The ground-level ozone pollution affecting parts of the Delhi-National Capital Region (NCR) was lower this year than in the last five years, but the duration of its exceedance was higher, a new analysis has found.
What is ozone?
- O3 is a colourless, odourless gas at ambient concentrations and is a major component of smog.
Stratospheric Ozone
- Stratospheric ozone, also known as the “ozone layer” forms high in the atmosphere when intense sunlight causes oxygen molecules (O2) to break up and re-form as ozone molecules (O3).
- These ozone molecules form the ozone layer and are commonly referred to as “good ozone.”
Ground-Level Ozone
- Ground-level ozone forms just above the earth’s surface (up to about 2 miles above ground) and impacts human, animal, and plant respiration.
- Ground level ozone is a highly reactive secondary pollutant.
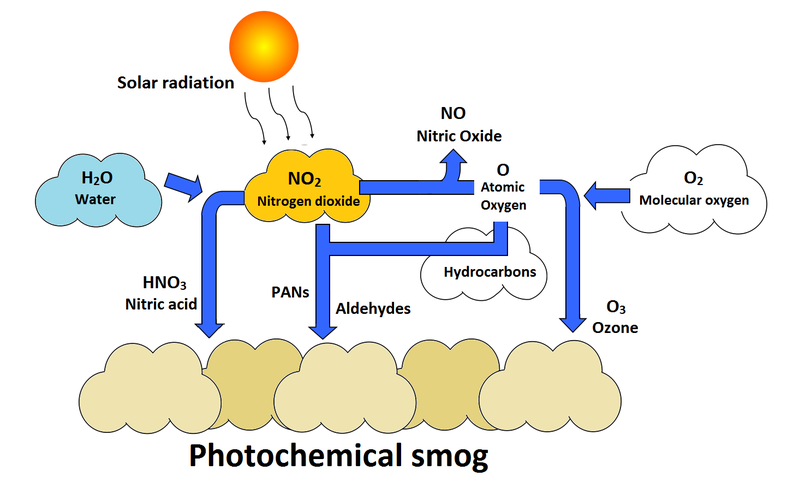
- This pollutant forms when primary pollutants, like hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, react with sunlight.
- Ozone irritates people’s lungs and is a major component of photochemical smog.
- Formation
- Ground level ozone is created by a chemical reaction between volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides.
- The sun and high temperatures act as catalysts to this reaction.
- Although ground-level ozone is less concentrated than stratospheric ozone, its impacts on human health and welfare make ground-level ozone “bad ozone.”
- Ground-level ozone is an irritant and can negatively affect human health and welfare.
- Ground-level ozone concentrations typically are highest on days warm/hot days with low humidity when wind is light or stagnant.
Health effects of ground-level ozone
- Make it more difficult to breathe deeply and vigorously
- Cause shortness of breath and pain when taking a deep breath
- Cause coughing and sore or scratchy throat
- Inflame and damage the airways
- Aggravate lung diseases such as asthma, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis
- Increase the frequency of asthma attacks
- Make the lungs more susceptible to infection
- Continue to damage the lungs even when the symptoms have disappeared
- Cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)

Effect on the environment
- Just as ground-level ozone can make it harder for people to breathe, it also makes it harder for plants to breathe.
- Reducing ground-level ozone can have the following impacts on vegetation:
- Protect forest communities
- Improve yields for timber and some crops, such as soybeans and winter wheat

What types of weather conditions contribute to high ozone?
- On any given day, there are enough emissions of NOx and VOC to produce high ozone.
- The key difference between a high ozone day and a low ozone day is the weather.
- Weather conditions associated with high ozone include:
- Lots of sunlight
- Slow wind speeds
- High peak temperatures
- Large differences between high and low temperatures for the day
- Low humidity




