Environment Chapter 1
पर्यावरण अध्याय 1
Environment (पर्यावरण)
Nature, place, people, things, etc. that surround the living organisms make the environment. The environment can broadly be classified into the natural and human environment. It is a combination of both natural as well as man-made phenomena. (प्रकृति, स्थान, लोग, वस्तुएँ आदि जो सजीवों को घेरे रहते हैं, पर्यावरण का निर्माण करते हैं। पर्यावरण को मोटे तौर पर प्राकृतिक और मानव पर्यावरण में वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है। यह प्राकृतिक और मानव निर्मित दोनों घटनाओं का एक संयोजन है।)
The natural environment comprises biotic (plants and animals) and abiotic-conditions (land, water, air, etc.), whereas the man-made phenomena comprise the activities and interactions among human beings (roads, bridges, etc.). (प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण में जैविक (पौधे और जानवर) और अजैविक-स्थितियां (भूमि, जल, वायु, आदि) शामिल हैं, जबकि मानव निर्मित घटना में मानव (सड़क, पुल, आदि) के बीच गतिविधियां और बातचीत शामिल हैं।)

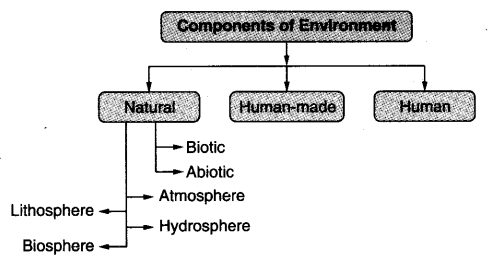
Natural Environment (प्रकृतिक वातावरण)
- Land, water, air, plants and animals comprise the natural environment. (भूमि, जल, वायु, पौधे और जानवर प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण का निर्माण करते हैं।)
- Lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere are the four domains of the natural environment. (स्थलमंडल, वायुमंडल, जलमंडल और जीवमंडल प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण के चार क्षेत्र हैं।)
- The lithosphere is the solid crust or the outermost layer of the earth where we live. It contains landforms like mountains, plateaus, plains and valleys. (लिथोस्फीयर पृथ्वी की ठोस पपड़ी या सबसे बाहरी परत है जहां हम रहते हैं। इसमें पहाड़, पठार, मैदान और घाटियाँ जैसे भू-आकृतियाँ शामिल हैं।)
- The hydrosphere is the domain of water. It comprises water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, etc. (जलमंडल जल का क्षेत्र है। इसमें नदियों, झीलों, समुद्रों, महासागरों आदि जैसे जल निकाय शामिल हैं।)
- The atmosphere is the thin layer of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays and scorching heat of the sun. (वायुमंडल हवा की पतली परत है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए है। यह हमें सूरज की हानिकारक किरणों और चिलचिलाती गर्मी से बचाता है।)
- The biosphere is a narrow zone of the earth where land, water and air interact with each other to support life. (बायोस्फीयर पृथ्वी का एक संकीर्ण क्षेत्र है जहां भूमि, जल और वायु जीवन का समर्थन करने के लिए एक दूसरे के साथ बातचीत करते हैं।)
What is Ecosystem (पारिस्थितिक तंत्र क्या है?)
- The relation between the living organisms as well as the relation between the organisms and their surrounding form the ecosystem.
- There could be an ecosystem of large rainforest, grassland, desert, mountains, lake, river, ocean and even a small pond. (जीवित जीवों के बीच का संबंध और साथ ही जीवों और उनके आसपास के बीच का संबंध पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र का निर्माण करता है।बड़े वर्षावन, घास के मैदान, रेगिस्तान, पहाड़, झील, नदी, समुद्र और यहां तक कि एक छोटा तालाब भी एक पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र हो सकता है।)

Human Environment (मानव पर्यावरण)
- Human beings interact with the environment and modify it according to their needs. (मनुष्य पर्यावरण के साथ अंतःक्रिया करते हैं और अपनी आवश्यकताओं के अनुसार इसे संशोधित करते हैं।)
- Early humans adapted themselves to their natural surroundings. (आरंभिक मानवों ने स्वयं को अपने प्राकृतिक परिवेश के अनुकूल बना लिया।)
- With time, humans learnt to grow new things, domesticate animals and lead a settled life. (समय के साथ, इंसानों ने नई चीज़ें उगाना, जानवरों को पालतू बनाना और एक व्यवस्थित जीवन जीना सीखा।)
- The industrial revolution, transportation and information revolution made communication easier and speedy across the world. (औद्योगिक क्रांति, परिवहन और सूचना क्रांति ने दुनिया भर में संचार को आसान और तेज बना दिया है।)
- Man is destroying the environment through deforestation, industrialisation, etc. (मनुष्य वनों की कटाई, औद्योगीकरण आदि के माध्यम से पर्यावरण को नष्ट कर रहा है।)
The environment in our basic life support system. It provides the air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat and the place where we live. Thus, the environment is the most important aspect of our life. (हमारे बुनियादी जीवन समर्थन प्रणाली में पर्यावरण। यह वह हवा प्रदान करता है जिसमें हम सांस लेते हैं, जो पानी हम पीते हैं, जो भोजन हम खाते हैं और वह स्थान जहां हम रहते हैं। इस प्रकार पर्यावरण हमारे जीवन का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण पहलू है।)
The natural environment consists of land, water, air, plants and animals. It refers to both biotic and abiotic conditions existing on the earth. (प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण में भूमि, जल, वायु, पौधे और जानवर शामिल हैं। यह पृथ्वी पर मौजूद जैविक और अजैविक दोनों स्थितियों को संदर्भित करता है।)
While biotic refers to the world of living organisms, such as plants and animals, abiotic refers to the world of non-living elements, such as land. (जबकि बायोटिक जीवित जीवों की दुनिया को संदर्भित करता है, जैसे पौधों और जानवरों को, अजैविक निर्जीव तत्वों की दुनिया को संदर्भित करता है, जैसे कि भूमि।)
The human environment refers to the activities, creations and interactions among human beings. (मानव पर्यावरण का तात्पर्य मनुष्यों के बीच गतिविधियों, कृतियों और अंतःक्रियाओं से है।)
Domains of environment—Lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere. (पर्यावरण के क्षेत्र – स्थलमंडल, जलमंडल, वायुमंडल और जीवमंडल।)
The lithosphere is the solid portion of the earth where we live. It is the domain that provides us forests, grasslands for grazing, land for agriculture and human settlements. It is where we find several minerals. (लिथोस्फीयर पृथ्वी का ठोस भाग है जहाँ हम रहते हैं। यह वह डोमेन है जो हमें जंगल, चराई के लिए घास के मैदान, कृषि के लिए भूमि और मानव बस्तियां प्रदान करता है। यह वह जगह है जहाँ हमें कई खनिज मिलते हैं।)
Hydrosphere refers to the water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, etc. that exist on the earth. (जलमंडल पृथ्वी पर मौजूद नदियों, झीलों, समुद्रों, महासागरों आदि जैसे जल निकायों को संदर्भित करता है।)
The atmosphere is the thin layer of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays and searching heat of the Sun. It consists of gases, dust and water vapour. (वायुमंडल हवा की पतली परत है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए है। यह हमें सूर्य की हानिकारक किरणों और खोजी गर्मी से बचाता है। इसमें गैसें, धूल और जलवाष्प होते हैं।)
Biosphere or the living world is comprised of plant and animal life. It is a narrow zone of the earth where land, water and air interact with each other to support life. (बायोस्फीयर या जीवित दुनिया में पौधे और पशु जीवन शामिल हैं। यह पृथ्वी का एक संकीर्ण क्षेत्र है जहाँ भूमि, जल और वायु जीवन का समर्थन करने के लिए एक दूसरे के साथ बातचीत करते हैं।)
The relation between the living organisms as well as the relation between the organisms and their surroundings form an ecosystem. (जीवित जीवों के साथ-साथ जीवों और उनके परिवेश के बीच संबंध एक पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र का निर्माण करते हैं।)
An ecosystem can be found in lakes, mountains, oceans, pond, etc. (एक पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र झीलों, पहाड़ों, महासागरों, तालाबों आदि में पाया जा सकता है।)
Human beings modify the natural environment as per their needs. (मनुष्य अपनी आवश्यकताओं के अनुसार प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण को संशोधित करता है।)
Environment: The place, people, things and nature that surround any living organism is called the environment.
पर्यावरण: वह स्थान, लोग, वस्तुएँ और प्रकृति जो किसी भी जीव को घेरे रहते हैं, पर्यावरण कहलाते हैं।
Biotic: It refers to the world of living organisms, such as plants and animals.
बायोटिक: यह पौधों और जानवरों जैसे जीवित जीवों की दुनिया को संदर्भित करता है।
Abiotic: It refers to the world of non-living elements such as land.
अजैविक: यह भूमि जैसे निर्जीव तत्वों की दुनिया को संदर्भित करता है।
Lithosphere: It is the solid crust or the hard top layer of the earth.
लिथोस्फीयर: यह ठोस क्रस्ट या पृथ्वी की कठोर शीर्ष परत है।
Hydrosphere: It refers to the water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, etc. on the earth. जलमंडल: यह पृथ्वी पर नदियों, झीलों, समुद्रों, महासागरों आदि जैसे जल निकायों को संदर्भित करता है।
Atmosphere: It is the thin layer of air that surrounds the earth.
वायुमंडल: यह हवा की पतली परत है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए है।
Ecosystem: The relation between the living organisms, as well as the relation between the organisms and their surroundings, form an ecosystem.
पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र: जीवित जीवों के बीच संबंध, साथ ही जीवों और उनके परिवेश के बीच संबंध, एक पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र का निर्माण करते हैं।
Barter system: A trade in which goods are exchanged without the use of money.
वस्तु विनिमय प्रणाली: एक ऐसा व्यापार जिसमें मुद्रा के उपयोग के बिना वस्तुओं का आदान-प्रदान होता है।
Inside Our Earth Chapter 2
हमारी पृथ्वी के अंदर अध्याय 2
What is Earth (पृथ्वी क्या है?)
- The earth comprises three layers: crust, mantle and core. (पृथ्वी में तीन परतें शामिल हैं: क्रस्ट, मेंटल और कोर।)
- Constant changes take place inside as well as outside the earth. (पृथ्वी के अंदर और बाहर लगातार परिवर्तन होते रहते हैं।)

What is the Interior of the Earth? (पृथ्वी का आंतरिक भाग क्या है?)
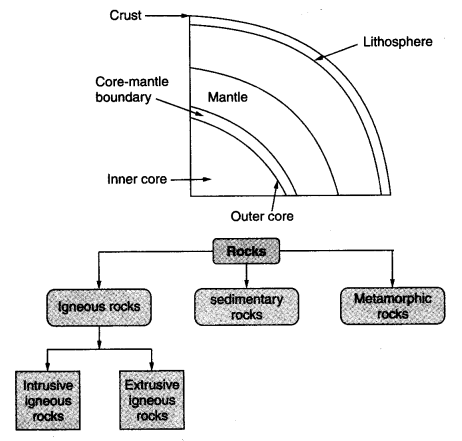
- The earth is made up of three concentric layers-crust, mantle and core. (पृथ्वी तीन संकेंद्रित परतों-क्रस्ट, मेंटल और कोर से बनी है।)
- The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface is called the crust. It is about 35 km thick on the continental masses and only 5 km thick on the ocean floor. It is made up of silica and alumina and thus called sial. (पृथ्वी की सतह पर सबसे ऊपरी परत को क्रस्ट कहा जाता है। यह महाद्वीपीय द्रव्यमान पर लगभग 35 किमी मोटा है और समुद्र तल पर केवल 5 किमी मोटा है। यह सिलिका और एल्यूमिना से बना होता है और इसलिए इसे सियाल कहा जाता है।)
- The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium called sima. Just below the crust is the mantle up to an extent of 2,900 km. (समुद्री पपड़ी मुख्य रूप से सिलिका और मैग्नीशियम से बनी होती है जिसे सिमा कहा जाता है। पपड़ी के ठीक नीचे 2,900 किमी की सीमा तक मेंटल है।)
- The innermost layer is the core with a radius of 3,500 km. As it is made of nickel and iron, it is called nife (ni-nickel and fe-ferrous i.e. iron). The central core has a very high temperature and pressure. (सबसे भीतरी परत 3,500 किमी की त्रिज्या वाली कोर है। निकल और लोहे के बने होने के कारण इसे निफे (नी-निकेल और फे-फेरस यानी लोहा) कहते हैं। केंद्रीय कोर में बहुत अधिक तापमान और दबाव होता है।)

Rocks and Minerals (चट्टानें और खनिज)
- The earth’s crust is made of various types of rocks. Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock. (पृथ्वी की पपड़ी विभिन्न प्रकार की चट्टानों से बनी है। पृथ्वी की पपड़ी बनाने वाले खनिज पदार्थ के किसी भी प्राकृतिक द्रव्यमान को चट्टान कहा जाता है।)
- There are three major types of rocks; igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. (चट्टानों के तीन प्रमुख प्रकार हैं; आग्नेय चट्टानें, अवसादी चट्टानें और रूपांतरित चट्टानें।)
- When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks thus formed are called igneous or primary rocks. They are of two types, extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rocks. (जब पिघला हुआ मैग्मा ठंडा हो जाता है, तो यह ठोस हो जाता है। इस प्रकार बनी चट्टानों को आग्नेय या प्राथमिक चट्टानें कहा जाता है। वे दो प्रकार के होते हैं, बहिर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें और अंतर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें।)
- Rocks roll down and break into small fragments and these smaller particles are called sediments. These sediments are transported, compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks. These types of rocks are called sedimentary rock. (चट्टानें लुढ़क कर छोटे-छोटे टुकड़ों में टूट जाती हैं और इन छोटे कणों को तलछट कहा जाता है। ये तलछट चट्टानों की परतें बनाने के लिए परिवहन, संकुचित और कठोर हो जाती हैं। इस प्रकार की चट्टानों को अवसादी चट्टानें कहते हैं।)
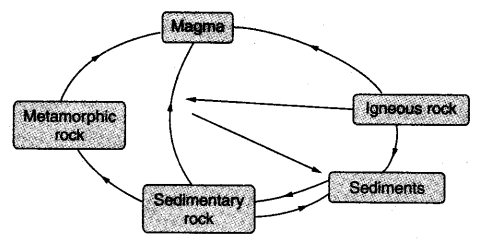
- Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure. The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is called the rock cycle. (आग्नेय और अवसादी चट्टानें अधिक गर्मी और दबाव में कायांतरित चट्टानों में बदल सकती हैं। शैल के एक से दूसरे में परिवर्तन की प्रक्रिया को शैल चक्र कहते हैं।)
- Rocks are made of different minerals. Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition. (चट्टानें विभिन्न खनिजों से बनी होती हैं। खनिज प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले पदार्थ होते हैं जिनमें कुछ भौतिक गुण और निश्चित रासायनिक संरचना होती है।)

