उपनदी: एक छोटी नदी या जलधारा जो किसी भी ओर से मुख्य नदी में अपना जल छोड़ कर मुख्य नदी में योगदान करती है।)
Delta: An area of land formed at the mouth of the river. It is usually triangular in shape. (डेल्टा: नदी के मुहाने पर बना भूमि का एक क्षेत्र। यह आमतौर पर आकार में त्रिकोणीय होता है।)
Corals: These are skeletons of tiny marine animals called polyps.
कोरल: ये छोटे समुद्री जानवरों के कंकाल हैं जिन्हें पॉलीप्स कहा जाता है।)
Tsunami: A strong and devastating harbour wave, generated due to an earthquake on the sea floor.
सुनामी: समुद्र तल पर भूकंप के कारण उत्पन्न एक मजबूत और विनाशकारी बंदरगाह लहर।)
Strait: A narrow passage of water connecting two large water bodies like seas and oceans. जलडमरूमध्य: समुद्र और महासागरों जैसे दो बड़े जल निकायों को जोड़ने वाला पानी का एक संकीर्ण मार्ग।)
India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife Chapter 8
भारत जलवायु वनस्पति और वन्य जीवन अध्याय 8
The weather is about day to day changes in the atmosphere. (मौसम वातावरण में दिन-प्रतिदिन परिवर्तन के बारे में है।)
The major seasons in India are: (भारत में प्रमुख ऋतुएँ हैं 🙂
- Cold weather season (ठंडे मौसम का मौसम)
- Hot weather season (गर्म मौसम का मौसम)
- South-West Monsoon season (दक्षिण-पश्चिम मानसून ऋतु)
- Season of Retreating monsoon (लौटते हुए मानसून की ऋतु)
Cold Weather Season or winter (ठंड का मौसम हो या सर्दी)
- During the winter season, cool, dry winds blow from North to the South. (शीत ऋतु में ठंडी, शुष्क हवाएँ उत्तर से दक्षिण की ओर चलती हैं।)
- The sunrays do not fall directly in the region. (इस क्षेत्र में सूर्य की किरणें सीधी नहीं पड़ती हैं।)

Hot Weather Season or summer (गर्म मौसम का मौसम या गर्मी)
- The sunrays more or less directly fall in this region. (इस क्षेत्र में सूर्य की किरणें कमोबेश सीधे पड़ती हैं।)
- Hot and dry winds are called loo. (गर्म एवं शुष्क पवनों को लू कहते हैं।)

South West Monsoon Season or Rainy Season (दक्षिण पश्चिम मानसून का मौसम या बरसात का मौसम)
- The winds blow from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal toward the land. (पवनें अरब सागर तथा बंगाल की खाड़ी से स्थल की ओर चलती हैं।)
Season of Retreating Monsoon or autumn (लौटते हुए मानसून या पतझड़ की ऋतु)
- Winds move back from the mainland to the Bay of Bengal. (पवनें मुख्य भूमि से वापस बंगाल की खाड़ी की ओर चलती हैं।)
- Most of the rain is brought by monsoon winds. (अधिकांश वर्षा मानसूनी पवनों द्वारा होती है।)
- The climate of a place is affected by its location, altitude, distance from the sea and relief. (किसी स्थान की जलवायु उसके स्थान, ऊँचाई, समुद्र से दूरी और उच्चावच से प्रभावित होती है।)
- Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives the world’s highest rainfall. (मेघालय में मावसिनराम में विश्व की सबसे अधिक वर्षा होती है।)

Natural Vegetation (प्राकृतिक वनस्पति)
- The grasses, shrubs and trees, which grow on their own without interference or help from human beings are called natural vegetation. (वे घास, झाड़ियाँ और पेड़ जो बिना किसी हस्तक्षेप या मानव सहायता के अपने आप उगते हैं, प्राकृतिक वनस्पति कहलाते हैं।)
- The vegetation of India can be divided into five types- (भारत की वनस्पति को पाँच प्रकारों में बाँटा जा सकता है-)
- Tropical evergreen forest (उष्णकटिबंधीय सदाबहार वन)
- Tropical deciduous forest (उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन)
- Thorny bushes (कंटीली झाड़ियाँ)
- Mountain vegetation (पर्वतीय वनस्पति)
- Mangrove forests. (मैंग्रोव वन)

