Current Affairs – 5 March 2024
ADITI Scheme
Recently, the Union Minister of Defence launched the ADITI scheme during DefConnect 2024.

About ADITI Scheme:
- Acing Development of Innovative Technologies with iDEX (ADITI) is a scheme to promote innovations in critical and strategic defence technologies.
- Aim: It aims to develop about 30 deep-tech critical and strategic technologies in the proposed timeframe.
- Eligibility: Under this scheme start-ups are eligible to receive grant-in-aid of up to Rs 25 crore for their research, development and innovation endeavours in defence technology.
- Time period: This scheme worth Rs 750 crore for the period 2023-24 to 2025-26.
- It falls under the iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) framework of Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
- It also envisages to create a ‘Technology Watch Tool’ to bridge the gap between the expectations and requirements of the modern Armed Forces and the capabilities of the defence innovation ecosystem.
- In the first edition of ADITI, 17 challenges – Indian Army (3), Indian Navy (5), Indian Air Force (5) and Defence Space Agency (4) – have been launched.
- To motivate young innovators, iDEX was expanded to iDEX Prime, with the assistance increasing from Rs 1.5 crore to Rs 10 crore.
Women, Business and Law Index
India’s ranked improved to 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Women, Business and Law index.

About Women, Business and Law Index:
- It is a World Bank index to measure how laws and regulations affect women’s economic opportunity on a scale from 0 to 100, where 100 means equal legal rights for men and women.
- The report covers eight related areas: Mobility, workplace, pay, marriage, parenthood, entrepreneurship, assets and pension.
- The data offer objective and measurable benchmarks for evaluating global progress toward legal gender equality.
- Highlights of 2024 Index:
- It is the 10th edition of the report.
- Globally, none of the countries has a full score in the new index, indicating that women did not enjoy equal rights in any of the countries.
- India’s ranking improved to 113 out of 190 countries.
- Indian women enjoyed 60% of the legal rights given to men as per the new report, lower than the global average of 64.2%.
Digital Intelligence Platform
Recently, the Minister of Communications, Railway, and Electronics & Information Technology launched the Department of Telecommunications (DoT)’s ‘Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)’ and ‘Chakshu’ facility on Sanchar Saathi portal.

About Digital Intelligence Platform:
- It is developed by the Department of Telecommunications.
- It is a secure and integrated platform for real time intelligence sharing, information exchange and coordination among the stakeholders, Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions (FIs), social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
- The portal also contains information regarding the cases detected as misuse of telecom resources.
- The shared information could be useful to the stakeholders in their respective domains.
- It also works as backend repository for the citizen-initiated requests on the Sanchar Saathi portal for action by the stakeholders.
- The DIP is accessible to the stakeholders over secure connectivity and the relevant information is shared based on their respective roles. The said platform is not accessible to citizens.
What is Chakshu?
- It is the latest addition to the citizen centric facilities already available on the Sanchar Saathi portal of DoT.
- It facilitates citizens to report suspected fraud communication received over call, SMS or WhatsApp with the intention of defrauding like KYC expiry or update of bank account/payment wallet/SIM/gas connection/electricity connection, sextortion, impersonation as government official/relative for sending money, disconnection of all mobile numbers by Department of Telecommunications etc.
- In case, a citizen is already a victim of cyber-crime or financial fraud, it is advised to report at cyber-crime helpline number 1930 or website https://www.cybercrime.gov.in of Government of India.
Project Seabird
The Defence Minister will inaugurate two big piers and seven towers with 320 homes for Navy officers and Defence civilians as part of Project Seabird at Naval Base Karwar in Karnataka.

About Project Seabird:
- The largest naval infrastructure project for India, it involves creation of a naval base at Karwar, Karnataka, on the west coast of India.
- History:
- In the post-Indo-Pak War of 1971 scenario, India learned that the Indian Navy needs an additional naval base since Mumbai Harbour faced congestion, which led to security issues for its Western Fleet.
- It was initially sanctioned in 1985, and the foundation stone was laid on October 24, 1986, by Rajiv Gandhi.
- This is a massive project with the first sealift facility in the country and a transfer system for docking and undocking ships and submarines.
- Its first phase, which included the construction of a deep-sea harbour, breakwaters dredging, a township, a naval hospital, a dockyard uplift centre and a ship lift, was commissioned in 2005.
- The development of phase 2 of INS Kadamba commenced in 2011.
- This phase is further divided into 2A and 2B. It was planned to expand the facilities to dock additional warships and a new Naval Air Station, among other projects.
- Once completed, it will be the largest naval base in the Eastern Hemisphere. It will be able to accommodate around 32 warships, 23 submarines and hangers for several aircraft.
HPV Vaccination
Every year, March 4 is observed as International HPV Awareness Day.
What is Human Papillomavirus (HPV)?
- HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses, of which more than 40 are spread through direct sexual contact.
- Among these, two HPV types cause genital warts, and about a dozen HPV types can cause certain types of cancer. More than 95% of cervical cancer is caused by the HPV virus.
- Transmission:
- It is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) globally.
- It also spreads through skin-to-skin contact.
- Once infected, most people do not develop any symptoms, thereby not being aware that they have the virus.
- Getting vaccinated against HPV helps prevent cancer in men and women.
- HPV Vaccination:
- It prevents HPV infections that can progress to cancer or genital warts.
- The HPV vaccination is more efficacious if given between the age group of 9-26 years.
- Once a person gets HPV, the vaccine may not be as effective.
- The HPV vaccine isn’t given during pregnancy.
Risa Textile
Tripura’s traditional tribal attire ‘risa’ received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag recently.