The earth is constantly undergoing changes inside and outside. Therefore, it is called a dynamic planet. (पृथ्वी के अंदर और बाहर लगातार बदलाव हो रहे हैं। इसलिए इसे गतिशील ग्रह कहा जाता है।)
The earth is made up of several concentric layers. The uppermost layer over the earth is the surface is called the crust. It is the thinnest of all the layers. (पृथ्वी कई संकेंद्रित परतों से बनी है। पृथ्वी के ऊपर सबसे ऊपरी परत सतह है जिसे क्रस्ट कहा जाता है। यह सभी परतों में सबसे पतली है।)
The mantle is just beneath the crust. (मेंटल भूपर्पटी के ठीक नीचे होता है।)
The innermost layer is the core with a radius of about 3500 km. (सबसे भीतरी परत कोर है जिसकी त्रिज्या लगभग 3500 किमी है।)
The central core has a very high temperature and pressure. (केंद्रीय कोर में बहुत अधिक तापमान और दबाव होता है।)
The earth’s crust is made up of several types of rocks. (पृथ्वी की पपड़ी कई प्रकार की चट्टानों से बनी है।)
There are three types of rocks—igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. (चट्टानें तीन प्रकार की होती हैं- आग्नेय चट्टानें, अवसादी चट्टानें और रूपांतरित चट्टानें।)
Igneous rocks are also called primary rocks. They are of two types—intrusive rocks and extrusive rocks. (आग्नेय चट्टानों को प्राथमिक चट्टानें भी कहा जाता है। वे दो प्रकार के होते हैं- घुसपैठ करने वाली चट्टानें और बहिर्भेदी चट्टानें।)
Extrusive igneous rocks have a very fine-grained structure. For example, basalt. (बहिर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानों में बहुत महीन दाने वाली संरचना होती है। उदाहरण के लिए, बेसाल्ट।)
Intrusive igneous rocks are formed deep inside the earth. Granite is an example of this rock. (घुसपैठ करने वाली आग्नेय चट्टानें पृथ्वी के अंदर गहरे में बनती हैं। ग्रेनाइट इस चट्टान का एक उदाहरण है।)
Sedimentary rocks are formed by the sediments, which are small fragments of rocks. For example, sandstone is made from grains of sand. (तलछटी चट्टानें तलछट से बनती हैं, जो चट्टानों के छोटे टुकड़े होते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, बलुआ पत्थर रेत के दानों से बनाया जाता है।)
Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure. For example, clay changes into slate and limestone into marble (आग्नेय और अवसादी चट्टानें बड़ी गर्मी और दबाव में कायांतरित चट्टानों में बदल सकती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, मिट्टी स्लेट में और चूना पत्थर संगमरमर में बदल जाती है)
Hard rocks are used for making roads, houses and buildings (कठोर चट्टानों का उपयोग सड़कें, घर और भवन बनाने में किया जाता है।)
One type of rock changes to another type under certain conditions in a cyclic manner. This process of transformation of the rock from one to another is known as the rock cycle. (एक प्रकार की चट्टान कुछ निश्चित परिस्थितियों में चक्रीय तरीके से दूसरे प्रकार में बदलती है। चट्टान के एक से दूसरे में परिवर्तन की इस प्रक्रिया को चट्टान चक्र के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Rocks are made up of various minerals (चट्टानें विभिन्न खनिजों से बनी होती हैं।)
Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition. Minerals are very essential for human beings. (खनिज प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले पदार्थ होते हैं जिनमें कुछ भौतिक गुण और निश्चित रासायनिक संरचना होती है। मनुष्य के लिए खनिज बहुत आवश्यक हैं।)
Crust: The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface. It is very thin.
पपड़ी: पृथ्वी की सतह पर सबसे ऊपर की परत। यह बहुत पतला होता है।
Soal: The continental mass of the crust consisting of silica and alumina is called sial (si-silica and al-alumina).
सोअल: सिलिका और एल्यूमिना से मिलकर क्रस्ट के महाद्वीपीय द्रव्यमान को सियाल (सी-सिलिका और अल-एल्यूमिना) कहा जाता है।
Sima: The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium. It is therefore called sima (si-silica and ma-magnesium).
सिमा: समुद्री पपड़ी में मुख्य रूप से सिलिका और मैग्नीशियम होते हैं। इसलिए इसे सिमा (सी-सिलिका और मा-मैग्नीशियम) कहा जाता है।
Mantle: This layer is just beneath the crust. It extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust.
मेंटल: यह परत क्रस्ट के ठीक नीचे होती है। यह 2900 किमी की गहराई तक फैली हुई है पपड़ी के नीचे
Rock: A rock is a natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust.
चट्टान: एक चट्टान खनिज पदार्थ का एक प्राकृतिक द्रव्यमान है जो पृथ्वी की पपड़ी बनाता है।
Igneous rock: These rocks are formed by cooling and solidifying molten magma.
आग्नेय चट्टानें: ये चट्टानें पिघले हुए मैग्मा को ठंडा और जमने से बनती हैं।
Lava: It is fiery red molten magma coming out from the interior of the earth on its surface.
लावा: यह पृथ्वी के भीतरी भाग से इसकी सतह पर निकलने वाला लाल रंग का पिघला हुआ मैग्मा है।
Extrusive igneous rock: When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in this way on the crust are called extrusive igneous rocks.
बहिर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें: जब पिघला हुआ लावा पृथ्वी की सतह पर आता है, तो यह तेजी से ठंडा होकर ठोस बन जाता है। भूपर्पटी पर इस प्रकार बनने वाली चट्टानों को बहिर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें कहते हैं।
Intrusive igneous rock: When the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust solid intrusive igneous rocks are formed.
अंतर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें: जब पिघला हुआ मैग्मा पृथ्वी की पपड़ी के अंदर गहराई तक ठंडा होता है तो ठोस अंतर्भेदी आग्नेय चट्टानें बनती हैं।
Sediments: These are small fragments of rocks.
तलछट: ये चट्टानों के छोटे-छोटे टुकड़े होते हैं।
Sedimentary rock: When loose sediments are compressed and hardened, layers of rocks are formed. These types of rocks are known as sedimentary rocks.
अवसादी चट्टानें: जब ढीले तलछट को संकुचित और कठोर किया जाता है, तो चट्टानों की परतें बन जाती हैं। इस प्रकार की चट्टानों को अवसादी चट्टानें कहते हैं।
Rock cycle: The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is known as the rock cycle.
शैल चक्र: शैल के एक से दूसरे में परिवर्तन की प्रक्रिया को शैल चक्र के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Mineral: Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition.
खनिज: खनिज प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले पदार्थ होते हैं जिनमें कुछ निश्चित भौतिक गुण और निश्चित रासायनिक संरचना होती है।
Our Changing Earth Chapter 3
हमारी बदलती पृथ्वी अध्याय 3
The lithosphere is broken down into a number of plates known as the Lithosphere plates.( लिथोस्फीयर कई प्लेटों में टूट जाता है जिन्हें लिथोस्फीयर प्लेट्स के रूप में जाना जाता है)
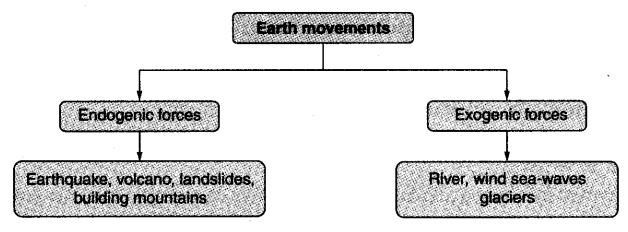
The movement of these plates causes changes on the surface of the earth. The forces that act in the interior of the earth are called endogenic forces, while the forces that work on the surface of the earth are called exogenic forces.( इन प्लेटों की गति से पृथ्वी की सतह पर परिवर्तन होता है। पृथ्वी के आंतरिक भाग में कार्य करने वाले बलों को अंतर्जनित बल कहा जाता है, जबकि पृथ्वी की सतह पर कार्य करने वाले बलों को बहिर्जात बल कहा जाता है।)
Endogenic force causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.(अंतर्जनित बल भूकंप और ज्वालामुखी विस्फोट का कारण बनता है)
Exogenic force causes weathering, erosion, deposition and gradation (बहिर्जनिक बल अपक्षय, अपरदन, निक्षेपण और उन्नयन का कारण बनता है)
Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s crust.(अपक्षय पृथ्वी की पपड़ी पर चट्टानों का टूटना है)
Erosion is the breaking away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice.( पानी, हवा और बर्फ जैसे विभिन्न एजेंटों द्वारा परिदृश्य को तोड़ना अपरदन है)
Sudden movements like earthquake and volcanoes cause most destruction over the surface of the earth. (भूकंप और ज्वालामुखी जैसी अचानक हलचलें पृथ्वी की सतह पर सबसे अधिक विनाश का कारण बनती हैं)
A volcano is a vent (opening) in the earth’s crust through which molten material erupts suddenly (ज्वालामुखी पृथ्वी की पपड़ी में एक छिद्र (छिद्र) है जिसके माध्यम से पिघला हुआ पदार्थ अचानक फूटता है)
The vibration in the plates of earth is called an earthquake.( पृथ्वी की प्लेटों में कंपन को भूकंप कहा जाता है)
The place in the crust where the movement starts is called the focus.( भूपर्पटी में वह स्थान जहां से गति प्रारंभ होती है, फोकस कहलाता है)
The place on the surface above the focus is called the epicenter.( धरातल पर फोकस के ऊपर के स्थान को अधिकेन्द्र कहते हैं)
It is measured by seismograph and intensity is measured by Richter scale.( इसे सिस्मोग्राफ से और तीव्रता को रिक्टर स्केल से मापा जाता है)
Although earthquakes cannot be predicted, the impact can certainly be minimized.( हालांकि भूकंप की भविष्यवाणी नहीं की जा सकती, लेकिन प्रभाव को निश्चित रूप से कम किया जा सकता है)
Major Landforms (प्रमुख स्थलरूप)
- The landscapes are continuously worn away by two forces, weathering and erosion.(भू-दृश्य लगातार दो बलों, अपक्षय और अपरदन द्वारा घिस जाते हैं।)
- Weathering is the breaking down of the rocks on the earth’s surface.(अपक्षय पृथ्वी की सतह पर चट्टानों का टूटना है।)
- Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice. ( कटाव पानी, हवा और बर्फ जैसे विभिन्न कारकों द्वारा भू-दृश्य को नष्ट करना है।)

Work of a River (नदी का काम)
- When the river tumbles at a steep angle over hard rocks or down a steep valley side, it forms a waterfall. (जब नदी कठोर चट्टानों पर खड़ी कोण पर या खड़ी घाटी की ओर नीचे गिरती है, तो यह एक जलप्रपात बनाती है।)
- As the river enters the plain, it twists and turns, forming large bends known as meanders ( जैसे ही नदी मैदान में प्रवेश करती है, यह मुड़ जाती है और मुड़ जाती है, जिससे बड़े मोड़ बन जाते हैं जिन्हें विसर्प कहा जाता है।)
- At this point of time, the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off called an ox-bow lake.( इस समय, विसर्प लूप नदी से कट जाता है और एक कट-ऑफ बनाता है जिसे ऑक्स-बो झील कहा जाता है।)
- During flooding, the river deposits layer of fine soil and other materials called sediments along its banks. This leads to the formation of a flat fertile plain called flood plain. (बाढ़ के दौरान, नदी अपने किनारों पर महीन मिट्टी और तलछट नामक अन्य सामग्री की परत जमा करती है। इससे समतल उपजाऊ मैदान का निर्माण होता है जिसे बाढ़ मैदान कहते हैं।)
- The raised banks along the river are called levees.( नदी के किनारे उठे हुए किनारे तटबंध कहलाते हैं।)
- The collection of sediments from all the mouths forms a delta.(सभी मुहानों से तलछट का संग्रह एक डेल्टा बनाता है।)

Work of Sea Waves (समुद्री लहरों का काम)
- The erosion and deposition of the sea waves give rise to coastal landforms.(समुद्री लहरों के अपरदन और निक्षेपण से तटीय भू-आकृतियों का निर्माण होता है।)
- Due to sea waves, hollow caves are formed on the rocks. They are called sea caves.( समुद्र की लहरों के कारण चट्टानों पर खोखली गुफाएँ बन जाती हैं। इन्हें समुद्री गुफा कहा जाता है।)
- As cavities become bigger in size, only the roof of the caves remains, thus forming sea arches. (जैसे-जैसे गुहाएँ आकार में बड़ी होती जाती हैं, गुफाओं की केवल छत ही बची रहती है, इस प्रकार समुद्री मेहराब बनते हैं।)
- The erosion further breaks the roof and only walls are left. It is called stacks.( कटाव से छत और टूट जाती है और केवल दीवारें बची रहती हैं। इसे ढेर कहा जाता है।)
- The steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above seawater is called sea cliff.( समुद्री जल के लगभग लंबवत ऊपर उठने वाले खड़ी चट्टानी तट को समुद्री चट्टान कहा जाता है।)

Work of Ice (बर्फ का काम)
- Glaciers are rivers of ice which erode the landscape by bulldozing soil and stones to expose the solid rocks below. (ग्लेशियर बर्फ की नदियाँ हैं जो नीचे की ठोस चट्टानों को उजागर करने के लिए मिट्टी और पत्थरों को बुलडोज़र से भूदृश्य को नष्ट कर देती हैं।)
- The materia carried by the glaciers, such as big and small rocks, sand and silt get deposited. These deposits form glacial moraines. (ग्लेशियर द्वारा ले जाए जाने वाले पदार्थ, जैसे बड़ी और छोटी चट्टानें, बालू और गाद जमा हो जाते हैं। ये निक्षेप हिमनद हिमोढ़ बनाते हैं।)

Work of Winds (हवाओं का काम)
- An active agent of erosion and deposition in the deserts is wind. It makes rocks in shape of a mushroom, called mushroom rocks. (रेगिस्तान में अपरदन और निक्षेपण का एक सक्रिय एजेंट हवा है। यह चट्टानों को मशरूम के आकार में बनाता है, जिसे मशरूम चट्टान कहा जाता है।)
- When the wind stops blowing, the sand falls and get deposited in low hill-like structures. These are called sand dunes.( जब हवा चलना बंद हो जाती है, तो रेत गिरती है और निचली पहाड़ी जैसी संरचनाओं में जमा हो जाती है। इन्हें बालू के टीले कहते हैं।)
- When the grains of sand is very fine and light, the wind can carry it over long distances. When such sand is deposited in large areas, it is called loess. ( जब रेत के कण बहुत महीन और हल्के होते हैं, तो हवा इसे लंबी दूरी तक ले जा सकती है। जब ऐसी बालू बड़े क्षेत्रों में जमा हो जाती है तो उसे लोएस कहते हैं।)