Tropical Rain Forest (उष्णकटिबंधीय रैन्फोरेस्ट)
- They are found in the areas which receive heavy rainfall. (ये उन क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं जहाँ भारी वर्षा होती है।)
- Many species of trees are found in this forest, they shed their leaves at different times of the year. They are called evergreen forests. (इस वन में कई प्रकार के वृक्ष पाए जाते हैं, वर्ष के अलग-अलग समय में इनके पत्ते झड़ जाते हैं। इन्हें सदाबहार वन कहा जाता है।)
- Important trees are mahogany, ebony and rosewood. (महत्वपूर्ण वृक्ष महोगनी, एबोनी और रोजवुड हैं।)

Tropical Deciduous Forest (उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन)
- They are also called monsoon forests. (इन्हें मानसूनी वन भी कहा जाता है।)
- Trees of these forests shed their leaves at a particular time of the year. (इन वनों के वृक्ष वर्ष के एक विशेष समय में अपनी पत्तियाँ गिराते हैं।)
- Important trees are sal, teak, peepal, neem and shisham. (महत्वपूर्ण पेड़ साल, सागौन, पीपल, नीम और शीशम हैं।)

Thorny Bushes (कांटेदार झाड़ियाँ)
- They are found in dry areas of the country. (ये देश के शुष्क क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं।)
- The leaves are in the form of spines to reduce the loss of water. (पानी की कमी को कम करने के लिए पत्तियाँ कांटों के रूप में होती हैं।)
- Important trees are cactus, Kaner, babool, keekar, etc. (कैक्टस, कनेर, बबूल, कीकर आदि प्रमुख वृक्ष हैं।)

Mountain Vegetation (पर्वतीय वनस्पति)
- At a height between 1500 metres and 2500 metres, most of the trees are conical in shape. These trees are called coniferous trees. (1500 मीटर से 2500 मीटर के बीच की ऊंचाई पर, अधिकांश पेड़ शंक्वाकार आकार के होते हैं। इन वृक्षों को शंकुधारी वृक्ष कहते हैं।)
- Important trees are chir, pine and deodar. (चीड़, चीड़ और देवदार महत्वपूर्ण वृक्ष हैं।)

Mangrove Forests (मैंग्रोव वन)
- These forests can survive in saline water. (ये वन खारे पानी में जीवित रह सकते हैं।)
- Sundari is a well-known species of trees. (सुंदरी वृक्षों की एक प्रसिद्ध प्रजाति है।)

