Current Affairs – 7 May 2024
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is an indispensable tool for those trying to look inside the human body without surgery.

- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is utilized to obtain images of soft tissues within the body.
- Soft tissue encompasses any tissue that hasn’t undergone calcification.
- It is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure widely used for imaging various body parts such as the brain, cardiovascular system, spinal cord, joints, muscles, liver, arteries, etc.
- MRI plays a crucial role in the observation and treatment of certain cancers like prostate and rectal cancer, and in tracking neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s, dementia, epilepsy, and stroke.
- Due to the use of strong magnetic fields, individuals with embedded metallic objects or implants, including pacemakers, may be unable to undergo MRI scans.
- Working principle:
- MRI reveals an image of a body part by utilizing the hydrogen atoms in that part.
- It harnesses the body’s natural magnetic properties to produce detailed images.
- Hydrogen nuclei (protons) are primarily used for imaging due to their abundance in water and fat.
- The machine includes a superconducting magnet that creates a stable magnetic field, aligning hydrogen atom spins.
- A radiofrequency pulse is emitted, exciting excess atoms.
- When the pulse ceases, these atoms emit energy, which is detected and converted into signals by a receiver.
- These signals are then processed by a computer to generate detailed 2D or 3D images of the scanned body part
Fusobacterium nucleatum
In a new study, a group of researchers has identified a distinct subtype of the Fusobacterium nucleatum that’s found in relatively greater quantities in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumours.
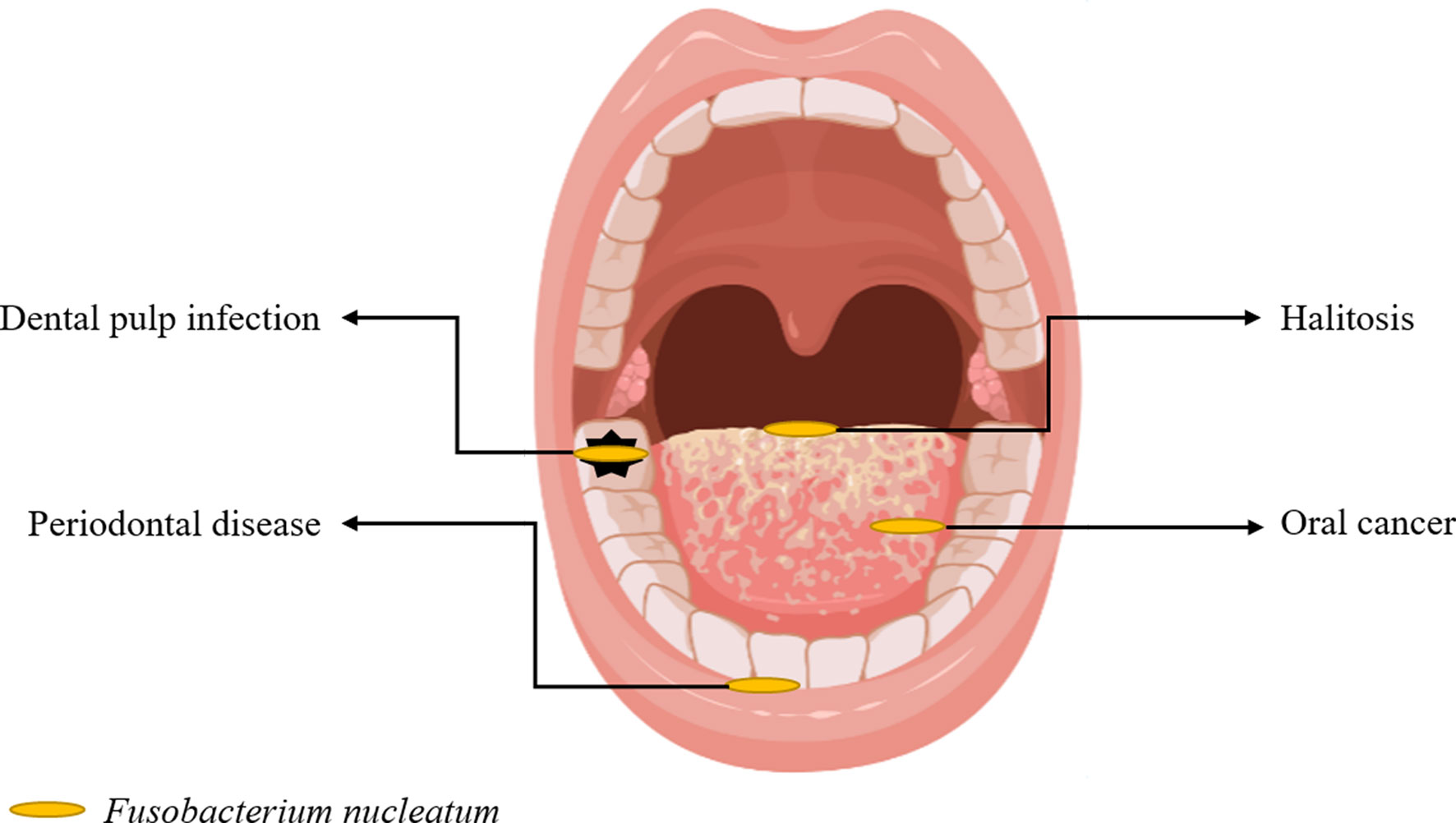
About Fusobacterium nucleatum:
- Fusobacteria are Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli with species-specific reservoirs in the human mouth, gastrointestinal tract and elsewhere.
- It has long been considered as an opportunistic pathogen given its frequent isolation and identification in anaerobic samples from patients with different infections.
- Highlights of the research:
- The researchers first analyzed the genomes of F. nucleatumtypes taken from human colorectal tumors and from the mouths of people without cancer. Out of its several known subspecies, only one, called nucleatum animalis (or Fna), was routinely found in the tumor samples.
- Additional genetic analyses revealed that Fna could be divided even further, into two separate groups.
- While both groups were found in about equal proportions in the mouth, only one, dubbed Fna C2, was found in colorectal tumor samples in substantial numbers.
- Fna C2’s higher resistance to acid, which could allow it to potentially reach the intestines directly from the mouth, through the stomach.
- Fna C2 also had the ability to hide inside certain tumor cells, which could protect it from the immune system. And it was able to use nutrients found in the gastrointestinal tract, which are very different from those found in the mouth.
Choline
Researchers recently discovered that an essential nutrient called choline is transported into the brain by a protein called FLVCR2.