The lithosphere is broken into numerous plates known as the lithospheric plates. These plates move around very slowly. The movement of these plates causes changes on the surface of the earth.
(लिथोस्फीयर कई प्लेटों में टूटा हुआ है जिन्हें लिथोस्फेरिक प्लेट्स के रूप में जाना जाता है। ये प्लेटें बहुत धीमी गति से घूमती हैं। इन प्लेटों की गति से पृथ्वी की सतह पर परिवर्तन होता है।)
The earth movements are divided on the basis of the forces which cause them.( पृथ्वी की गतियों को उन शक्तियों के आधार पर विभाजित किया जाता है जो उन्हें उत्पन्न करती हैं।)
The forces which act in the interior of the earth are known as endogenic forces.( वे बल जो पृथ्वी के आन्तरिक भाग में कार्य करते हैं अंतर्जनित बल कहलाते हैं।)
The forces which work on the surface of the earth are called as exogenic forces.( वे बल जो पृथ्वी की सतह पर कार्य करते हैं बहिर्जनिक बल कहलाते हैं।)
Endogenic forces sometimes produce sudden movements which cause earthquakes and volcanoes.
(अंतर्जनित बल कभी-कभी अचानक गति उत्पन्न करते हैं जो भूकंप और ज्वालामुखी का कारण बनते हैं।)
A volcano is an opening in the earth’s crust through which molten material erupts suddenly.
( ज्वालामुखी पृथ्वी की पपड़ी में एक छेद है जिसके माध्यम से पिघला हुआ पदार्थ अचानक फट जाता है।)
When the lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. The vibrations can travel all round the earth. These vibrations are known as earthquakes.( जब लिथोस्फेरिक प्लेटें चलती हैं, तो पृथ्वी की सतह कंपन करती है। कंपन पृथ्वी के चारों ओर यात्रा कर सकते हैं। इन कंपनों को भूकंप के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
The place in the crust where the movement starts is known as the focus.( भूपर्पटी में वह स्थान जहां से गति प्रारंभ होती है, फोकस कहलाता है।)
The epicentre of the earthquake is the place on the surface above the focus. (भूकंप का केंद्र फोकस के ऊपर की सतह पर जगह है।)
Maximum damage occurs near the epicentre. (अधिकतम क्षति उपरिकेंद्र के पास होती है।)
Some common earthquake prediction methods include studying animal behaviour, fish in the ponds get agitated, and snakes come to the surface.( कुछ सामान्य भूकंप भविष्यवाणी विधियों में जानवरों के व्यवहार का अध्ययन करना, तालाबों में मछलियाँ उत्तेजित होना और सांप सतह पर आना शामिल हैं।)
The damage caused due to earthquakes can be minimised if we are prepared beforehand.( अगर पहले से तैयारी कर ली जाए तो भूकंप से होने वाले नुकसान को कम किया जा सकता है।)
During an earthquake, one can take shelter under a kitchen counter, table or desk, against an inside corner or wall. One should be away from fireplaces, areas around chimneys, windows, etc. (भूकंप के दौरान, कोई किचन काउंटर, टेबल या डेस्क के नीचे, किसी अंदरूनी कोने या दीवार के नीचे शरण ले सकता है। चिमनियों, खिड़कियों आदि के आस-पास के क्षेत्रों से दूर रहना चाहिए।
Weathering and erosion are two processes due to which the landscape is being continuously worn away. (अपक्षय और अपरदन ऐसी दो प्रक्रियाएँ हैं जिनके कारण भू-दृश्य लगातार घिसता जा रहा है।)
Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface. Erosion is the wearing ‘away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind, etc. (अपक्षय पृथ्वी की सतह पर चट्टानों का टूटना है। अपरदन विभिन्न कारकों जैसे पानी, हवा आदि द्वारा भू-दृश्य से दूर हो जाना है।)
When the river tumbles at a steep angle over very hard rocks or down a steep valley side it forms a waterfall.( जब नदी बहुत कठोर चट्टानों पर खड़ी कोण पर या खड़ी घाटी की तरफ से नीचे गिरती है तो यह एक जलप्रपात बनाती है।)
Large bends formed by twisting and turning of the river while entering the plain are called meanders.
(मैदान में प्रवेश करते समय नदी के मुड़ने और मुड़ने से बनने वाले बड़े मोड़ विसर्प कहलाते हैं।)
An oxbow lake is a cut-off lake formed due to cut off of a meander loop.( ऑक्सबो झील एक विसर्प लूप के कटने के कारण बनी एक कट-ऑफ झील है।)
Flood plains are fertile areas formed by the deposition of fine soil and other material (sediments) during floods.( बाढ़ के मैदान बाढ़ के दौरान महीन मिट्टी और अन्य सामग्री (तलछट) के जमाव से बनने वाले उपजाऊ क्षेत्र होते हैं।)
Levees are the raised banks of the rivers.( तटबंध नदियों के उठे हुए किनारे होते हैं।)
The streams which distribute the waters of a river are known as distributaries.( वे धाराएँ जो किसी नदी के जल को वितरित करती हैं, वितरिकाओं के रूप में जानी जाती हैं।)
The triangular deposits at the mouth of a river from the delta, which is very fertile.( डेल्टा से किसी नदी के मुहाने पर त्रिभुजाकार निक्षेप, जो बहुत उपजाऊ होता है।)
The erosion and deposition of the sea waves give rise to coastal landforms.( समुद्री लहरों के अपरदन और निक्षेपण से तटीय भू-आकृतियों का निर्माण होता है।)
Hallow like caves are formed on the rocks at the coast due to erosional work of sea waves. These formations are called sea caves. When these cavities become very big, only the roof of the caves remains, forming sea arches.( समुद्र की लहरों के अपरदन कार्य के कारण तट पर चट्टानों पर खोखली गुफाओं का निर्माण होता है। इन संरचनाओं को समुद्री गुफाएँ कहा जाता है। जब ये गुहाएँ बहुत बड़ी हो जाती हैं, तो केवल गुफाओं की छत ही बची रहती है, जिससे समुद्री मेहराब बनते हैं।)
This roof sometimes breaks due to erosion and thus only walls are left. These wall-like features are known as stacks.( यह छत कभी-कभी कटाव के कारण टूट जाती है और इस प्रकार केवल दीवारें ही रह जाती हैं। दीवार जैसी इन विशेषताओं को ढेर के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
The steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above seawater is called sea cliff.( समुद्री जल से लगभग लंबवत ऊपर उठने वाले खड़ी चट्टानी तट को समुद्री चट्टान कहा जाता है।)
The sea waves deposit sediments along the shores forming beaches.( समुद्र की लहरें तटों के किनारे तलछट जमा कर समुद्र तटों का निर्माण करती हैं।)
The landscape is eroded due to glaciers which are rivers of ice. The material carried by the glacier such as rocks, sand and silt gets deposited and forms glacial moraines.( हिमनदों, जो बर्फ की नदियाँ हैं, के कारण भू-दृश्य का क्षरण होता है। हिमनद द्वारा वहन की जाने वाली चट्टानें, रेत और गाद जमा हो जाती हैं और हिमोढ़ हिमोढ़ का निर्माण करती हैं।)
The wind is an active agent of erosion and deposition in the deserts. When the wind blows, it lifts and transports said from one place to another. When it stops blowing the sand falls and gets deposited in low hill-like structures known as sand dunes.( हवा रेगिस्तान में कटाव और निक्षेपण का एक सक्रिय एजेंट है। जब हवा चलती है, तो यह एक जगह से दूसरी जगह उठाती है और ट्रांसपोर्ट करती है। जब यह उड़ना बंद कर देता है तो रेत गिर जाती है और रेत के टीलों के रूप में जानी जाने वाली निचली पहाड़ी जैसी संरचनाओं में जमा हो जाती है।)
When very fine and light and gets deposited in large areas, it called loess.( जब बहुत महीन और हल्का होता है और बड़े क्षेत्रों में जमा हो जाता है तो इसे लोएस कहते हैं।)
Endogenic forces: The forces that act in the interior of the earth are called endogenic forces.
अंतर्जनित बल: वे बल जो पृथ्वी के आंतरिक भाग में कार्य करते हैं, अंतर्जनित बल कहलाते हैं।
Exogenic forces: The forces that act on the surface of the earth are called as exogenic forces.
बहिर्जनिक बल: पृथ्वी की सतह पर कार्य करने वाले बल बहिर्जनिक बल कहलाते हैं।
Earthquake: The vibrations caused by the movement of the lithospheric plates are called earthquakes.
भूकंप: स्थलमंडलीय प्लेटों की गति के कारण होने वाले कंपन को भूकंप कहा जाता है।)
Focus: The place in the crust where the movement starts is called the focus.
फोकस: क्रस्ट में वह स्थान जहां से गति शुरू होती है, फोकस कहलाता है।
Epicentre: The place on the surface above the focus is called the epicentre.
अधिकेंद्र: केंद्र के ऊपर सतह पर स्थित स्थान को अधिकेंद्र कहा जाता है।
Weathering: The breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface is known as weathering.
अपक्षय: पृथ्वी की सतह पर चट्टानों का टूटना अपक्षय कहलाता है।
Erosion: The wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice is called erosion.
अपरदन: पानी, हवा और बर्फ जैसे विभिन्न कारकों द्वारा भू-दृश्य के घिस जाने को अपरदन कहा जाता है।
Waterfall: A place where a river or stream fails from a high place for example over a cliff or rock is known as waterfall.
जलप्रपात (Waterfall): वह स्थान जहाँ नदी या जलधारा किसी ऊँचे स्थान से उदाहरण के लिए चट्टान या चट्टान पर गिरती है, जलप्रपात के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Meander: Large bends formed by the twisting and turning of a river while entering a plain are known as meanders.
विसर्प: मैदान में प्रवेश करते समय नदी के मुड़ने और मुड़ने से बनने वाले बड़े मोड़ विसर्प कहलाते हैं।
Flood plains: Floodplains are areas where fine soil and other material get deposited during floods. These are very fertile.
बाढ़ के मैदान: बाढ़ के मैदान ऐसे क्षेत्र होते हैं जहाँ बाढ़ के दौरान महीन मिट्टी और अन्य सामग्री जमा हो जाती है। ये बहुत उपजाऊ होती हैं।
Levees: The raised banks of a river is known as levees.
तटबंध: नदी के उठे हुए किनारे तटबंध कहलाते हैं।
Distributary: As the river approaches the sea, the speed of the flowing water decreases and the river begins to break up into a number of streams called distributaries.
वितरिका: जैसे-जैसे नदी समुद्र के पास पहुँचती है, बहते पानी की गति कम हो जाती है और नदी कई धाराओं में विभाजित होने लगती है जिन्हें वितरिकाएँ कहा जाता है।
Delta: It is a triangular area of land where a river has split into many smaller rivers before entering the sea.
डेल्टा: यह भूमि का एक त्रिकोणीय क्षेत्र है जहाँ एक नदी समुद्र में प्रवेश करने से पहले कई छोटी नदियों में विभाजित हो जाती है।
Sea caves: Sea caves are hollow like caves formed on the rocks.
समुद्री गुफाएँ: समुद्री गुफाएँ चट्टानों पर बनी गुफाओं की तरह खोखली होती हैं।
Sea arches: When the cavities become very big, only the roof of the caves remains known as sea arches.
समुद्री मेहराब: जब गुहाएँ बहुत बड़ी हो जाती हैं, तो केवल गुफाओं की छत ही समुद्री मेहराब के रूप में जानी जाती है।
Stacks: Further erosion breaks the roof and only wall-like features remain. These features are called stacks.
ढेर: आगे का कटाव छत को तोड़ देता है और केवल दीवार जैसी विशेषताएं रह जाती हैं। इन सुविधाओं को ढेर कहा जाता है।
Seacliff: The steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above seawater is called sea cliff.
समुद्र तट की पहाड़ी (Sea Cliff) : समुद्री जल के लगभग लंबवत ऊपर उठने वाले खड़ी चट्टानी तट को समुद्र तट की पहाड़ी कहते हैं।
Beaches: The sea waves deposit sediments along the shores to form beaches.
समुद्र तट: समुद्र की लहरें समुद्र तट बनाने के लिए किनारों पर तलछट जमा करती हैं।
Mushroom rocks: In deserts, rocks in the shape of a mushroom are very common. These are called mushroom rocks.
मशरूम चट्टानें: रेगिस्तान में, मशरूम के आकार की चट्टानें बहुत आम हैं। इन्हें मशरूम रॉक कहा जाता है।
Sand dunes: In deserts, when the winds stop blowing, the sand falls and gets deposited in low hill-like structures known as sand dunes.
रेत के टीले: रेगिस्तान में, जब हवाएँ चलना बंद कर देती हैं, तो रेत गिर जाती है और रेत के टीलों के रूप में जानी जाने वाली निचली पहाड़ी जैसी संरचनाओं में जमा हो जाती है।
Loess: When very fine and light grains of sand gets deposited in large areas, it is called loess.
लोएस (Loess)- जब बालू के बहुत महीन एवं हल्के कण बड़े क्षेत्र में जमा हो जाते हैं तो इसे लोएस कहते हैं।
Air Chapter 4
वायु अध्याय 4
Our atmosphere is surrounded by a huge blanket of air called atmosphere.( हमारा वायुमण्डल वायु के एक विशाल आवरण से घिरा हुआ है जिसे वायुमण्डल कहते हैं।)
Composition of the Atmosphere (वायुमंडल की रचना)
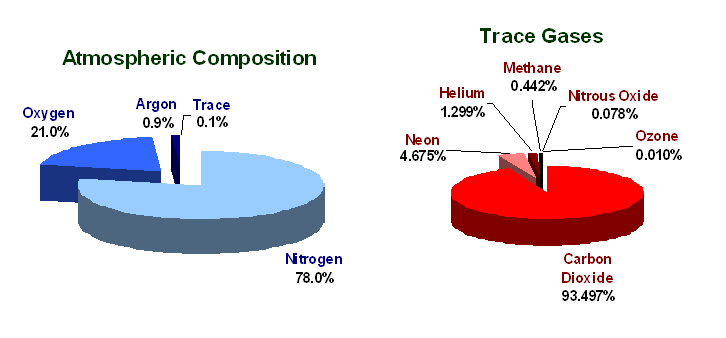
- Nitrogen and oxygen are the two gases which make up the bulk of the atmosphere.( नाइट्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन दो गैसें हैं जो वायुमंडल का बड़ा हिस्सा बनाती हैं।)
- Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.(कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, हीलियम, ओजोन, आर्गन और हाइड्रोजन कम मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं।)
- Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.( इन गैसों के अलावा हवा में छोटे धूल के कण भी मौजूद होते हैं।)
Structure of the Atmosphere (वायुमंडल की संरचना)
- Our atmosphere is divided into five layers starting from the earth’s surface. (हमारा वायुमंडल पृथ्वी की सतह से शुरू करके पाँच परतों में विभाजित है।)
- The first layer is the Troposphere whose average height is 13 km. The troposphere is the layer in which the air we breathe exist. Almost all weather phenomena occur here.(पहली परत क्षोभमंडल है जिसकी औसत ऊंचाई 13 किमी है। क्षोभमंडल वह परत है जिसमें हम जिस हवा में सांस लेते हैं वह मौजूद है। लगभग सभी मौसमी घटनाएँ यहाँ घटित होती हैं।)
- The second layer is the Stratosphere which extends up to 50 km.( दूसरी परत समताप मंडल है जो 50 किमी तक फैली हुई है।)
- The third layer is the Mesosphere which extends up to the height of 80 km. (तीसरी परत मेसोस्फीयर है जो 80 किमी की ऊंचाई तक फैली हुई है।)
- The fourth layer is the Thermosphere which extends from 80 km to 400 km.(चौथी परत थर्मोस्फीयर है जो 80 किमी से 400 किमी तक फैली हुई है।)
- The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is Exosphere which has very thin air.(वायुमंडल की सबसे ऊपरी परत एक्सोस्फीयर है जिसमें बहुत पतली हवा होती है।)
Weather and Climate (मौसम और जलवायु)
- Weather is the Hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere. (मौसम वातावरण की घंटे-दर-घंटे, दिन-प्रतिदिन की स्थिति है।)
- Climate is the weather conditions for a large period and of a large area. (जलवायु एक बड़ी अवधि और एक बड़े क्षेत्र की मौसम की स्थिति है।)
Temperature (तापमान)
- The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is called temperature. (वायु की गर्माहट और ठंडक की मात्रा को तापमान कहते हैं।)
- The temperature of the atmosphere changes not only between day and night but also from season to season, an important factor that influences the distribution of temperature is insolation. (वातावरण का तापमान न केवल दिन और रात के बीच बल्कि मौसम से मौसम में भी बदलता है, तापमान के वितरण को प्रभावित करने वाला एक महत्वपूर्ण कारक सूर्यातप है।)
- Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.(सूर्यातप पृथ्वी द्वारा अवरोधित आने वाली सौर ऊर्जा है।)
- The amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards the poles.( सूर्यातप की मात्रा भूमध्य रेखा से ध्रुवों की ओर घटती जाती है।)
- Temperature is measured in Celsius and Fahrenheit. (तापमान सेल्सियस और फ़ारेनहाइट में मापा जाता है।)
Air Pressure (हवा का दबाव)
- Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface.(वायुदाब को पृथ्वी की सतह पर वायु के भार द्वारा डाले गए दाब के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है।)
- Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by the temperature of the air at a given place.(क्षैतिज रूप से वायुदाब का वितरण किसी दिए गए स्थान पर वायु के तापमान से प्रभावित होता है।)
- In areas having a lower temperature, the air is cold.(कम तापमान वाले क्षेत्रों में हवा ठंडी होती है।)
- The air always moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.(हवा हमेशा उच्च दबाव वाले क्षेत्रों से कम दबाव वाले क्षेत्रों की ओर चलती है।)
Wind (हवा)
- The movement of air from high-pressure areas to the low-pressure area is called Wind.( उच्च दाब क्षेत्र से निम्न दाब क्षेत्र की ओर वायु की गति पवन कहलाती है।)
- Winds can be broadly divided into three types: permanent winds, seasonal winds and local winds.(पवनों को मोटे तौर पर तीन प्रकारों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है: स्थायी पवनें, मौसमी पवनें और स्थानीय पवनें।)
- On 25 October 1999, cyclonic winds originated as depression and affected Odisha killing thousands of people.(25 अक्टूबर 1999 को, चक्रवाती हवाओं की उत्पत्ति डिप्रेशन के रूप में हुई और इसने ओडिशा को प्रभावित किया जिससे हजारों लोग मारे गए।)
Moisture (नमी)
- When water evaporates from land and other water bodies, it becomes water vapour. (जब पानी भूमि और अन्य जल निकायों से वाष्पित होता है, तो यह जल वाष्प बन जाता है।)
- Moisture in the air at any time is known as humidity.(हवा में किसी भी समय नमी को आर्द्रता के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
- When the water vapour rises, it starts cooling. The water vapour condenses causing the formation of droplets of water.(जब जलवाष्प ऊपर उठता है तो यह ठंडा होने लगता है। जलवाष्प संघनित होकर जल की बूंदों का निर्माण करता है।)
- When these droplets of water become too heavy to float in the air, they come down as precipitation.(जब पानी की ये बूंदें हवा में तैरने के लिए बहुत भारी हो जाती हैं, तो वर्षण के रूप में नीचे आ जाती हैं।)
- Precipitation is the falling of moisture in the form of rainfall, snow, fog, sleet and hailstones.(वर्षा, बर्फ, कोहरे, ओले और ओलों के रूप में नमी का गिरना है।
- On the basis of mechanism, there are three types of rainfall: the convectional rainfall, the orographic rainfall and the cyclonic rainfall.( क्रियाविधि के आधार पर वर्षा तीन प्रकार की होती है: संवहन वर्षा, पर्वतीय वर्षा और चक्रवाती वर्षा।)
- Rainfall is very important for the survival of plants and animals.( पौधों और जानवरों के जीवित रहने के लिए वर्षा बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है।)
The atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. It consists of the main nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities. (वायुमंडल हवा का एक पतला आवरण है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए है। यह सूर्य की हानिकारक किरणों से हमारी रक्षा करता है। इसमें मुख्य नाइट्रोजन (78%) और ऑक्सीजन (21%) शामिल हैं। कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, हीलियम, ओजोन, आर्गन और हाइड्रोजन कम मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं।)
Nitrogen is very important for plants. Their survival depends on this gas.( पौधों के लिए नाइट्रोजन बहुत जरूरी है। उनका जीवित रहना इसी गैस पर निर्भर करता है।)
Oxygen is essential for humans and animals. They breathe in oxygen, produced by green plants during photosynthesis.( मनुष्यों और जानवरों के लिए ऑक्सीजन आवश्यक है। वे प्रकाश संश्लेषण के दौरान हरे पौधों द्वारा निर्मित ऑक्सीजन में सांस लेते हैं।)
Green plants take in carbon dioxide which is released by humans and animals. Thus, there is a mutual relation between the plants and the humans or animals. Hence, we should protect plants and trees for our own benefit.( हरे पौधे कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड लेते हैं जो मनुष्यों और जानवरों द्वारा छोड़ी जाती है। इस प्रकार, पौधों और मनुष्यों या जानवरों के बीच एक पारस्परिक संबंध है। इसलिए हमें अपने फायदे के लिए पेड़-पौधों की रक्षा करनी चाहिए।)
The atmosphere is divided into five layers starting from the earth’s surface. These layers are—Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere.( वायुमंडल को पृथ्वी की सतह से शुरू करके पांच परतों में बांटा गया है। ये परतें हैं- ट्रोपोस्फीयर, स्ट्रैटोस्फीयर, मेसोस्फीयर, थर्मोस्फीयर और एक्सोस्फीयर।)
The troposphere is the layer in which the air we breathe exists. Almost all weather phenomena occur here.( क्षोभमंडल वह परत है जिसमें हम जिस हवा में सांस लेते हैं वह मौजूद है। लगभग सभी मौसमी घटनाएँ यहाँ घटित होती हैं।)
The stratosphere contains a layer of ozone gas.( समताप मंडल में ओजोन गैस की एक परत होती है।)
The mesosphere extends up to the height of 80 km. Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space.( मेसोस्फीयर 80 किमी की ऊंचाई तक फैला हुआ है। इस परत में उल्कापिंड अंतरिक्ष से प्रवेश करते ही जल जाते हैं।)
Thermosphere helps in radio transmission.( थर्मोस्फीयर रेडियो प्रसारण में मदद करता है।)
Exosphere is the uppermost layer, where the air is very thin.( एक्सोस्फीयर सबसे ऊपरी परत है, जहां हवा बहुत पतली होती है।)
Weather is hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.( मौसम घंटे-दर-घंटे, वातावरण की दिन-प्रतिदिन की स्थिति है।)
Climate is the average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time.( जलवायु किसी स्थान की लंबी अवधि के लिए मौसम की औसत स्थिति है।)
The temperature of the atmosphere remains changing. The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.( वातावरण का तापमान बदलता रहता है। हवा की गर्माहट और ठंडक की डिग्री को तापमान के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Insolation is an important factor that influences the distribution of temperature. The amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards the poles. Therefore, the temperature decreases in the same way.( सूर्यातप एक महत्वपूर्ण कारक है जो तापमान के वितरण को प्रभावित करता है। सूर्यातप की मात्रा भूमध्य रेखा से ध्रुवों की ओर घटती जाती है। इसलिए, तापमान उसी तरह घटता है।)
Air above us presses us from all directions with a great force on our body and our body exerts a counter pressure.( हमारे ऊपर की हवा हमारे शरीर पर एक बड़ी ताकत के साथ हमें सभी दिशाओं से दबाती है और हमारा शरीर इसके विपरीत दबाव डालता है।)
Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly.( वायुदाब पृथ्वी की सतह पर वायु के भार द्वारा डाला गया दाब है। जैसे-जैसे हम वायुमंडल की परतों में ऊपर जाते हैं, दबाव तेजी से कम होता जाता है।)
Low pressure is associated with cloudy skies and wet weather. High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies. The air always moves from high-pressure areas to a low-pressure area.( कम दबाव बादल भरे आसमान और गीले मौसम से जुड़ा है। उच्च दबाव स्पष्ट और धूप वाले आसमान से जुड़ा हुआ है। वायु सदैव उच्च दाब क्षेत्र से निम्न दाब क्षेत्र की ओर चलती है।)
Wind is the movement of air from the high-pressure area to low pressure areas. Wind may be gentle. At times it may be strong and devastating.( पवन उच्च दाब क्षेत्र से निम्न दाब क्षेत्र की ओर वायु की गति है। हवा कोमल हो सकती है। कई बार यह मजबूत और विनाशकारी हो सकता है।)
Winds are of three types—Permanent winds, Seasonal winds and Local winds.( हवाएँ तीन प्रकार की होती हैं-स्थायी हवाएँ, मौसमी हवाएँ और स्थानीय हवाएँ।)
Moisture means humidity. A humid day is one when the air is the fall of water vapour. On a humid day, clothes take longer to dry and sweat from our body does not evaporate easily.( आद्रता का अर्थ है नमी। आर्द्र दिन वह होता है जब वायु जलवाष्प का गिरना होता है। उमस भरे दिन में कपड़े सूखने में अधिक समय लेते हैं और हमारे शरीर से पसीना आसानी से वाष्पित नहीं होता है।)
Clouds are masses of water droplets. When these droplets of water become very heavy they come down as precipitation. Precipitation that comes down to the earth in liquid form is called rain.(बादल पानी की बूंदों का समूह होते हैं। जब जल की ये बूँदें अत्यधिक भारी हो जाती हैं तो वर्षण के रूप में नीचे आ जाती हैं। वह वर्षा जो द्रव रूप में पृथ्वी पर नीचे आती है, वर्षा कहलाती है।)
There are three types of rain on the basis of mechanism—the conventional rainfall, the orographic rainfall and the cyclonic rainfall.( तंत्र के आधार पर वर्षा तीन प्रकार की होती है- पारम्परिक वर्षा, पर्वतीय वर्षा और चक्रवाती वर्षा।)
Constituents of air (वायु के घटक)