Weather is about day to day changes in the atmosphere. It may be hot or cold, Sunny or cloudy, windy or calm. (मौसम वातावरण में दिन-प्रतिदिन परिवर्तन के बारे में है। यह गर्म या ठंडा, धूप या बादल, हवा या शांत हो सकता है।)
There are four main seasons in India—cold weather season (winter) December to February, hot weather season (summer) March to May, southwest monsoon season (rainy) June to September and season of retreating monsoon (autumn) October to November. (भारत में चार मुख्य ऋतुएँ होती हैं- ठंड का मौसम (सर्दी) दिसंबर से फरवरी, गर्म मौसम का मौसम (ग्रीष्म) मार्च से मई, दक्षिण-पश्चिम मानसून का मौसम (वर्षा) जून से सितंबर और पीछे हटने वाला मानसून (शरद ऋतु) अक्टूबर से नवंबर तक।)
The hot wind called loo blows during summer. (गर्मी के दिनों में लू नामक गर्म हवा चलती है।)
Climate is about the average weather condition which has been measured over many years. (जलवायु औसत मौसम की स्थिति के बारे में है जिसे कई वर्षों में मापा गया है।)
The climate of India is a monsoon type. It means, most of the rain is brought by monsoon winds. (भारत की जलवायु मानसून प्रकार की है। अर्थात अधिकांश वर्षा मानसूनी पवनों द्वारा होती है।)
The climate of a place is affected by its location, attitude, distance from the sea and relief. (किसी स्थान की जलवायु उसके स्थान, दृष्टिकोण, समुद्र से दूरी और उच्चावच से प्रभावित होती है।)
Jaisalmer and Bikaner in Rajasthan are very hot, Drass and Kargil in Jammu and Kashmir are very cold and coastal places are moderate. Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives the world’s highest rainfall. (राजस्थान में जैसलमेर और बीकानेर बहुत गर्म हैं, जम्मू और कश्मीर में द्रास और कारगिल बहुत ठंडे हैं और तटीय स्थान मध्यम हैं। मेघालय के मावसिनराम में विश्व की सबसे अधिक वर्षा होती है।)
India has a wide range of natural vegetation—Tropical evergreen forest, Tropical deciduous forest, Thorny bushes, Mountain vegetation and Mangrove forests. (भारत में प्राकृतिक वनस्पति की एक विस्तृत श्रृंखला है-उष्णकटिबंधीय सदाबहार वन, उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन, कांटेदार झाड़ियाँ, पर्वतीय वनस्पति और मैंग्रोव वन।)
Tropical rain forests occur in the areas which receive heavy rainfall. (उष्णकटिबंधीय वर्षा वन उन क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं जहां भारी वर्षा होती है।)
Tropical deciduous forests are also called monsoon forests. (उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वनों को मानसून वन भी कहा जाता है।)
Thorny bushes are found in dry areas of the country. (देश के शुष्क क्षेत्रों में कंटीली झाड़ियाँ पाई जाती हैं।)
Mangrove forests are found in Sunderbans in West Bengal and in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. (मैंग्रोव वन पश्चिम बंगाल के सुंदरबन और अंडमान और निकोबार द्वीप समूह में पाए जाते हैं।)
Forests are very useful for all living beings. They are the natural habitat of wildlife. (वन सभी जीवों के लिए बहुत उपयोगी हैं। वे वन्यजीवों के प्राकृतिक आवास हैं।)
Van Mahotsav is a programme which involves more and more people in making the earth green. (वन महोत्सव एक ऐसा कार्यक्रम है जिसमें अधिक से अधिक लोगों को पृथ्वी को हरा-भरा बनाने में शामिल किया जाता है।)
The tiger is our national animal. Gir forest of Gujarat is the home of Asiatic lions. (बाघ हमारा राष्ट्रीय पशु है। गुजरात का गिर जंगल एशियाई शेरों का घर है।)
The peacock is our national bird. (मोर हमारा राष्ट्रीय पक्षी है।)
There are several hundreds of species of snakes found in India. (भारत में सांपों की सैकड़ों प्रजातियां पाई जाती हैं।)
The government has started Project Tiger and Project Elephant to protect these animals. (सरकार ने इन जानवरों की सुरक्षा के लिए प्रोजेक्ट टाइगर और प्रोजेक्ट हाथी शुरू किया है।)
Weather: Weather is about day to day changes in the atmosphere. It includes changes in temperature, rainfall and sunshine etc.
मौसम: मौसम वातावरण में दिन-प्रतिदिन होने वाले परिवर्तनों के बारे में है। इसमें तापमान, वर्षा और धूप आदि में परिवर्तन शामिल हैं।)
Loo: It is a hot and dry wind that blows during the day in summer.
लू: यह एक गर्म और शुष्क हवा है जो गर्मियों में दिन के समय चलती है।)
Climate: Climate is the average weather condition which has been measured over many years. जलवायु: जलवायु औसत मौसम की स्थिति है जिसे कई वर्षों में मापा गया है।)
Monsoon: The word monsoon has been taken from the Arabic word ‘mansim’ which means seasons.
मानसून: मानसून शब्द अरबी शब्द ‘मानसीम’ से लिया गया है जिसका अर्थ है मौसम।)
Wildlife: All the wild animals and birds found in the forests, national parks and Sanctuaries.
वन्य जीव: जंगलों, राष्ट्रीय उद्यानों और अभयारण्यों में पाए जाने वाले सभी जंगली जानवर और पक्षी।)
Van Mahotsav: It is a special programme organized from time to time to promote people for planting more and more trees.
वन महोत्सव: लोगों को अधिक से अधिक पेड़ लगाने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए समय-समय पर आयोजित होने वाला यह एक विशेष कार्यक्रम है।)
Natural vegetation: The grasses, shrubs and trees that grow on their own without human interference or help are known as natural vegetation.
प्राकृतिक वनस्पति: घास, झाड़ियाँ और पेड़ जो बिना मानवीय हस्तक्षेप या सहायता के अपने आप उगते हैं, प्राकृतिक वनस्पति कहलाते हैं।)
Migratory birds: Birds that migrate to our country in the winter season every year. They arrive in December and stay till early March.
प्रवासी पक्षी: वे पक्षी जो हर साल सर्दियों के मौसम में हमारे देश में प्रवास करते हैं। वे दिसंबर में आते हैं और मार्च की शुरुआत तक रहते हैं।)
Thankyou !! we hope you like it
DOWNLOAD NCERT NOTES CLASS 6 GEOGRAPHY