About Choline:
- It is an essential nutrient that supports various bodily functions, including cellular growth and metabolism. It exists as both water-soluble and fat-soluble molecules. The body transports and absorbs choline differently depending on its form.
- The body can also produce small amounts of choline on its own in the liver, but not enough to meet daily needs. As a result, humans must obtain some choline from the diet.
- The richest dietary sources of choline are meat, fish, dairy, and eggs. Many fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain choline as well.
- Functions:
- Cell structure: It is a constituent of an important class of lipids (fats) called phospholipids (e.g., lecithin), which form structural elements of cell membranes. Therefore, all plant and animal cells need choline to preserve their structural integrity.
- It serves as a source of the methyl groups (―CH3 groups), which are required in various metabolic processes.
- Liver Health: Choline is also required to clear cholesterol from your liver. Deficiencies cause fat and cholesterol accumulation in your liver, which puts you at risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- A healthy nervous system: This nutrient is required to make acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter. It’s involved in memory, muscle movement, regulating the heartbeat, and other basic functions.
- Choline also plays important roles in modulating gene expression, cell membrane signaling, lipid transport and metabolism, and early brain development.
- It is also “food” for beneficial gut bacteria.
- Choline deficiency can lead to health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and muscular damage.
Diffusion transformer (DiT)
The new AI model ‘Sora’ is powered by Diffusion transformer (DiT)

- Sora – An AI model developed by OpenAI that process the prompts in natural language and generate minute-long videos in high definition using diffusion transformer model.
| AI models |
|
- DiT – Diffusion transformer, is essentially a class of diffusion models that are based on the transformer architecture.
- Developed by – William Peebles at UC Berkeley.
- Aim – To improve the performance of diffusion models by switching the commonly used U-Net backbone with a transformer.
U-Net is an architecture employed in diffusion models for iterative image denoising but it may not provide the best solution all the time.
- Principle
- Use concept of diffusion – For predicting videos
- Use the strength of transformers – For next-level scaling
- Working – It make videos by breaking them down into smaller parts, adding a bit of randomness (noises), and then cleaning things up based on the text.
- Latent diffusion process – Noise is gradually transformed into the target image by reversing the diffusion process guided by a transformer network.
- Diffusion timesteps – It act like checkpoints and at each checkpoint, DiT looks at the picture and decides to make it better.
Runway’s Gen-2 and Google’s Lumiere had previously showcased some breathtaking capabilities of video generation that could potentially replace filmmaking in the future.
Marrakesh Agreement
2024 marks the 30thanniversary of signing of Marrakesh Agreement.
- An agreement that fundamentally reshaped the international trading system by introducing a more robust and comprehensive structure for trade relations.
- Signed in – 1994, by 123 countries.
- Shared vision – To transform the world through trade.
- Outcome – Establishment of World Trade Organization (WTO) in 1995.
- Headquarters – Geneva Switzerland
- India is a member
- Achievements – While the GATT mainly dealt with trade in goods, the WTO and its agreements also cover trade in services and intellectual property.
- It has helped to bring about a major expansion in global trade, with the objective of raising living standards, increasing employment and promoting sustainable development.
- More than 1.5 billion people have been lifted out of extreme poverty.
- The WTO’s membership has expanded to 164 members, representing over 98% of international trade.
- In 2015, the WTO reached a significant milestone with the receipt of its 500th trade dispute for settlement.
- Expansion of the Information Technology Agreement.
- TRIPS Agreement amended to ease access to affordable medicine
- Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) enters into force.
- Challenges – Bias of favouring wealthier nations due to their greater negotiating power.
- Promoting policies that sometimes conflict with the economic interests and developmental needs of poorer countries.
- Issues such as agricultural subsidies remain highly contentious.
Ukraine Unveils AI-Powered Digital Spokesperson for Foreign Ministry