Atmosphere: Atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth.
वायुमंडल: वायुमंडल हवा का एक पतला आवरण है जो पृथ्वी को घेरे हुए है।)
Global warming: When the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere increases due to the increases in carbon dioxide, it is known as global warming.
ग्लोबल वार्मिंग: जब कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड में वृद्धि के कारण पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल का तापमान बढ़ जाता है, तो इसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Weather: The hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere is known as weather.
मौसम: वायुमंडल की घंटे-दर-घंटे, दिन-प्रतिदिन की स्थिति को मौसम के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Climate: The average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time is known as the climate of a place.
जलवायु: किसी स्थान की दीर्घकाल की औसत मौसमी दशाओं को उस स्थान की जलवायु कहते हैं।)
Temperature: The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.
तापमान: हवा की गर्माहट और ठंडक की डिग्री को तापमान के रूप में जाना जाता है।0
Isolation: Isolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
अलगाव: अलगाव पृथ्वी द्वारा अवरोधित आने वाली सौर ऊर्जा है।
Air pressure: The pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface is known as air pressure.
वायुदाब: वायु के भार द्वारा पृथ्वी की सतह पर डाले गए दाब को वायुदाब कहते हैं।
Wind: Wind is the movement of air from the high-pressure area to low pressure areas.
पवन: पवन उच्च दाब क्षेत्र से निम्न दाब क्षेत्र की ओर वायु की गति है।
Moisture: Water vapour present in the atmosphere is known as moisture.
नमी: वायुमण्डल में उपस्थित जलवाष्प को नमी कहते हैं।
Humidity: Moisture in the air is known as humidity.
आर्द्रता (Humidity): वायु में उपस्थित नमी को आर्द्रता कहते हैं।
Cloud: It is a mass of water droplets.
बादल: यह पानी की बूंदों का समूह होता है।
Precipitation: Falling of water on the earth in the form of rainfall is known as precipitation.
वर्षण: जल का पृथ्वी पर वर्षा के रूप में गिरना वर्षण कहलाता है।
Thermometer: It is an instrument that measures temperature.
थर्मामीटर: यह एक ऐसा यंत्र है जो तापमान को मापता है।
Barometer: It measures atmospheric pressure.
बैरोमीटर: यह वायुमंडलीय दबाव को मापता है।
Rain gauge: It measures the amount of rainfall.
वर्षामापी: यह वर्षा की मात्रा को मापता है।
Wind vane: It shows the direction of the wind.
विंड वेन: यह हवा की दिशा दिखाता है।
Water Chapter 5
जल अध्याय 5
3/4th of earth’s surface is covered by water, so the earth is called the blue planet.(पृथ्वी की सतह का 3/4 भाग जल से ढका है, इसलिए पृथ्वी को नीला ग्रह कहा जाता है।)
The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water vapour. When the water vapour cools down, it condenses and forms clouds. From there, it may fall on the land or sea in the form of rain, snow or sleet(सूर्य के ताप से जलवाष्प का वाष्पीकरण होता है। जब जलवाष्प ठण्डा हो जाता है तो यह संघनित होकर बादल बनाता है। वहां से यह बारिश, बर्फ या ओले के रूप में जमीन या समुद्र पर गिर सकता है)
The process by which water changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the water cycle.( वह प्रक्रिया जिसके द्वारा जल अपना रूप बदलता है और महासागरों, वायुमंडल और भूमि के बीच घूमता है, जल चक्र के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Our earth is like a terrarium.( हमारी धरती एक टेरारियम की तरह है।)
The major source of fresh water are the rivers, ponds, springs and glaciers.( मीठे पानी के प्रमुख स्रोत नदियाँ, तालाब, झरने और ग्लेशियर हैं।)
The ocean bodies and the seas contain salty water.( The ocean bodies and the seas contain salty water)
Distribution of Water on Earth (पृथ्वी पर जल का वितरण)
- About three-fourths of the earth’s surface is covered by water.(पृथ्वी की सतह का लगभग तीन-चौथाई भाग पानी से ढका है।)
- On earth 97% of water is saline and 3% of water is fresh water.( पृथ्वी पर 97% पानी खारा है और 3% पानी ताजा पानी है।)
- The following table gives the distribution of water in percentage:(निम्न तालिका प्रतिशत में पानी का वितरण देती है:)

- Water is absolutely essential for survival.( जीवित रहने के लिए पानी नितांत आवश्यक है।)
Movements (मूव्मन्ट )
- Unlike the calm water of ponds and lakes, ocean water keeps moving continuously.(तालाबों और झीलों के शांत जल के विपरीत समुद्र का जल निरंतर गतिमान रहता है।)
- The movements which occur in oceans are of three types: waves, tides and currents.( महासागरों में होने वाली हलचलें तीन प्रकार की होती हैं: लहरें, ज्वार और धाराएँ।)
Waves (लहर )
- When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves.(जब समुद्र की सतह पर पानी बारी-बारी से ऊपर उठता और गिरता है तो उसे लहरें कहते हैं।)
- An earthquake, a volcanic eruption or underwater landslides can shift large amounts of ocean water. As a result, huge tidal wave may be formed which is called tsunami.( एक भूकंप, एक ज्वालामुखी विस्फोट या पानी के नीचे के भूस्खलन से समुद्र के पानी की बड़ी मात्रा स्थानांतरित हो सकती है। इसके परिणामस्वरूप एक विशाल ज्वारीय लहर बन सकती है जिसे सुनामी कहा जाता है।)
- Tsunami in South and South-East Asian coast had caused havoc in December 2004.(दिसंबर 2004 में दक्षिण और दक्षिण-पूर्व एशियाई तट पर सुनामी ने तबाही मचाई थी)
Tides (ज्वार)
- The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called a tide.(समुद्र के पानी का एक दिन में दो बार लयबद्ध तरीके से उठना और गिरना ज्वार कहलाता है।
- Tides are of two types: spring tides and neap tides. (ज्वार दो प्रकार के होते हैं: वसंत ज्वार और लघु ज्वार।)

Ocean Currents (सागर की लहरें)
- Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in different directions(महासागरीय धाराएँ विभिन्न दिशाओं में समुद्र की सतह पर लगातार बहने वाली जलधाराएँ हैं)
- Ocean currents are of two types, warm and cold (महासागरीय धाराएँ दो प्रकार की होती हैं, गर्म और ठंडी)
- The Labrador Ocean current is a cold current, while the Gulf Stream is a warm current(लैब्राडोर महासागर धारा एक ठंडी धारा है, जबकि गल्फ स्ट्रीम एक गर्म धारा है)
Water is very important for our survival. It continuously changes its form and circulates between oceans and atmosphere. (पानी हमारे जीने के लिए बहुत जरूरी है। यह लगातार अपना रूप बदलता रहता है और महासागरों और वायुमंडल के बीच घूमता रहता है।)
We get fresh water from the rivers, ponds, springs and glaciers.( हमें नदियों, तालाबों, झरनों और हिमनदों से ताजा पानी मिलता है।)
The ocean bodies and the seas contain salty water.( महासागरों और समुद्रों में खारा पानी होता है।)
Three-fourth of the earth surface is covered by water. But all the water on earth is not available to us. 97.3% of water is saline or salty found in oceans and seas. Only 3% is fresh water. Its 3% is available to us, which we use in our daily life.( पृथ्वी की सतह का तीन-चौथाई भाग जल से ढका है। लेकिन पृथ्वी पर जितना पानी है वह हमारे लिए उपलब्ध नहीं है। 97.3% पानी खारा या खारा है जो महासागरों और समुद्रों में पाया जाता है। केवल 3% ताजा पानी है। इसका 3% हमारे पास उपलब्ध होता है, जिसे हम अपने दैनिक जीवन में प्रयोग करते हैं।)
Many countries are facing water scarcity due to this fact. What is available is also not fit for drinking because it is polluted badly due to a variety of reasons.( इस तथ्य के कारण कई देश पानी की कमी का सामना कर रहे हैं। जो उपलब्ध है वह पीने योग्य भी नहीं है क्योंकि वह अनेक कारणों से बुरी तरह प्रदूषित है।)
Ponds and lakes have calm water whereas ocean water keeps moving continuously. The movements that occur in oceans can be categorized as waves, tides and currents.( तालाबों और झीलों में शांत जल होता है जबकि समुद्र का जल निरंतर गतिमान रहता है। महासागरों में होने वाली हलचलों को लहरों, ज्वार और धाराओं के रूप में वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है।)
When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they known as waves.(जब समुद्र की सतह पर पानी बारी-बारी से ऊपर उठता और गिरता है, तो उन्हें लहरें कहा जाता है।)
During stormy weather, huge waves are formed. These waves are very strong and cause heavy destruction. (तूफानी मौसम के दौरान बड़ी लहरें बनती हैं। ये लहरें बहुत तेज होती हैं और भारी तबाही मचाती हैं।)
Tsunami, a huge tidal wave, is very strong. The tsunami of 2004 caused widespread damage in the coastal areas of India.( सुनामी, एक विशाल ज्वारीय लहर, बहुत शक्तिशाली होती है। 2004 की सूनामी ने भारत के तटीय क्षेत्रों में व्यापक क्षति की।)
Tides are the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water which occur twice in a day. It is high tide when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. It is low tide when waterfalls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore.( ज्वार-भाटा समुद्र के पानी का लयबद्ध उतार-चढ़ाव है जो दिन में दो बार होता है। यह उच्च ज्वार है जब पानी अपने उच्चतम स्तर तक बढ़ कर तट के अधिकांश भाग को ढक लेता है। यह निम्न ज्वार है जब जलप्रपात अपने निम्नतम स्तर पर आ जाता है और किनारे से हट जाता है।)
During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line and the tides are highest. These tides are called spring tides. (पूर्णिमा और अमावस्या के दिनों में, सूर्य, चंद्रमा और पृथ्वी एक ही रेखा में होते हैं और ज्वार-भाटे सबसे अधिक होते हैं। इन ज्वारों को वसंत ज्वार कहते हैं।)
When the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and earth resulting in low tides. These tides are called neap tides. (जब चंद्रमा अपनी पहली और आखिरी तिमाही में होता है, तो समुद्र का पानी सूर्य और पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण खिंचाव से तिरछे विपरीत दिशाओं में खींचा जाता है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप निम्न ज्वार आते हैं। इन ज्वारों को लघु ज्वार कहते हैं।)
High tides help in navigation.( उच्च ज्वार नेविगेशन में मदद करते हैं।)
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions(महासागरीय धाराएँ निश्चित दिशाओं में समुद्र की सतह पर निरंतर बहने वाली जल की धाराएँ हैं।)
Ocean currents may be warm or cold. The Labrador Ocean current is cold current while the Gulf Stream is a warm current.( महासागरीय धाराएँ गर्म या ठंडी हो सकती हैं। लैब्राडोर महासागरीय जलधारा ठंडी जलधारा है जबकि गल्फ स्ट्रीम उष्ण जलधारा है।)
The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing grounds of the world (वे क्षेत्र जहाँ गर्म और ठंडी धाराएँ मिलती हैं, दुनिया का सबसे अच्छा मछली पकड़ने का मैदान प्रदान करते हैं)
Evaporation: It is the process through which water turns into vapour.
वाष्पीकरण: यह वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा पानी वाष्प में बदल जाता है।
Condensation: It is the process in which water vapour turns into water droplets.
संघनन: यह वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें जल वाष्प पानी की बूंदों में बदल जाता है।
Water cycle: It is the process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land.
जल चक्र: यह वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा जल लगातार अपना रूप बदलता रहता है और महासागरों, वायुमंडल और भूमि के बीच घूमता रहता है।
Terrarium: It is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants.
टेरारियम: यह छोटे घरेलू पौधों को रखने के लिए एक कृत्रिम घेरा है।
Precipitation: Falling of moisture in the form of rainfall, snow, sleet and hailstone.
अवक्षेपण: वर्षा, हिमपात, ओले और ओलों के रूप में नमी का गिरना।
Waves: When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves.
लहरें: जब समुद्र की सतह पर पानी बारी-बारी से ऊपर उठता और गिरता है तो उसे लहरें कहते हैं।
Tsunami: Tsunami is a huge tidal wave.
सुनामी: सुनामी एक विशाल ज्वारीय लहर है।
Tide: Tide is the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water that occurs twice in a day.
ज्वार: ज्वार समुद्र के पानी का लयबद्ध उतार-चढ़ाव है जो दिन में दो बार होता है।
Springtide: During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line and the tides are highest. These tides are called spring tides.
वसंत ज्वार : पूर्णिमा और अमावस्या के दिनों में, सूर्य, चंद्रमा और पृथ्वी एक ही रेखा में होते हैं और ज्वार-भाटे सबसे अधिक होते हैं। इन ज्वारों को वसंत ज्वार कहते हैं।
Neap tide: When the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and earth resulting in low tides. These tides are called neap tides.
लघु ज्वार: जब चंद्रमा अपनी पहली और आखिरी तिमाही में होता है, तो समुद्र का पानी सूर्य और पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण खिंचाव से तिरछे विपरीत दिशाओं में खींचा जाता है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप निम्न ज्वार आते हैं। इन ज्वारों को लघु ज्वार कहते हैं।
Ocean currents: These are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions.
महासागरीय धाराएँ: ये निश्चित दिशाओं में समुद्र की सतह पर निरंतर बहने वाली जलधाराएँ हैं।
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Chapter 6
प्राकृतिक वनस्पति और वन्य जीवन अध्याय 6
Natural vegetation means the plants that grow naturally without human interference.( प्राकृतिक वनस्पति का अर्थ है ऐसे पौधे जो मानवीय हस्तक्षेप के बिना स्वाभाविक रूप से विकसित होते हैं।)
Natural vegetation can be categorised into three categories namely; forest, grassland and desert(प्राकृतिक वनस्पति को तीन श्रेणियों में वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है; जंगल, चरागाह और रेगिस्तान)
The change in the type of natural vegetation occurs mainly because of the changes of climatic conditions.( प्राकृतिक वनस्पति के प्रकार में परिवर्तन मुख्य रूप से जलवायु परिस्थितियों में परिवर्तन के कारण होता है।)
Forests (जंगलों)
- Forests grow where temperature and rainfall are plentiful to support a tree cover.( वन वहाँ उगते हैं जहाँ वृक्षों के आच्छादन को सहारा देने के लिए तापमान और वर्षा प्रचुर मात्रा में होती है।)
- Forests are of six types: Tropical Evergreen, Tropical Deciduous, Temperate Evergreen, Temperate Deciduous, Mediterranean Vegetation, and Coniferous forests(वन छह प्रकार के होते हैं: उष्णकटिबंधीय सदाबहार, उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती, शीतोष्ण सदाबहार, शीतोष्ण पर्णपाती, भूमध्यसागरीय वनस्पति और शंकुधारी वन)
- Tropical Evergreen Forests are those which occur in the region near the equator and close to the tropics.( उष्णकटिबंधीय सदाबहार वन वे हैं जो भूमध्य रेखा के पास और उष्णकटिबंधीय के करीब के क्षेत्र में पाए जाते हैं।)
- Tropical Deciduous Forests are monsoon forests which shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water.( उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन मानसूनी वन हैं जो जल संरक्षण के लिए शुष्क मौसम में अपनी पत्तियाँ गिरा देते हैं।)
- Temperate Evergreen Forests are located in the mid-latitudinal coastal region.( समशीतोष्ण सदाबहार वन मध्य अक्षांशीय तटीय क्षेत्र में स्थित हैं।)
- Temperate Deciduous Forests are those which shed their leaves in the dry season.(समशीतोष्ण पर्णपाती वन वे हैं जो शुष्क मौसम में अपने पत्ते गिरा देते हैं।)
- Mediterranean Vegetation is found around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe.(भूमध्यसागरीय वनस्पति यूरोप में भूमध्य सागर के आसपास पाई जाती है।)
- Coniferous Forests are found in areas along the Taiga.(शंकुधारी वन टैगा के किनारे के क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं।)
Grasslands (घास के मैदानों)
- Grasslands are found in the regions of moderate rainfall. They are of two types—Tropical Grasslands, which have tall coarse grass, and Temperate Grasslands घास के मैदान मध्यम वर्षा वाले क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं। वे दो प्रकार के होते हैं-उष्णकटिबंधीय घास के मैदान, जिनमें लंबी मोटी घास होती है, और शीतोष्ण घास के मैदान।
- Tropical Grasslands occurs on either side of the equator and extend till the tropics. Tropical Grassland of Africa is called Savannah. (उष्णकटिबंधीय घास के मैदान भूमध्य रेखा के दोनों ओर पाए जाते हैं और उष्णकटिबंधीय तक फैले हुए हैं। अफ्रीका के उष्ण कटिबंधीय घास के मैदान को सवाना कहते हैं।)
- Temperate Grasslands are in mid-latitudes and are called prairies, steppes, etc. The grass is usually short here.(समशीतोष्ण घास के मैदान मध्य अक्षांश में होते हैं और इन्हें प्रेयरी, स्टेपीज़ आदि कहा जाता है। आमतौर पर यहाँ घास छोटी होती है।)

Thorny Bushes (कांटेदार झाड़ियाँ)
- Thorny bushes are found in the dry desert-like regions.(कँटीली झाड़ियाँ शुष्क मरुस्थल जैसे प्रदेशों में पाई जाती हैं।)
- These are found in areas with scanty rain and scorching heat.(ये कम वर्षा और चिलचिलाती गर्मी वाले क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं।)

Tundra Vegetation (टुंड्रा वनस्पति)
- Mosses, lichens and very small Shrubs are found in cold regions. This is called tundra type vegetation. (काई, लाइकेन और बहुत छोटी झाड़ियाँ ठंडे प्रदेशों में पाई जाती हैं। इसे टुंड्रा प्रकार की वनस्पति कहते हैं।)
- It is found in polar areas.( यह ध्रुवीय क्षेत्रों में पाया जाता है।)
Trees, grass, lichen, mosses, etc. that grow naturally without human interference constitute natural vegetation. (पेड़, घास, लाइकेन, काई आदि जो मानवीय हस्तक्षेप के बिना प्राकृतिक रूप से उगते हैं, प्राकृतिक वनस्पति का गठन करते हैं।)
The growth of natural vegetation depends on temperature and moisture. It also depends on factors such as slope and thickness of soil.( प्राकृतिक वनस्पति का विकास तापमान और नमी पर निर्भर करता है। यह ढलान और मिट्टी की मोटाई जैसे कारकों पर भी निर्भर करता है।)
Natural vegetation is classified into three categories—forests, grasslands and shrubs.( प्राकृतिक वनस्पति को तीन श्रेणियों में बांटा गया है- वन, घास के मैदान और झाड़ियाँ)
The changes in the type of natural vegetation occur mainly because of the changes in climatic condition. (प्राकृतिक वनस्पति के प्रकार में परिवर्तन मुख्य रूप से जलवायु परिस्थितियों में परिवर्तन के कारण होता है।)
Forests grow where temperature and rainfall are plentiful to support a tree cover. Forests may be dense and open.( वन वहाँ उगते हैं जहाँ वृक्षों के आवरण को सहारा देने के लिए तापमान और वर्षा प्रचुर मात्रा में होती है। वन घने और खुले हो सकते हैं।)
Tropical evergreen forests also known as tropical rainforests are very dense and are found in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics. Hardwood trees such as rosewood, ebony, and mahogany are common here.( उष्णकटिबंधीय सदाबहार वन, जिन्हें उष्णकटिबंधीय वर्षावन के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, बहुत घने होते हैं और भूमध्य रेखा के पास और उष्णकटिबंधीय के करीब के क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं। शीशम, आबनूस और महोगनी जैसे कठोर लकड़ी के पेड़ यहाँ आम हैं।)
Tropical deciduous forests are monsoon forests. They are found in the large part of India, Northern Australia and in Central America. They shed their leaves in dry seasons. Trees like sal, teak, neem and shisham are found here.( उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन मानसून वन हैं। वे भारत, उत्तरी ऑस्ट्रेलिया और मध्य अमेरिका के बड़े हिस्से में पाए जाते हैं। शुष्क मौसम में ये अपनी पत्तियाँ गिरा देते हैं। यहां साल, सागौन, नीम और शीशम जैसे पेड़ पाए जाते हैं।)
Temperate evergreen forests are commonly found along the eastern margin of the continents. In these forests both hard and softwood trees such as oak, pine, eucalyptus, etc. are found.( समशीतोष्ण सदाबहार वन आमतौर पर महाद्वीपों के पूर्वी किनारे पर पाए जाते हैं। इन वनों में बलूत, चीड़, यूकेलिप्टस आदि कठोर तथा मुलायम दोनों प्रकार के वृक्ष पाए जाते हैं।)
Temperate deciduous forests are found in the northeastern part of USA, China, New Zealand and Chile. They shed their leaves in the dry season. Trees like oak, ash, beech etc. and animals like deer, foxes, and wolves are common in these forests.( समशीतोष्ण पर्णपाती वन संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका, चीन, न्यूजीलैंड और चिली के उत्तरपूर्वी भाग में पाए जाते हैं। शुष्क मौसम में ये अपनी पत्तियाँ गिरा देते हैं। ओक, राख, बीच आदि जैसे पेड़ और हिरण, लोमड़ी और भेड़िये जैसे जानवर इन जंगलों में आम हैं।)
Mediterranean vegetation is mostly found in the areas around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. Mediterranean vegetation is mainly comprised of citrus fruits such as oranges, figs, olives and grapes.( भूमध्यसागरीय वनस्पति ज्यादातर यूरोप, अफ्रीका और एशिया में भूमध्य सागर के आसपास के क्षेत्रों में पाई जाती है। भूमध्यसागरीय वनस्पति में मुख्य रूप से खट्टे फल जैसे संतरे, अंजीर, जैतून और अंगूर शामिल हैं।)
Coniferous forests are also known as Traga. These forests are found in the higher latitudes of Northern hemisphere. They are also found in the higher altitudes. The trees are tall, softwood evergreen trees. Chir, pine, cedar is an important variety of trees in these forests. Animals such as silver fox, mink, and polar bear are common here.( शंकुधारी वनों को ट्रागा के नाम से भी जाना जाता है। ये वन उत्तरी गोलार्ध के उच्च अक्षांशों में पाए जाते हैं। वे अधिक ऊंचाई पर भी पाए जाते हैं। पेड़ लम्बे, मुलायम लकड़ी वाले सदाबहार पेड़ हैं। इन वनों में चीड़, चीड़, देवदार वृक्षों की महत्वपूर्ण प्रजातियाँ हैं। सिल्वर फॉक्स, मिंक और पोलर बियर जैसे जानवर यहां आम हैं।)
Grasslands include tropical and temperate grasslands. Tropical grasslands grow in the areas of moderate to low amount of rainfall. Savannah grasslands of Africa present a suitable example of these types of grasslands. Animals like elephants, zebras, giraffes, dear are commonly found here (घास के मैदानों में उष्णकटिबंधीय और समशीतोष्ण घास के मैदान शामिल हैं। उष्णकटिबंधीय घास के मैदान मध्यम से कम वर्षा वाले क्षेत्रों में उगते हैं। अफ्रीका के सवाना घास के मैदान इस प्रकार के घास के मैदानों का एक उपयुक्त उदाहरण प्रस्तुत करते हैं। हाथी, जेब्रा, जिराफ, डियर जैसे जानवर आमतौर पर यहां पाए जाते हैं)
Temperate grasslands are found in the mid-latitudinal zones and in the interior part of the continents. Short and nutritious grass in found here. Common animals are buffaloes, bison, antelopes etc (समशीतोष्ण घास के मैदान मध्य अक्षांशीय क्षेत्रों और महाद्वीपों के आंतरिक भाग में पाए जाते हैं। यहाँ छोटी और पौष्टिक घास पाई जाती है। आम जानवर भैंस, बाइसन, मृग आदि हैं)
Thorny bushes are found in the dry deserts. Here, vegetation cover is scarce because of poor rain and scorching heat.( शुष्क मरुस्थलों में काँटेदार झाड़ियाँ पाई जाती हैं। यहाँ, कम वर्षा और चिलचिलाती गर्मी के कारण वनस्पति आवरण दुर्लभ है।)
Polar Regions are cold and their natural vegetation is limited here. Only mosses, lichens and very small shrubs are found here. Vegetation found in the Polar Regions is called Tundra type of vegetation. Seal, walruses, musk-oxen, Arctic owl etc. are common here.( ध्रुवीय क्षेत्र ठंडे होते हैं और उनकी प्राकृतिक वनस्पति यहाँ सीमित होती है। यहाँ केवल काई, लाइकेन और बहुत छोटी झाड़ियाँ पाई जाती हैं। ध्रुवीय प्रदेशों में पाई जाने वाली वनस्पति को टुण्ड्रा प्रकार की वनस्पति कहते हैं। सील, वालरस, कस्तूरी-बैल, आर्कटिक उल्लू आदि यहाँ आम हैं।)
Human beings are dependent on the environment.( मनुष्य पर्यावरण पर निर्भर है।)
To grow food, build homes and develop better means of transport and communication, human beings have modified the environment.( भोजन उगाने, घर बनाने और परिवहन और संचार के बेहतर साधन विकसित करने के लिए मनुष्य ने पर्यावरण को संशोधित किया है।)
Settlements (बस्तियों)
- Settlements are places where people build their homes.(बस्तियाँ वे स्थान हैं जहाँ लोग अपना घर बनाते हैं।)
- The settlements earlier grew near the river valleys as the water was easily available and the land was fertile.(पहले बस्तियाँ नदी घाटियों के पास विकसित होती थीं क्योंकि पानी आसानी से उपलब्ध था और भूमि उपजाऊ थी।)
- Settlements can be permanent or temporary.(पहली बस्तियाँ नदी घाटियों के पास विकसित होती थीं क्योंकि पानी आसानी से उपलब्ध था और कर्तव्य दिखा रही थी।)
- Settlements which are occupied for a short time are called temporary settlements(ऐसी बस्तियाँ जो थोड़े समय के लिए अधिवासित होती हैं, अस्थायी बस्तियाँ कहलाती हैं)
- In permanent settlements, people build homes to live in.(स्थायी बस्तियों में लोग रहने के लिए घर बनाते हैं।)
- Settlements can be rural or urban. Rural settlements can be compact or scattered.(बस्तियाँ ग्रामीण या शहरी हो सकती हैं। ग्रामीण बस्तियाँ सघन या बिखरी हुई हो सकती हैं)
- People in rural areas practice agriculture. In the urban area, people are mostly engaged in services.(ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में लोग कृषि करते हैं। शहरी क्षेत्र में, लोग ज्यादातर सेवाओं में लगे हुए हैं।)
Transport (यातायात)
- Transport is the means by which people and goods move.(परिवहन वह साधन है जिसके द्वारा लोग और सामान चलते हैं।)
- With the invention of the wheel, transport became easier.(पहिए के आविष्कार के साथ, परिवहन आसान हो गया।)
- Earlier donkeys, mules, bullocks and camels were used for transportation.(पहले गधों, खच्चरों, बैलों और ऊँटों का उपयोग परिवहन के लिए किया जाता था।)
- Earlier traders took the land route or sea route for transportation. Now it takes only 6-8 hours to travel from India to Europe.(पहले व्यापारी परिवहन के लिए स्थल मार्ग या समुद्री मार्ग का प्रयोग करते थे। अब भारत से यूरोप का सफर करने में सिर्फ 6-8 घंटे लगते हैं।)
- The four major means of transport are roadways, railways, waterways and airways.(परिवहन के चार प्रमुख साधन सड़क मार्ग, रेलवे, जलमार्ग और वायुमार्ग हैं)
Roadways (सड़क मार्ग)
- The most commonly used means of transport, especially for short distances, are roads. They can be metalled or unmetalled.(परिवहन का सबसे अधिक इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला साधन, विशेष रूप से कम दूरी के लिए, सड़कें हैं। वे धातु या बिना धातु के हो सकते हैं।)
Railways (रेलवे)
- Railways are the fastest means of land transport and can carry bulky materials over a long distance.( रेलवे जमीनी परिवहन का सबसे तेज साधन है और भारी सामान को लंबी दूरी तक ले जा सकता है।)
- The railways carry people over long distances quickly and economically.( रेलवे लोगों को जल्दी और आर्थिक रूप से लंबी दूरी तक ले जाती है।)
- The invention of the steam engine and the industrial revolution helped in the speedy development of rail transport.(भाप के इंजन के आविष्कार और औद्योगिक क्रांति ने रेल परिवहन के तीव्र विकास में मदद की।)
- Diesel and electric engine have largely replaced the steam engines.(डीज़ल और बिजली के इंजनों ने बड़े पैमाने पर भाप के इंजनों का स्थान ले लिया है।)
- Now superfast trains have been introduced to make travelling faster.(यात्रा को तेज करने के लिए अब सुपरफास्ट ट्रेनें शुरू की गई हैं।)
- Indian Railways network is the largest in Asia.(भारतीय रेल नेटवर्क एशिया में सबसे बड़ा है।)
Waterways (जलमार्ग)
- Waterways are the cheapest means of transportation for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.( लंबी दूरी तक भारी और भारी सामान ले जाने के लिए जलमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे सस्ता साधन है।)
- There are mainly two types of routes, inland waterways and sea routes.(मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकार के मार्ग हैं, अंतर्देशीय जलमार्ग और समुद्री मार्ग।)
- Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways.( नौगम्य नदियों और झीलों का उपयोग अंतर्देशीय जलमार्गों के रूप में किया जाता है।)
- Sea routes are connected through ports.(समुद्री मार्ग बंदरगाहों के माध्यम से जुड़े हुए हैं।)
Airways (हवाई मार्ग)
- Airways are the fastest and most expensive mode of transport.(वायुमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे तेज और सबसे महंगा साधन है।)
- It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways.(यह सबसे दूरस्थ और दूरस्थ क्षेत्रों तक पहुँचने के लिए परिवहन का एकमात्र साधन है, खासकर जहाँ सड़कें और रेलमार्ग नहीं हैं।)
- Some major airports in the world are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo etc.(दुनिया के कुछ प्रमुख हवाई अड्डे दिल्ली, मुंबई, न्यूयॉर्क, लंदन, पेरिस, फ्रैंकफर्ट और काहिरा आदि हैं।)
Communication (संचार)
- Process of conveying the message to others is known as communication.(संदेश को दूसरों तक पहुँचाने की प्रक्रिया को संचार कहते हैं।)
- Different modes of communication are used to provide information, to educate as well as to entertain.(जानकारी प्रदान करने, शिक्षित करने के साथ-साथ मनोरंजन करने के लिए संचार के विभिन्न तरीकों का उपयोग किया जाता है।)
- Communication is of two types namely, personal and mass communication.(संचार दो प्रकार का होता है, व्यक्तिगत और जन संचार)
- Through newspaper, radio and television, we can communicate with a large number of people. They are, therefore, called mass media.(समाचार पत्र, रेडियो और टेलीविजन के माध्यम से हम बड़ी संख्या में लोगों से संवाद कर सकते हैं। इसलिए उन्हें मास मीडिया कहा जाता है।)
- Satellites, Internet, Wireless telephone are the main modes of communication.(उपग्रह, इंटरनेट, वायरलेस टेलीफोन संचार के मुख्य साधन हैं)
- Places, where people build their homes, are called settlements. Early settlements grew near the river valleys because of the easy availability of water and fertile land there.(जिन स्थानों पर लोग अपने घर बनाते हैं, उन्हें बस्तियाँ कहते हैं। जल और उपजाऊ भूमि की आसान उपलब्धता के कारण प्रारंभिक बस्तियाँ नदी घाटियों के पास विकसित हुईं।)
By and by human settlements became larger with the development of trade, commerce and manufacturing.( धीरे-धीरे मानव बस्तियां व्यापार, वाणिज्य और विनिर्माण के विकास के साथ बड़ी होती गईं।)

Natural vegetation: Trees, grass, lichens, mosses, etc. that grow naturally without the interference of human beings are called natural vegetation.
प्राकृतिक वनस्पति: पेड़, घास, लाइकेन, काई आदि जो मनुष्य के हस्तक्षेप के बिना प्राकृतिक रूप से उगते हैं, प्राकृतिक वनस्पति कहलाते हैं।
Forests: They grow where temperature and rainfall are plentiful to support a tree cover. Forests may be dense and open.
वन: वे वहाँ उगते हैं जहाँ वृक्षों के आवरण को सहारा देने के लिए तापमान और वर्षा प्रचुर मात्रा में होती है। वन घने और खुले हो सकते हैं।
Grasslands: They grow in the region of moderate rain.
घास के मैदान: ये मध्यम वर्षा वाले क्षेत्र में उगते हैं।
Shrubs: These consists of thorny shrubs and scrubs.
झाड़ियाँ: इनमें कांटेदार झाड़ियाँ और झाड़ियाँ होती हैं।
Anaconda: It is one of the world’s largest snakes found in the tropical rainforest. Taiga. It means pure or untouched in the Russian language.
एनाकोंडा: यह उष्णकटिबंधीय वर्षावन में पाए जाने वाले दुनिया के सबसे बड़े सांपों में से एक है। टैगा। इसका मतलब रूसी भाषा में शुद्ध या अछूता है।
Human Environment – Settlement Transport and Communication Chapter 7
मानव पर्यावरण – आवास परिवहन और संचार अध्याय 7
Human beings are dependent on the environment.( मनुष्य पर्यावरण पर निर्भर है।)
To grow food, build homes and develop better means of transport and communication, human beings have modified the environment.( भोजन उगाने, घर बनाने और परिवहन और संचार के बेहतर साधन विकसित करने के लिए मनुष्य ने पर्यावरण को संशोधित किया है।)
Settlements (बस्तियों)
- Settlements are places where people build their homes.(बस्तियाँ वे स्थान हैं जहाँ लोग अपना घर बनाते हैं।)
- The settlements earlier grew near the river valleys as the water was easily available and the land was fertile.(पहले बस्तियाँ नदी घाटियों के पास विकसित होती थीं क्योंकि पानी आसानी से उपलब्ध था और भूमि उपजाऊ थी।)
- Settlements can be permanent or temporary.(बस्तियाँ स्थायी या अस्थायी हो सकती हैं।)
- Settlements which are occupied for a short time are called temporary settlements (ऐसी बस्तियाँ जो थोड़े समय के लिए अधिवासित होती हैं, अस्थायी बस्तियाँ कहलाती हैं)
- In permanent settlements, people build homes to live in.(स्थायी बस्तियों में लोग रहने के लिए घर बनाते हैं।)
- Settlements can be rural or urban. Rural settlements can be compact or scattered.
- बस्तियाँ ग्रामीण या शहरी हो सकती हैं। ग्रामीण बस्तियाँ सघन या बिखरी हुई हो सकती हैं।
- People in rural areas practice agriculture. In the urban area, people are mostly engaged in services.( ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में लोग कृषि करते हैं। शहरी क्षेत्र में, लोग ज्यादातर सेवाओं में लगे हुए हैं।)

Transport (यातायात)
- Transport is the means by which people and goods move.(परिवहन वह साधन है जिसके द्वारा लोग और सामान चलते हैं।)
- With the invention of the wheel, transport became easier.(पहिए के आविष्कार के साथ, परिवहन आसान हो गया।)
- Earlier donkeys, mules, bullocks and camels were used for transportation.( पहले गधों, खच्चरों, बैलों और ऊँटों का उपयोग परिवहन के लिए किया जाता था।)
- Earlier traders took the land route or sea route for transportation. Now it takes only 6-8 hours to travel from India to Europe.(पहले व्यापारी परिवहन के लिए स्थल मार्ग या समुद्री मार्ग का प्रयोग करते थे। अब भारत से यूरोप का सफर करने में सिर्फ 6-8 घंटे लगते हैं।)
- The four major means of transport are roadways, railways, waterways and airways(परिवहन के चार प्रमुख साधन सड़क मार्ग, रेलवे, जलमार्ग और वायुमार्ग हैं)

Roadways (सड़क मार्ग)
- The most commonly used means of transport, especially for short distances, are roads. They can be metalled or unmetalled.

Railways (रेलवे)
- Railways are the fastest means of land transport and can carry bulky materials over a long distance.(रेलवे जमीनी परिवहन का सबसे तेज साधन है और भारी सामान को लंबी दूरी तक ले जा सकता है।)
- The railways carry people over long distances quickly and economically.(रेलवे लोगों को जल्दी और आर्थिक रूप से लंबी दूरी तक ले जाती है।)
- The invention of the steam engine and the industrial revolution helped in the speedy development of rail transport.(भाप के इंजन के आविष्कार और औद्योगिक क्रांति ने रेल परिवहन के तीव्र विकास में मदद की।)
- Diesel and electric engine have largely replaced the steam engines.(डीज़ल और बिजली के इंजनों ने बड़े पैमाने पर भाप के इंजनों का स्थान ले लिया है।)
- Now superfast trains have been introduced to make travelling faster.( यात्रा को तेज करने के लिए अब सुपरफास्ट ट्रेनें शुरू की गई हैं।)
- Indian Railways network is the largest in Asia.(भारतीय रेल नेटवर्क एशिया में सबसे बड़ा है।)

Waterways (जलमार्ग)
- Waterways are the cheapest means of transportation for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.( लंबी दूरी तक भारी और भारी सामान ले जाने के लिए जलमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे सस्ता साधन है।)
- There are mainly two types of routes, inland waterways and sea routes.(मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकार के मार्ग हैं, अंतर्देशीय जलमार्ग और समुद्री मार्ग।)
- Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways.( नौगम्य नदियों और झीलों का उपयोग अंतर्देशीय जलमार्गों के रूप में किया जाता है।)
- Sea routes are connected through ports.(समुद्री मार्ग बंदरगाहों के माध्यम से जुड़े हुए हैं।)

Airways (हवाई मार्ग)
- Airways are the fastest and most expensive mode of transport.(वायुमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे तेज और सबसे महंगा साधन है।)
- It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways.(यह सबसे दूरस्थ और दूरस्थ क्षेत्रों तक पहुँचने के लिए परिवहन का एकमात्र साधन है, खासकर जहाँ सड़कें और रेलमार्ग नहीं हैं।)
- Some major airports in the world are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo etc.(दुनिया के कुछ प्रमुख हवाई अड्डे दिल्ली, मुंबई, न्यूयॉर्क, लंदन, पेरिस, फ्रैंकफर्ट और काहिरा आदि हैं।)

Communication (संचार)
- Process of conveying the message to others is known as communication.(संदेश को दूसरों तक पहुँचाने की प्रक्रिया को संचार कहते हैं।)
- Different modes of communication are used to provide information, to educate as well as to entertain.(जानकारी प्रदान करने, शिक्षित करने के साथ-साथ मनोरंजन करने के लिए संचार के विभिन्न तरीकों का उपयोग किया जाता है।)
- Communication is of two types namely, personal and mass communication(संचार दो प्रकार का होता है, व्यक्तिगत और जन संचार)
- Through newspaper, radio and television, we can communicate with a large number of people. They are, therefore, called mass media.(समाचार पत्र, रेडियो और टेलीविजन के माध्यम से हम बड़ी संख्या में लोगों से संवाद कर सकते हैं। इसलिए उन्हें मास मीडिया कहा जाता है।)
- Satellites, Internet, Wireless telephone are the main modes of communication(उपग्रह, इंटरनेट, वायरलेस टेलीफोन संचार के मुख्य साधन हैं)
- Places, where people build their homes, are called settlements. Early settlements grew near the river valleys because of the easy availability of water and fertile land there.(जिन स्थानों पर लोग अपने घर बनाते हैं, उन्हें बस्तियाँ कहते हैं। जल और उपजाऊ भूमि की आसान उपलब्धता के कारण प्रारंभिक बस्तियाँ नदी घाटियों के पास विकसित हुईं।)
By and by human settlements became larger with the development of trade, commerce and manufacturing.( धीरे-धीरे मानव बस्तियां व्यापार, वाणिज्य और विनिर्माण के विकास के साथ बड़ी होती गईं।)
Settlements are of two types—permanent and temporary.
People make their temporary settlements in deep forests, hot and cold deserts and mountains and practise hunting, gathering, shifting cultivation, etc. Under permanent settlements, people build homes to live in.
बस्तियाँ दो प्रकार की होती हैं- स्थायी और अस्थायी।
लोग गहरे जंगलों, गर्म और ठंडे रेगिस्तानों और पहाड़ों में अपनी अस्थायी बस्तियाँ बनाते हैं और शिकार, संग्रहण, झूम खेती आदि का अभ्यास करते हैं। स्थायी बस्तियों के तहत लोग रहने के लिए घर बनाते हैं।
Human settlements may be rural and urban. The villages are rural settlement where people do farming, fishing, forestry, etc.( मानव बस्तियां ग्रामीण और शहरी हो सकती हैं। गाँव ग्रामीण बस्तियाँ हैं जहाँ लोग खेती, मछली पकड़ना, वानिकी आदि करते हैं।)
Rural settlements can be compact or scattered. In a compact settlement, houses are built closely to each other. In a scattered settlement house are spaced over an extensive area.( ग्रामीण बस्तियाँ सघन या बिखरी हुई हो सकती हैं। सघन अधिवास में मकान एक-दूसरे के निकट निर्मित होते हैं। एक बिखरी हुई बस्ती में घर एक विस्तृत क्षेत्र में स्थित होते हैं।)
Houses under rural settlements are built of mud, clay, stones, straw, etc.( ग्रामीण बस्तियों के अंतर्गत घर मिट्टी, मिट्टी, पत्थर, पुआल आदि के बने होते हैं।)
Urban settlements are found in towns and cities. People here are engaged in manufacturing, trading and services.( शहरी बस्तियाँ कस्बों और शहरों में पाई जाती हैं। यहां के लोग निर्माण, व्यापार और सेवाओं में लगे हुए हैं।)
Transport is essential to go from one place to another. In the early days, people travelled long distances on foot. They used animals to carry their goods. Gradually, several means of transport developed, although animals like donkeys, mules, bullocks and camels continued to be used even today.( एक जगह से दूसरी जगह जाने के लिए ट्रांसपोर्ट जरूरी है। शुरुआती दिनों में लोग पैदल ही लंबी दूरी तय करते थे। वे अपना सामान ढोने के लिए जानवरों का इस्तेमाल करते थे। धीरे-धीरे परिवहन के कई साधन विकसित हो गए, हालाँकि गधे, खच्चर, बैल और ऊँट जैसे जानवरों का उपयोग आज भी होता रहा)
An aeroplane is the fastest mode of transport. It saves our precious time and energy.( एक हवाई जहाज परिवहन का सबसे तेज साधन है। यह हमारे कीमती समय और ऊर्जा की बचत करता है।)
The four means of transport are—roadways, railways, waterways and airways.( परिवहन के चार साधन हैं-सड़क, रेलमार्ग, जलमार्ग और वायुमार्ग।)
Roads can be metalled and unmetalled.( सड़कें पक्की और कच्ची हो सकती हैं।)
Manali-Leh highway in the Himalayan Mountain is one of the highest roadways in the world (हिमालय पर्वत में मनाली-लेह राजमार्ग दुनिया के सबसे ऊंचे सड़क मार्गों में से एक है)
Roads built underground are called subways/under paths. Flyovers are built over raised structures (भूमिगत बनी सड़कों को सबवे/अंडरपाथ कहा जाता है। फ्लाईओवर ऊंचे ढांचों पर बनाए जाते हैं)
The railways carry people and heavy goods over long distances. The railway network is well developed over the plain areas.( रेलवे लोगों और भारी सामानों को लंबी दूरी तक ले जाती है। रेलवे नेटवर्क मैदानी क्षेत्रों में अच्छी तरह से विकसित है।)
The Indian railway network is well developed and is the largest in Asia.( भारतीय रेलवे नेटवर्क अच्छी तरह से विकसित है और एशिया में सबसे बड़ा है।)
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are used for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances. There are two types of waterways inland waterways and sea routes (जलमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे सस्ता साधन है। इनका उपयोग भारी और भारी सामान को लंबी दूरी तक ले जाने के लिए किया जाता है। जलमार्ग अंतर्देशीय जलमार्ग और समुद्री मार्ग दो प्रकार के होते हैं)
Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways.( नौगम्य नदियों और झीलों का उपयोग अंतर्देशीय जलमार्ग के रूप में किया जाता है।)
Sea routes and oceanic routes are mostly used for transporting merchandise and goods from one country to another. These routes are connected with the ports.( समुद्री मार्गों और समुद्री मार्गों का उपयोग ज्यादातर माल और सामान को एक देश से दूसरे देश में ले जाने के लिए किया जाता है। ये मार्ग बंदरगाहों से जुड़े हुए हैं।)
Some important ports of the world are—Singapore and Mumbai in Asia, New York, Los Angeles in North America, Rio de Janeiro in South America, Durban and Cape Town in Africa, Sydney in Australia, London and Rotterdam in Europe.( दुनिया के कुछ महत्वपूर्ण बंदरगाह हैं- एशिया में सिंगापुर और मुंबई, उत्तरी अमेरिका में न्यूयॉर्क, लॉस एंजिल्स, दक्षिण अमेरिका में रियो डी जनेरियो, अफ्रीका में डरबन और केप टाउन, ऑस्ट्रेलिया में सिडनी, लंदन और यूरोप में रॉटरडैम।)
Airways are the fastest means of transport. It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways.( वायुमार्ग परिवहन का सबसे तेज साधन है। यह सबसे दूरस्थ और दूर के क्षेत्रों तक पहुँचने के लिए परिवहन का एकमात्र साधन है, खासकर जहाँ सड़कें और रेलमार्ग नहीं हैं।)
Helicopters are useful in most inaccessible areas and in the time of calamities for rescuing people and other associated works.( हेलीकॉप्टर अधिकांश दुर्गम क्षेत्रों में और आपदा के समय लोगों को बचाने और अन्य संबंधित कार्यों के लिए उपयोगी होते हैं।)
Some important airports are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo.( कुछ महत्वपूर्ण हवाई अड्डे दिल्ली, मुंबई, न्यूयॉर्क, लंदन, पेरिस, फ्रैंकफर्ट और काहिरा हैं।)
The process by which we convey messages to others is known as communication.( वह प्रक्रिया जिसके द्वारा हम दूसरों को संदेश देते हैं, संचार कहलाती है।)
Newspapers, radio and television are important means of communication. They are called mass media because we can communicate with a large number of people at the same time (समाचार पत्र, रेडियो और टेलीविजन संचार के महत्वपूर्ण साधन हैं। उन्हें मास मीडिया कहा जाता है क्योंकि हम एक ही समय में बड़ी संख्या में लोगों के साथ संवाद कर सकते हैं)
The satellites have made communication even faster.( उपग्रहों ने संचार को और भी तेज कर दिया है।)
Wireless telephonic communications through cellular phones have become very popular today (सेलुलर फोन के माध्यम से वायरलेस टेलीफोनिक संचार आज बहुत लोकप्रिय हो गया है)
The Internet provides us with worldwide information and interaction.( इंटरनेट हमें विश्वव्यापी जानकारी और सहभागिता प्रदान करता है।)

Settlement: It refers to a place where people build their homes. ,
अधिवासः यह उस स्थान को संदर्भित करता है जहां लोग अपने घरों का निर्माण करते हैं। ,
Site: It refers to a place where a building or a settlement develops.
स्थल: यह उस जगह को संदर्भित करता है जहां एक इमारत या बस्ती विकसित होती है।
Transhumance: It is a seasonal movement of people.
ट्रांसहुमेंस: यह लोगों का एक मौसमी आंदोलन है।
Compact settlement: It is a closely built area of dwellings.
सघन अधिवासः यह आवासों का निकट निर्मित क्षेत्र होता है।
Scattered settlement: When dwellings are spaced over an extensive area.
बिखरी हुई बस्तियाँ: जब आवास एक विस्तृत क्षेत्र में स्थित होते हैं।
Transport: It is the means by which people and goods move from one place to another
परिवहन: यह वह साधन है जिसके द्वारा लोग और सामान एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर जाते हैं
Metalled roads: These are pucca roads and are used in all the weather.
पक्की सड़कें: ये पक्की सड़कें होती हैं और इनका उपयोग सभी मौसमों में किया जाता है।
Unmetalled roads: These are Kutcha roads. They are out of work during the rainy season.
कच्ची सड़कें: ये कच्ची सड़कें होती हैं। बरसात के दिनों में इनका काम ठप हो जाता है।
Subways: Underground roads are called subways.
भूमिगत मार्ग: भूमिगत सड़कों को सबवे कहा जाता है।
Flyovers: These are built over raised structures.
फ्लाईओवर: ये उभरे हुए ढांचों पर बने होते हैं।
Communication: The process through which we convey messages to others.
संचार: वह प्रक्रिया जिसके द्वारा हम दूसरों तक संदेश पहुँचाते हैं।
Mass Media: Newspapers, radio and television are called mass media because they communicate with a large number of people at the same time.
संचार मीडिया: समाचार पत्र, रेडियो और टेलीविजन को मास मीडिया कहा जाता है क्योंकि वे एक ही समय में बड़ी संख्या में लोगों के साथ संवाद करते हैं।
Human Environment Interactions – The Tropical and the Subtropical Region Chapter 8
मानव पर्यावरण अंतःक्रियाएँ – उष्णकटिबंधीय और उपोष्णकटिबंधीय क्षेत्र अध्याय 8
Human beings interact with the environment and are dependent on it for a number of things.( मनुष्य पर्यावरण के साथ अंतःक्रिया करता है और कई चीजों के लिए उस पर निर्भर है।)
Life in the Amazon Basin (अमेज़ॅन बेसिन में जीवन)
- The Amazon River Basin lies near the equator.(अमेज़न नदी बेसिन भूमध्य रेखा के पास स्थित है।)
- Amazon River was discovered by a Spanish explorer, Vicente Yanez Pinzon.(अमेज़ॅन नदी की खोज एक स्पेनिश खोजकर्ता विसेंट यानेज़ पिनज़ोन ने की थी।)
- The Amazon basin lies in the tropical region close to the equator between 10°N and 10°S, and the river Amazon flows through this region.(अमेज़न बेसिन भूमध्य रेखा के करीब 10°N और 10°S के बीच उष्णकटिबंधीय क्षेत्र में स्थित है, और अमेज़न नदी इस क्षेत्र से होकर बहती है।)
- The Amazon River basin drains portions of Brazil, parts of Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Columbia and a small part of Venezuela.(अमेज़ॅन नदी बेसिन ब्राजील के कुछ हिस्सों, पेरू के कुछ हिस्सों, बोलीविया, इक्वाडोर, कोलंबिया और वेनेजुएला के एक छोटे हिस्से को बहाती है।)
Climate (जलवायु)
- The Amazon basin stretches directly on the equator and is characterized by hot and wet climate throughout the year.(अमेज़ॅन बेसिन सीधे भूमध्य रेखा पर फैला है और पूरे वर्ष गर्म और आर्द्र जलवायु की विशेषता है।)
- There are heavy rainfall and high humidity.(भारी वर्षा और उच्च आर्द्रता हैं।)
Rainforest (वर्षा वन)
- As it rains heavily, thick forests grow in this region.(जैसे ही भारी बारिश होती है, इस क्षेत्र में घने जंगल उग आते हैं।)
- The forests are in fact so thick that the dense roof created by leaves and branches do not allow the sunlight to reach the ground.(जंगल वास्तव में इतने घने होते हैं कि पत्तियों और शाखाओं से बनी घनी छत सूरज की रोशनी को जमीन तक नहीं पहुंचने देती।)
- The rainforest is rich in flora and fauna.(वर्षावन वनस्पतियों और जीवों से समृद्ध है।)
- The basin is home to thousands of species of insects.(बेसिन कीड़ों की हजारों प्रजातियों का घर है।)
People of the Rainforests (वर्षावन के लोग)
- People grow most of their food in small areas after clearing some trees in the forest(जंगल में कुछ पेड़ों को काटकर लोग अपना अधिकांश भोजन छोटे क्षेत्रों में उगाते हैं)
- Slash and burn agriculture is prevalent.(स्लेश एंड बर्न कृषि प्रचलित है।)
- The development activities are leading to the gradual destruction of the biologically diverse rainforest.( विकास गतिविधियां जैविक रूप से विविध वर्षावनों के क्रमिक विनाश की ओर ले जा रही हैं।)
The Amazon Basin lies in the equatorial region. The river Amazon flows through this region. Numerous tributaries join the Amazon River to form the Amazon Basin.( अमेज़न बेसिन विषुवतीय क्षेत्र में स्थित है। अमेज़न नदी इस क्षेत्र से होकर बहती है। अमेज़न बेसिन बनाने के लिए कई सहायक नदियाँ अमेज़न नदी में मिलती हैं।)
The river basin drains portions of Brazil, parts, of Peru Bolivia, Equador, Columbia and a small part of Venezuela.( नदी बेसिन ब्राजील के कुछ हिस्सों, पेरू बोलिविया, इक्वाडोर, कोलंबिया और वेनेजुएला के एक छोटे से हिस्से से निकलती है।)
The climate of the Amazon Basin is hot and wet throughout the year. It rains almost every day. During day time temperatures are high but at night the temperature goes down.( अमेज़न बेसिन की जलवायु साल भर गर्म और नम रहती है। लगभग हर दिन बारिश होती है। दिन के समय तापमान अधिक होता है लेकिन रात के समय तापमान नीचे चला जाता है।)
Thick forests are found in the Amazon Basin. As sunlight does not reach the ground, only shade tolerant vegetation grows here, for examples, orchids and bromeliads.( अमेज़न बेसिन में घने जंगल पाए जाते हैं। चूंकि सूरज की रोशनी जमीन तक नहीं पहुंचती है, केवल छाया सहिष्णु वनस्पति यहां उगती है, उदाहरण के लिए, ऑर्किड और ब्रोमेलियाड।)
The rainforest is rich in fauna. A variety of birds is found here. Apart from animals like monkeys, sloth, etc. various species of reptiles and snakes are also found in these forests.( वर्षावन जीवों में समृद्ध है। यहां तरह-तरह के पक्षी पाए जाते हैं। इन वनों में बंदर, स्लॉथ आदि जानवरों के अलावा सरीसृपों और सांपों की विभिन्न प्रजातियां भी पाई जाती हैं।)
The Basin is also the home to thousands of species to insects.( बेसिन कीड़ों की हजारों प्रजातियों का घर भी है।)
The people of the Amazon Basin are mainly engaged in agriculture. They grow tapioca, pineapple and sweet potato. Their staple food is manioc. They also grow cash crops like coffee, maize and cocoa (अमेज़ॅन बेसिन के लोग मुख्य रूप से कृषि में लगे हुए हैं। वे साबूदाना, अनानास और शकरकंद उगाते हैं। उनका मुख्य भोजन मैनिओक है। वे कॉफी, मक्का और कोको जैसी नकदी फसलें भी उगाते हैं)
The life of the people of the Amazon basin is slowly changing, in 1970 the Trans-Amazon highway made all parts of the rainforest accessible. Aircraft and helicopters are also used for reaching various places.( अमेज़ॅन बेसिन के लोगों का जीवन धीरे-धीरे बदल रहा है, 1970 में ट्रांस-अमेज़ॅन राजमार्ग ने वर्षावन के सभी हिस्सों को सुलभ बना दिया। विभिन्न स्थानों पर पहुंचने के लिए वायुयान और हेलीकॉप्टरों का भी इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।)
Due to these developmental activities, a large area of the rainforest has been disappearing annually in the Amazon Basin.( इन विकासात्मक गतिविधियों के कारण, अमेज़ॅन बेसिन में वर्षावन का एक बड़ा क्षेत्र सालाना गायब हो रहा है।)
Life in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin (गंगा–ब्रह्मपुत्र बेसिन में जीवन)
- The tributaries of rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra together from the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin in the Indian subcontinent.( भारतीय उपमहाद्वीप में गंगा-ब्रह्मपुत्र बेसिन से गंगा और ब्रह्मपुत्र नदियों की सहायक नदियाँ एक साथ।)
- The plains of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra, the mountains and the foothills of the Himalayas and the Sundarbans delta are the main features of this basin.(गंगा और ब्रह्मपुत्र के मैदान, हिमालय के पर्वत और तलहटी और सुंदरबन डेल्टा इस बेसिन की मुख्य विशेषताएं हैं।)
- The area of the basin enjoys a monsoon climate. The summers are hot and the winters cool (बेसिन का क्षेत्र मानसूनी जलवायु का आनंद उठाता है। ग्रीष्मकाल गर्म और सर्दियाँ ठंडी होती हैं)
- The basin area has a varied topography. The mountain areas of the basin have thin population. The plain area has thick population.(बेसिन क्षेत्र की स्थलाकृति विविध है। बेसिन के पहाड़ी क्षेत्रों में पतली आबादी है। मैदानी क्षेत्र में घनी आबादी है।)
- Agriculture is the chief occupation of the people. The main crop is paddy. Some other crops like the wheat, maize, grain, millets etc. and some cash crops like sugarcane and jute are also grown.(कृषि लोगों का मुख्य व्यवसाय है। मुख्य फसल धान है। कुछ अन्य फ़सलें जैसे गेहूँ, मक्का, अनाज, बाजरा आदि और कुछ नकदी फ़सलें जैसे गन्ना और जूट भी उगाई जाती हैं।)
- Tropical deciduous trees grow in the Ganga, Brahmaputra plain. Teak, sal and peepal are also found. The delta is covered with mangrove forests.(उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती पेड़ गंगा, ब्रह्मपुत्र के मैदान में उगते हैं। सागौन, साल और पीपल भी पाए जाते हैं। डेल्टा मैंग्रोव वनों से आच्छादित है।)
- The basin is rich in wildlife. A variety of fish is found here. Fish and rice is the staple food of the people living in the area.(बेसिन वन्य जीवन से समृद्ध है। यहां तरह-तरह की मछलियां पाई जाती हैं। मछली और चावल इस क्षेत्र में रहने वाले लोगों का मुख्य भोजन है।)
- Several big towns and cities such as Allahabad, Kanpur, Varanasi, Lucknow, Patna and Kolkata are there in the Ganga-Brahmaputra plain.( गंगा-ब्रह्मपुत्र के मैदान में इलाहाबाद, कानपुर, वाराणसी, लखनऊ, पटना और कोलकाता जैसे कई बड़े शहर और शहर हैं।)
- All four means of transport are available here.(यहाँ यातायात के चारों साधन उपलब्ध हैं।)
- Tourism is also an important activity of the basin. Tourists from different parts of the world come to see the Taj Mahal, Buddhists stupas, Imambara, wildlife sanctuaries etc (पर्यटन भी बेसिन की एक महत्वपूर्ण गतिविधि है। दुनिया के विभिन्न हिस्सों से पर्यटक ताजमहल, बौद्ध स्तूप, इमामबाड़ा, वन्यजीव अभयारण्य आदि देखने आते हैं)
Mouth: The place where a river flows into another body of water is known as the river’s mouth.
मार्ग: वह स्थान जहाँ एक नदी पानी के दूसरे शरीर में बहती है, नदी के मुहाने के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Tributaries: These are small rivers that join the main river.
सहायक नदियाँ: ये छोटी नदियाँ हैं जो मुख्य नदी में मिलती हैं।
Bromeliads: These are special plants that store water in their leaves.
ब्रोमेलियाड: ये विशेष पौधे हैं जो अपनी पत्तियों में पानी जमा करते हैं।
Slash and Burn Agriculture: It is a type of cultivation in which farmers clear a patch of land by cutting down trees and bushes. These are then burnt which releases the nutrients into the soil. Now the field becomes ready for growing crops.
स्लैश एंड बर्न कृषि: यह एक प्रकार की खेती है जिसमें किसान पेड़ों और झाड़ियों को काटकर जमीन के एक टुकड़े को साफ करते हैं। इसके बाद इन्हें जलाया जाता है जिससे पोषक तत्व मिट्टी में मिल जाते हैं। अब खेत फसल उगाने के लिए तैयार हो जाता है।
Manioc: This is the staple food of the people of the Amazon basin.
मैनिओक: यह अमेज़न बेसिन के लोगों का मुख्य भोजन है।
Maloca: Large apartment like houses with steeply slanting roofs are called malocas.
मलोका (Maloca) : बड़े अपार्टमेंट जैसे मकान जिनकी छतें खड़ी तिरछी होती हैं, मलोका कहलाते हैं।
Population Density: It refers to the number of persons that live in one sq. km. of area.
जनसंख्या घनत्व: यह एक वर्ग किमी में रहने वाले व्यक्तियों की संख्या को संदर्भित करता है। क्षेत्र के।
Terrace Farming: It is a type of farming in which terraces are built on steep slopes to create flat surfaces on which crops are grown. The slope is removed so that water does not run off rapidly.
टैरेस फार्मिंग: यह एक प्रकार की खेती है जिसमें खड़ी ढलानों पर चबूतरे बनाकर समतल सतह बनाई जाती है, जिस पर फसलें उगाई जाती हैं। ढलान को हटा दिया जाता है ताकि पानी तेजी से न बहे।
Piranha: It is a type of fish that eats flesh.
पिरान्हा: यह एक प्रकार की मछली है जो मांस खाती है।
Life in the Temperate Grasslands Chapter 9
समशीतोष्ण घास के मैदानों में जीवन अध्याय 9
Grassland is a region where grasses from the dominant type of plant life.( घास का मैदान एक ऐसा क्षेत्र है जहां पौधों के जीवन के प्रमुख प्रकार से घास होती है।)
Depending upon the climate conditions, grasslands can be divided into two categories, the Temperate Grasslands and the Tropical Grasslands.( जलवायु परिस्थितियों के आधार पर, घास के मैदानों को दो श्रेणियों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है, शीतोष्ण घास के मैदान और उष्णकटिबंधीय घास के मैदान।)
The Prairies (प्रेयरीज)
- Prairies are the Temperate Grassland found in North America. They are bound by the Rocky Mountains ‘the West and the Great Lakes in the East.(प्रेयरी उत्तरी अमेरिका में पाए जाने वाले शीतोष्ण घास के मैदान हैं। वे रॉकी पर्वत ‘पश्चिम और पूर्व में महान झीलों से बंधे हैं।)
- For the most part, Prairies are tree-less but, near the low-lying area’s woodlands can be found. The prairies are bound by the Rocky Mountains in the West and the Great Lakes in the East.( अधिकांश भाग के लिए, प्रेयरी वृक्ष विहीन होते हैं, लेकिन निचले इलाकों के पास वनस्थल पाए जा सकते हैं। प्रेयरी पश्चिम में रॉकी पर्वत और पूर्व में महान झीलों से बंधे हैं।)
- Prairies cover major parts of the USA and Canada.(प्रेयरी संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका और कनाडा के प्रमुख भागों को कवर करते हैं।)
Climate (मौसम)
- Climate is of continental type with extreme temperature ie with warm summers and very cold winters.( जलवायु महाद्वीपीय प्रकार की होती है जिसमें अत्यधिक तापमान होता है अर्थात गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल और बहुत ठंडी सर्दियाँ।)
- The annual rainfall is moderate and is ideal for the growth of grass.(वार्षिक वर्षा मध्यम है और घास के विकास के लिए आदर्श है।)
Flora and Fauna (वनस्पति और जीव)
- Prairies are practically tree-less but the places where water is available, trees such as willows, alders and poplars grow.(प्रेयरी व्यावहारिक रूप से पेड़ रहित होते हैं लेकिन जिन स्थानों पर पानी उपलब्ध होता है, वहां विलो, एल्डर और पोपलर जैसे पेड़ उगते हैं।)
- Places that receive rainfall of over 50 cm, are suitable for farming as the soil is fertile.( 50 सेमी से अधिक वर्षा वाले स्थान खेती के लिए उपयुक्त होते हैं क्योंकि मिट्टी उपजाऊ होती है।)
- The prairies are known as the ‘Granaries of the world’ because surplus wheat is produced here.(प्रेयरी को ‘दुनिया के अन्न भंडार’ के रूप में जाना जाता है क्योंकि यहां अधिशेष गेहूं का उत्पादन होता है।)
- Bison or American buffalo is the most important animal.(बाइसन या अमेरिकी भैंसा सबसे महत्वपूर्ण जानवर है।)
People (लोग)
- Large-scale cattle farms called ranches are looked after by the sturdy men called cowboys (रैंच कहे जाने वाले बड़े पैमाने के मवेशी फार्मों की देखभाल काउबॉय कहे जाने वाले हृष्ट-पुष्ट लोगों द्वारा की जाती है।)
- Large scale farming with modern technology is done here.(यहां आधुनिक तकनीक से बड़े पैमाने पर खेती की जाती है।)
The Velds (स्तपी)
- The Temperate Grasslands of South Africa are called the velds.(दक्षिण अफ्रीका के शीतोष्ण घास के मैदानों को वेल्ड कहा जाता है।)
- Velds are rolling plateaus with varying heights ranging from 600 m to 1100 m. (वेल्ड 600 मीटर से 1100 मीटर तक की अलग-अलग ऊंचाई वाले रोलिंग पठार हैं।
- It is bound by the Drakensberg Mountains on the east.(यह पूर्व में ड्रेकेन्सबर्ग पर्वत से घिरा है।)

Climate (मौसम)
- The welds have a mild climate due to the influence of the Indian Oceans.(भारतीय महासागरों के प्रभाव के कारण वेल्ड की जलवायु हल्की होती है।)
- Here the summers are short and warm.(यहाँ गर्मियाँ छोटी और गर्म होती हैं।)
- The velds receive rainfall mainly in the summer months from November to February(वेल्ड में मुख्य रूप से गर्मी के महीनों में नवंबर से फरवरी तक वर्षा होती है)
- Winters are cold and dry. Temperature varies between 5°C and 10°C and July is the coldest month.(सर्दियाँ ठंडी और शुष्क होती हैं। तापमान 5 डिग्री सेल्सियस और 10 डिग्री सेल्सियस के बीच बदलता रहता है और जुलाई सबसे ठंडा महीना होता है।)
Flora and Fauna (वनस्पति और जीव)
- Vegetation cover is sparse.(वनस्पति आवरण विरल है।)
- Red grass grows in bush velds.(बुश वेल्ड में लाल घास उगती है।)
People (लोग)
- Velds are known for cattle rearing and mining.(वेल्ड पशुपालन और खनन के लिए जाने जाते हैं।)
- The main crops are maize, wheat, barley, oats and potatoes.( मुख्य फ़सलें मक्का, गेहूँ, जौ, जई और आलू हैं।)
- The velds have a rich reserve of minerals.(वेल्ड में खनिजों का प्रचुर भण्डार है।)
- Iron and steel industry has developed where coal and iron are present.(लोहा और इस्पात उद्योग वहाँ विकसित हुआ है जहाँ कोयला और लोहा मौजूद है।)
- Johannesburg is known as the gold capital of the world.(जोहान्सबर्ग को दुनिया की सोने की राजधानी के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Grassland is a region where grasses form the dominant type of plant life. Grasslands make up almost a quarter of the total land surface.( घास का मैदान एक ऐसा क्षेत्र है जहां पौधों के जीवन के प्रमुख प्रकार से घास होती है। घास के मैदान कुल भूमि की सतह का लगभग एक चौथाई हिस्सा बनाते हैं।)
The world’s grasslands are divided into two categories: those that occur in the temperate region and those that occur in the tropical region.( दुनिया के घास के मैदानों को दो श्रेणियों में बांटा गया है: वे जो समशीतोष्ण क्षेत्र में पाए जाते हैं और वे जो उष्णकटिबंधीय क्षेत्र में पाए जाते हैं।)
The prairies are the temperate grasslands in North America. They are bound by the Rocky Mountains in the west and the Great Lakes in the East.( प्रेयरी उत्तरी अमेरिका में समशीतोष्ण घास के मैदान हैं। वे पश्चिम में रॉकी पर्वत और पूर्व में महान झीलों से बंधे हैं।)
The prairies are located in the heart of the continent and therefore we find here the continental type of climate which is characterised by extreme temperatures.( प्रेयरी महाद्वीप के केंद्र में स्थित हैं और इसलिए हम यहां महाद्वीपीय प्रकार की जलवायु पाते हैं जो अत्यधिक तापमान की विशेषता है।)
The annual rainfall is moderate and is ideal for the growth of grass. ‘Chinook’, a local wind, blow here.( वार्षिक वर्षा मध्यम है और घास के विकास के लिए आदर्श है। ‘चिनूक’, एक स्थानीय हवा, यहाँ बहती है।)
Trees are not there in the prairies. Only trees like willows, alders and poplars grow.( प्रेयरी में पेड़ नहीं होते हैं। विलो, एल्डर और पोपलर जैसे पेड़ ही उगते हैं।)
Crops like maize, potatoes, soybeans, cotton and alfa-alfa are grown in the areas where rainfall is over 50 cm.( मक्का, आलू, सोयाबीन, कपास और अल्फा-अल्फ़ा जैसी फसलें उन क्षेत्रों में उगाई जाती हैं जहाँ वर्षा 50 सेमी से अधिक होती है।)
In the areas with poor rainfall, grasses are short and sparse. In these areas, cattle¬rearing is done. Bison or the American buffalo is the most important animal of this region.( कम वर्षा वाले क्षेत्रों में घास छोटी और विरल होती है। इन क्षेत्रों में पशुपालन किया जाता है। बाइसन या अमेरिकी भैंसा इस क्षेत्र का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण जानवर है।)
The people of this region are hardworking. The USA and Canada are located in this region.( इस क्षेत्र के लोग मेहनती होते हैं। संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका और कनाडा इस क्षेत्र में स्थित हैं।)
The prairies are known as the ‘Granaries of the world’ because surplus wheat is produced here (प्रेयरी को ‘विश्व के अन्न भंडार’ के रूप में जाना जाता है क्योंकि यहाँ अधिशेष गेहूं का उत्पादन होता है।)
Dairy farming is also a major industry.( दूध उद्योग भी एक प्रमुख उद्योग है।)
Minerals such as coal and iron are found in abundance. Roads, railways and canals— all are in good condition and play an important role in making this region the most industrialised one in the world (कोयला और लोहा जैसे खनिज प्रचुर मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं। सड़कें, रेलवे और नहरें- सभी अच्छी स्थिति में हैं और इस क्षेत्र को दुनिया में सबसे अधिक औद्योगिक बनाने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं)
The velds are the temperate grasslands of South Africa. They are bound by the Drakensberg Mountains on the east. To its west lies the Kalahari Desert. On the northeastern part, high velds are located that attain a height of more than 1600 m in some places.( वेल्ड दक्षिण अफ्रीका के शीतोष्ण घास के मैदान हैं। वे पूर्व में ड्रैकेंसबर्ग पर्वत से बंधे हैं। इसके पश्चिम में कालाहारी मरुस्थल है। उत्तरपूर्वी भाग में, उच्च वेल्ड स्थित हैं जो कुछ स्थानों पर 1600 मीटर से अधिक की ऊँचाई प्राप्त करते हैं।)
The velds are characterised by a mild climate. They receive rainfall mainly in the summer months from November to February.( वेल्ड की विशेषता सुहावनी जलवायु है। वे मुख्य रूप से नवंबर से फरवरी तक गर्मियों के महीनों में वर्षा प्राप्त करते हैं।)
The velds do not have much vegetation. Grasses dominate the landscape. The popular varieties of grass are—red grass, acacia and maroola.( वेल्ड में अधिक वनस्पति नहीं होती है। घास परिदृश्य पर हावी है। घास की लोकप्रिय किस्में हैं- लाल घास, बबूल और मरूला।)
The animals found in this region are—lions, leopards, cheetah and kudu.( इस क्षेत्र में पाए जाने वाले जानवर हैं-शेर, तेंदुआ, चीता और कुडू।)
Cattle rearing and mining are two important activities in the velds. Soils are not very fertile.( वेल्ड में मवेशी पालन और खनन दो महत्वपूर्ण गतिविधियां हैं। मिट्टी बहुत उपजाऊ नहीं होती है।)
The main crops are maize, wheat, barley, oats and potato. Cash crops grown here are tobacco, sugarcane and cotton.( मुख्य फ़सलें मक्का, गेहूँ, जौ, जई और आलू हैं। यहाँ उगाई जाने वाली नकदी फ़सलें तंबाकू, गन्ना और कपास हैं।)
The people of this region are mostly engaged in sheep rearing.( इस क्षेत्र के लोग ज्यादातर भेड़ पालन में लगे हैं।)
Merino sheep are very popular because its wool is very warm.( मेरिनो भेड़ बहुत लोकप्रिय हैं क्योंकि इसकी ऊन बहुत गर्म होती है।)
Dairy farming is also an important activity Dairy product like butter, cheese is produced for both domestic supply and also for export.( दूध उद्योग भी एक महत्वपूर्ण गतिविधि डेयरी उत्पाद जैसे मक्खन, पनीर का उत्पादन घरेलू आपूर्ति और निर्यात दोनों के लिए किया जाता है।)
The velds have a rich reserve of minerals. Gold and diamond mining are major occupations of people of this region.( वेल्ड में खनिजों का प्रचुर भण्डार है। सोना और हीरा खनन इस क्षेत्र के लोगों का प्रमुख व्यवसाय है।)
Johannesburg is famous for gold. It is known as the gold capital in the world.( जोहान्सबर्ग सोने के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। इसे दुनिया में सोने की राजधानी के रूप में जाना जाता है।)
Kimberley is famous for its diamond mines.( किम्बर्ले अपनी हीरे की खानों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।)
Grassland: A region where grasses form the dominant type of plant life.
घास का मैदान: एक ऐसा क्षेत्र जहां पौधों के जीवन के प्रमुख प्रकार से घास होती है।
Prairie: The word prairie has been originated from Latin word priata which means meadow.
प्रेयरी: प्रेयरी शब्द की उत्पत्ति लैटिन शब्द प्रियाता से हुई है जिसका अर्थ घास का मैदान होता है।
Red Indians: native Americans.
रेड इंडियन्स: अमेरिकी मूल-निवासी।
Chinook: It is a hot wind that blows in winter and therefore raises the temperature within a short time.
चिनूक: यह एक गर्म हवा है जो सर्दियों में चलती है और इसलिए थोड़े समय में तापमान बढ़ा देती है।
Ranches: They are large cattle farms.
फार्मों: वे बड़े पशु फार्म हैं।
Bison: The American buffalo.
बाइसन: द अमेरिकन भैंस।
Cowboys: The sturdy men who look after the ranches.
काउबॉय: मजबूत आदमी जो खेत की देखभाल करते हैं।
Combine: A single machine which can combine the tasks of sowing, ploughing and threshing, i.e., a three-in-one.
कम्बाइन: एक मशीन जो बुवाई, जुताई और थ्रेशिंग के कार्यों को जोड़ सकती है, यानी थ्री-इन-वन।
Veld: Velds are the temperate grasslands of South Africa.
वेल्ड: वेल्ड दक्षिण अफ्रीका के शीतोष्ण घास के मैदान हैं।
Life in the Deserts Chapter 10
रेगिस्तान में जीवन अध्याय 10
Deserts are characterised by low rainfall, scanty vegetation and extreme temperatures (मरुस्थल की विशेषता कम वर्षा, अल्प वनस्पति और अत्यधिक तापमान है)
Depending on the temperature, there can be hot deserts or cold deserts (तापमान के आधार पर गर्म रेगिस्तान या ठंडे रेगिस्तान हो सकते हैं)
The Hot Desert – Sahara
गर्म मरुस्थल – सहारा
- The Sahara Desert in Africa is the world’s largest hot desert.(अफ्रीका में सहारा रेगिस्तान दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा गर्म रेगिस्तान है।)
- It touches 11 countries and has got gravel plains and elevated plateaus with a bare rocky surface.( यह 11 देशों को छूता है और बजरी के मैदान और नंगे चट्टानी सतह वाले ऊंचे पठार हैं।)
- The climate of Sahara is scorching hot and parched dry with temperature as high as 50° (सहारा की जलवायु चिलचिलाती गर्म और 50 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक के तापमान के साथ सूखी सूखी है)
- The nights are freezing cold with the temperature nearing zero degrees.(तापमान शून्य डिग्री के करीब होने के साथ रातें ठंडी हो रही हैं।)
- Vegetation in the Sahara Desert includes cactus, date palms and acacia. Camels, hyenas, jackals, foxes, scorpions, snakes and lizards are the main animal species found here (सहारा रेगिस्तान में वनस्पति में कैक्टस, खजूर और बबूल शामिल हैं। ऊंट, लकड़बग्घा, सियार, लोमड़ी, बिच्छू, सांप और छिपकली यहां पाई जाने वाली प्रमुख पशु प्रजातियां हैं)
- Despite its harsh climate, Sahara is inhabited by various groups of people. The main groups are Bedouins and Tuaregs.(अपनी कठोर जलवायु के बावजूद, सहारा में विभिन्न समूहों के लोग रहते हैं। मुख्य समूह बेडौइन और तुआरेग हैं।)
- The oasis in the Sahara and the Nile Valley in Egypt supports the settled population.(मिस्र में सहारा और नील घाटी में नखलिस्तान बसे हुए लोगों का समर्थन करते हैं।)
- The discovery of oil is constantly transforming this region. Other important minerals found here are iron, phosphorus, manganese and uranium.(तेल की खोज लगातार इस क्षेत्र को बदल रही है। यहाँ पाए जाने वाले अन्य महत्वपूर्ण खनिज लोहा, फास्फोरस, मैंगनीज और यूरेनियम हैं।)
- More and more nomadic tribes are taking to city life.(अधिक से अधिक खानाबदोश जनजातियां शहरी जीवन अपना रही हैं।)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)
The Cold Desert – Ladakh (शीत मरुस्थल – लद्दाख)
- Ladakh is a cold desert lying in the Great Himalayas, on the eastern side of Jammu and Kashmir (लद्दाख जम्मू और कश्मीर के पूर्वी हिस्से में, महान हिमालय में स्थित एक ठंडा रेगिस्तान है।)
- The altitude in Ladakh varies from 3,000 m in Kargil to more than 8,000 m in the Karakoram.(लद्दाख में ऊंचाई कारगिल में 3,000 मीटर से काराकोरम में 8,000 मीटर से अधिक है)
- The area experiences freezing winds and burning hot sunlight.(इस क्षेत्र में ठंडी हवाएं चलती हैं और धूप जलती है।)
- Due to high aridity, the vegetation is sparse. Groves of willows and poplars are seen in the valleys.( उच्च शुष्कता के कारण वनस्पति विरल है। घाटियों में विलो और चिनार के वृक्ष दिखाई देते हैं।)
- The animals of Ladakh are wild goats, wild sheep, yak and special kinds of dogs.(लद्दाख के जानवर जंगली बकरियां, जंगली भेड़, याक और विशेष प्रकार के कुत्ते हैं।)
- The animals are reared as they provide milk, meat and hides.(जानवरों को पाला जाता है क्योंकि वे दूध, मांस और खाल प्रदान करते हैं।)
- The population consists of either Muslims or Buddhists.(जनसंख्या में या तो मुसलमान या बौद्ध शामिल हैं।)
- Some famous Buddhist monasteries are Hemis, Thiksey, Shey and Lamayuru.(हेमिस, थिकसे, शे और लामायुरू कुछ प्रसिद्ध बौद्ध मठ हैं।)
- In the summer season, the people are busy cultivating barley, potatoes, peas, beans and turnips.( गर्मी के मौसम में लोग जौ, आलू, मटर, सेम और शलजम की खेती में व्यस्त हैं।)
- Tourism is a major activity with several tourists streaming in from within India and abroad (पर्यटन एक प्रमुख गतिविधि है जिसमें भारत और विदेशों से कई पर्यटक आते हैं)
- People of Ladakh have over the centuries learnt to live in balance and harmony with nature (लद्दाख के लोगों ने सदियों से प्रकृति के साथ संतुलन और सामंजस्य में रहना सीखा है)
- Pashmina wool of this region is famous.( इस क्षेत्र की पश्मीना ऊन प्रसिद्ध है।)
- Leh and Kargil are the main towns in Ladakh.(लेह और कारगिल लद्दाख में प्रमुख शहर हैं।)

The desert areas of the world are characterised by low rainfall, scanty vegetation and extreme temperatures. Depending on the temperatures there are hot deserts as well as cold deserts (दुनिया के रेगिस्तानी क्षेत्रों में कम वर्षा, अल्प वनस्पति और अत्यधिक तापमान की विशेषता है। तापमान के आधार पर गर्म मरुस्थल के साथ-साथ ठंडे मरुस्थल भी होते हैं)
Sahara is a hot desert covering a large part of North Africa and Ladakh is a cold desert lying in the Great Himalayas on the eastern side of Jammu and Kashmir in India.(सहारा एक गर्म रेगिस्तान है जो उत्तरी अफ्रीका के एक बड़े हिस्से को कवर करता है और लद्दाख भारत में जम्मू और कश्मीर के पूर्वी हिस्से में महान हिमालय में स्थित एक ठंडा रेगिस्तान है।)
Sahara is the world’s largest desert.( सहारा विश्व का सबसे बड़ा मरुस्थल है।)
The Sahara desert touches eleven countries—Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia and Western Sahara.(सहारा रेगिस्तान ग्यारह देशों को छूता है – अल्जीरिया, चाड, मिस्र, लीबिया, माली, मॉरिटानिया, मोरक्को, नाइजर, सूडान, ट्यूनीशिया और पश्चिमी सहारा।)
The Sahara desert is the vast stretches of sand. There are also gravel plains and elevated plantains with a bare rocky surface.(सहारा मरुस्थल रेत का विशाल विस्तार है। बजरी के मैदान और नंगे चट्टानी सतह वाले ऊंचे पौधे भी हैं।)
The climate of the Sahara desert is scorching hot and parched dry. The rainy season is very short. The day temperature may soar as high as 50°C. But nights may be freezing cold.( सहारा मरुस्थल की जलवायु चिलचिलाती गर्म और सूखी सूखी है। वर्षा ऋतु बहुत कम होती है। दिन का तापमान 50 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक जा सकता है। लेकिन रातें कड़ाके की ठंड हो सकती हैं।)
Vegetation in the Sahara desert is comprised of cactus, date, palms and acacia. Date palms are found near an oasis. So far animals are concerned camels, hyenas, jackals, foxes, scorpions, several varieties of snakes and lizards are found in this dessert.( सहारा रेगिस्तान में वनस्पति में कैक्टस, खजूर, ताड़ और बबूल शामिल हैं। खजूर के पेड़ एक नखलिस्तान के पास पाए जाते हैं। जंतुओं की बात करें तो ऊंट, लकड़बग्घे, सियार, लोमड़ी, बिच्छू, कई प्रकार के सांप और छिपकली इस मिठाई में पाए जाते हैं।)
Various groups of people such as the Bedouins and Tuaregs live in the Sahara desert. These groups are a nomadic tribe and they rear goats, sheep, camels and horses. They get milk and hides from these animals. These nomadic tribes wear heavy robes to protect themselves from dust storms and hot winds.( लोगों के विभिन्न समूह जैसे बेडौइन और तुआरेग सहारा रेगिस्तान में रहते हैं। ये समूह खानाबदोश जनजाति हैं और वे बकरियां, भेड़, ऊंट और घोड़े पालते हैं। वे इन जानवरों से दूध और खाल प्राप्त करते हैं। ये खानाबदोश जनजातियां धूल भरी आंधी और गर्म हवाओं से खुद को बचाने के लिए भारी वस्त्र पहनती हैं।)
People get water from the oasis in the Sahara desert and the Nile valley in Egypt. They grow crops like rice, wheat, barley and beans.( लोगों को सहारा रेगिस्तान और मिस्र में नील घाटी में नखलिस्तान से पानी मिलता है। वे चावल, गेहूं, जौ और बीन्स जैसी फसलें उगाते हैं।)
The Sahara desert is undergoing fast change due to the discovery of oil in Algeria, Libya and Egypt. Other minerals found here are iron, phosphorus, manganese and uranium.( अल्जीरिया, लीबिया और मिस्र में तेल की खोज के कारण सहारा रेगिस्तान तेजी से बदलाव के दौर से गुजर रहा है। यहाँ पाए जाने वाले अन्य खनिज लोहा, फास्फोरस, मैंगनीज और यूरेनियम हैं।)
Trucks are now used in the salt trade.( ट्रकों का उपयोग अब नमक के व्यापार में किया जाता है।)
The nomadic herdsmen with a change of time are now migrating to cities for better job opportunities in oil and gas operations.( खानाबदोश चरवाहे समय के बदलाव के साथ अब तेल और गैस के संचालन में बेहतर रोजगार के अवसरों के लिए शहरों की ओर पलायन कर रहे हैं।)
Ladakh is a cold desert. The Karakoram Range in the north and the Zanskar mountains in the south enclose it. Several rivers flow through Ladakh. Several glaciers are found here, for example, the Gangotri glacier.( लद्दाख एक ठंडा रेगिस्तान है। उत्तर में काराकोरम रेंज और दक्षिण में ज़ांस्कर पर्वत इसे घेरते हैं। कई नदियाँ लद्दाख से होकर बहती हैं। यहाँ अनेक हिमनद पाए जाते हैं, जैसे गंगोत्री हिमनद।)
The climate of Ladakh is extremely cold and dry. The day temperatures in summer are just above zero degree and the night temperatures are below – 30°C. This desert receives very little rainfall. There is always a chance of both sunstroke and frostbite.( लद्दाख की जलवायु बेहद ठंडी और शुष्क है। गर्मियों में दिन का तापमान शून्य डिग्री से ठीक ऊपर होता है और रात का तापमान -30 डिग्री सेल्सियस से नीचे होता है। इस मरुस्थल में बहुत कम वर्षा होती है। सनस्ट्रोक और शीतदंश दोनों का खतरा हमेशा बना रहता है।)
Ladakh has poor vegetation. There are scanty patches of grasses. Groves of willows and poplars are seen in the valleys.( लद्दाख में खराब वनस्पति है। घास के छोटे-छोटे टुकड़े हैं। घाटियों में विलो और चिनार के वृक्ष दिखाई देते हैं।)
Several species of birds such as robins, redstarts, Tibetan snow cock, raven and hoopoe are found here. The animals of Ladakh are wild goats, wild sheep, yak and special kinds of dogs.( रॉबिन्स, रेडस्टार्ट्स, तिब्बती स्नो कॉक, रेवेन और हूपो जैसे पक्षियों की कई प्रजातियाँ यहाँ पाई जाती हैं। लद्दाख के जानवरों में जंगली बकरियां, जंगली भेड़, याक और विशेष प्रकार के कुत्ते हैं।)
People living in this desert are either Muslims or Buddhists.( इस रेगिस्तान में रहने वाले लोग या तो मुसलमान हैं या बौद्ध।)
Famous Buddhist monasteries are Hemis, Thiksey, Shey and Lamayuru.( हेमिस, थिकसे, शे और लामायुरु प्रसिद्ध बौद्ध मठ हैं।)
People grow crops like barley, potatoes, peas beans and turnips during the summer season. During the winter months they are engaged in festivities and ceremonies.( गर्मी के मौसम में लोग जौ, आलू, मटर, बीन्स और शलजम जैसी फसलें उगाते हैं। सर्दियों के महीनों के दौरान वे उत्सव और समारोहों में व्यस्त रहते हैं।)
The women of Ladakh are hardworking. They can manage indoor and outdoor activities skilfully (लद्दाख की महिलाएं मेहनती होती हैं। वे घर के अंदर और बाहर की गतिविधियों को कुशलता से प्रबंधित कर सकते हैं)
Leh is the capital of Ladakh.( लेह लद्दाख की राजधानी है।)
Ladakh is a famous tourist place. The tourists from within India and abroad like to visit the gompas (लद्दाख एक प्रसिद्ध पर्यटन स्थल है। देश-विदेश के पर्यटक गोम्पा को देखना पसंद करते हैं)
Ladakh is being modernised fast. But people are very conscious here. They know the ways to live in balance and harmony with nature.( लद्दाख का तेजी से आधुनिकीकरण किया जा रहा है। लेकिन यहां के लोग काफी जागरूक हैं। वे प्रकृति के साथ संतुलन और सद्भाव में रहने के तरीके जानते हैं।)
Desert: It refers to an arid area characterised by extremely high or low temperatures with poor vegetation.
मरुस्थल: यह एक ऐसे शुष्क क्षेत्र को संदर्भित करता है जिसमें खराब वनस्पति के साथ अत्यधिक उच्च या निम्न तापमान होता है।
Oasis: It is an area in the desert where there is water and where plants grow.
नखलिस्तान: यह मरुस्थल का वह क्षेत्र है जहाँ पानी होता है और जहाँ पौधे उगते हैं।
Shahtoosh: It is kind of wool obtained from Chiru or the Tibetan antelope.
शाहतोश: यह चीरू या तिब्बती मृग से प्राप्त ऊन का प्रकार है।
Gangri: It is a glacier found in Ladakh.
गंगरी: यह लद्दाख में पाया जाने वाला एक ग्लेशियर है।
Tuaregs: These are nomads of the Sahara desert.
तुआरेग: ये सहारा रेगिस्तान के खानाबदोश हैं।
Bedouins: These are nomads of the Sahara desert.
बेडौइन: ये सहारा रेगिस्तान के खानाबदोश हैं।
Khapa-chan: Ladakh is also known by this name. It means snow land.
खापा–चान: लद्दाख को इसी नाम से भी जाना जाता है। इसका अर्थ है हिम भूमि।