About Risa Textile:
- It is a handwoven cloth used as a female upper garment and also as headgear, a stole, or a present to express respect.
- It is woven in colourful designs and has a crucial social and religious significance.
- Adolescent Tripuri girls are first given a risa to wear in an event called Risa Sormani, around age 12 to 14.
- Religious relevance: The risa is used in religious festivals such as Garia Puja by tribal communities, a turban by men during weddings and festivals, a cummerbund over the dhoti, a head scarf by young girls and boys and a muffler during winters.
- It is presented as a mark of honour to distinguished recipients.
- Risa is common in almost all 19 indigenous tribal communities of Tripura.
- The traditional Tripuri female attire consists of three parts — risa, rignai and rikutu.
- Risa is a handwoven cloth used as a female upper garment.
- Rignai is primarily worn as the lower garment and literally means ‘to wear’.
- Rituku is mainly used as a wrap, or like a ‘chunri’ or a ‘pallu’ of the Indian saree. It is also used to cover the heads of newly married Tripuri women.
- The complete Tripuri attire is claimed to have originated even before the time of the Manikya kings, who ruled Tripura for over 500 years starting from the 15th century.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Germany recently announced that it would allow carbon capture and off-shore storage for certain industrial sectors.
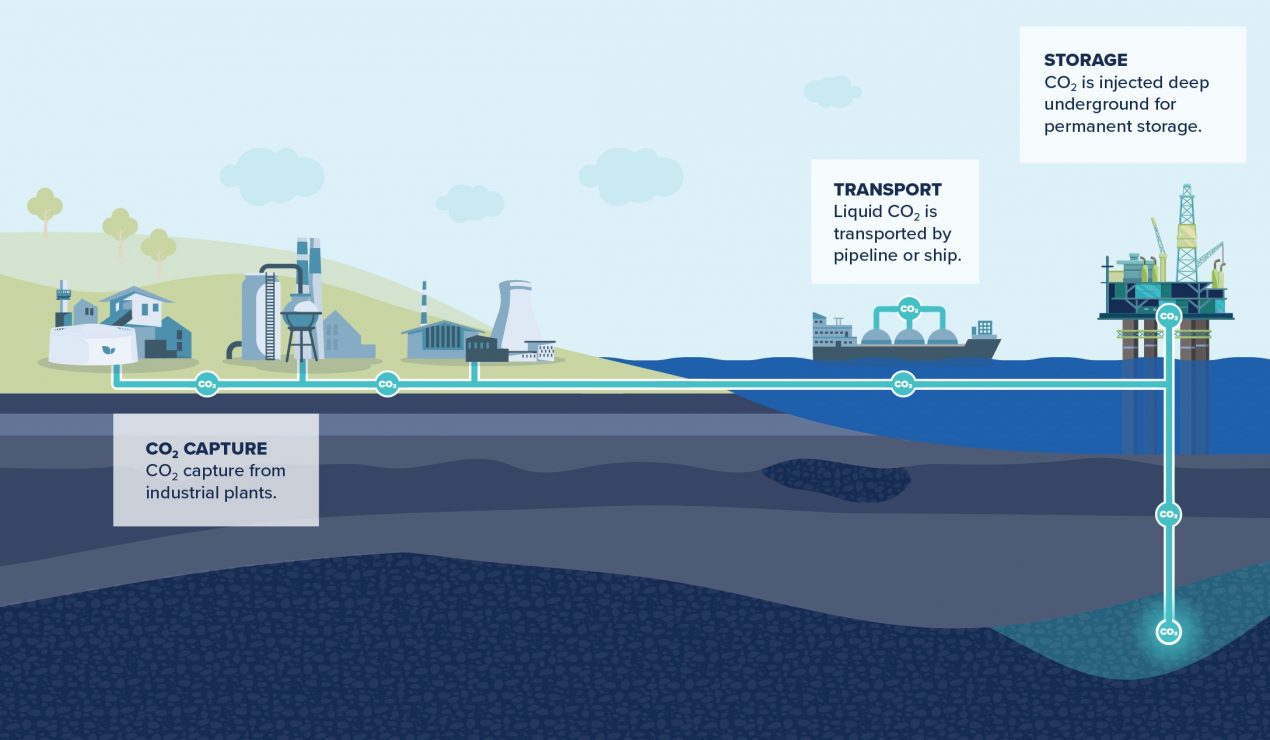
About Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- It’s a three-step process, involving: capturing the carbon dioxide produced by power generation or industrial activity, such as steel or cement making; transporting it; and then storing it deep underground.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gases and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapour. The water is condensed through cooling and CO2 is separated and captured.
- Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient, but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Possible storage sites for carbon emissions include saline aquifers or depleted oil and gas reservoirs.
Cavum clouds
Recently, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration shared captivating pictures Cavum clouds as seen from space.
About Cavum clouds:
- These clouds are also known as “hole-punch clouds or fallstreak holes.”
- How are Cavum clouds formed?
- These are form when aeroplanes pass through layers of altocumulus clouds, which are mid-level clouds containing supercooled water droplets (water below freezing temperature but still in liquid form).
- As the aircraft moves through, a process known as adiabatic expansion can cause the water droplets to freeze into ice crystals.
- These ice crystals eventually become too heavy and fall out of the cloud layer, creating a hole in the clouds.
- They are formed when planes pass through at a relatively steep angle.
What are Altocumulus clouds?
- These are typically found in groups or heaps clumped together.
- They’re found in the middle layer of the troposphere, lower than cirrocumulus and higher than their cumulus and stratocumulus counterparts.
- The term mackerel sky is also common to altocumulus (and cirrocumulus) clouds that display a pattern resembling fish scales.
Copper Age
Archaeologists in Italy recently made a remarkable discovery of a 5,000-year-old cemetery that belonged to a Copper Age society.
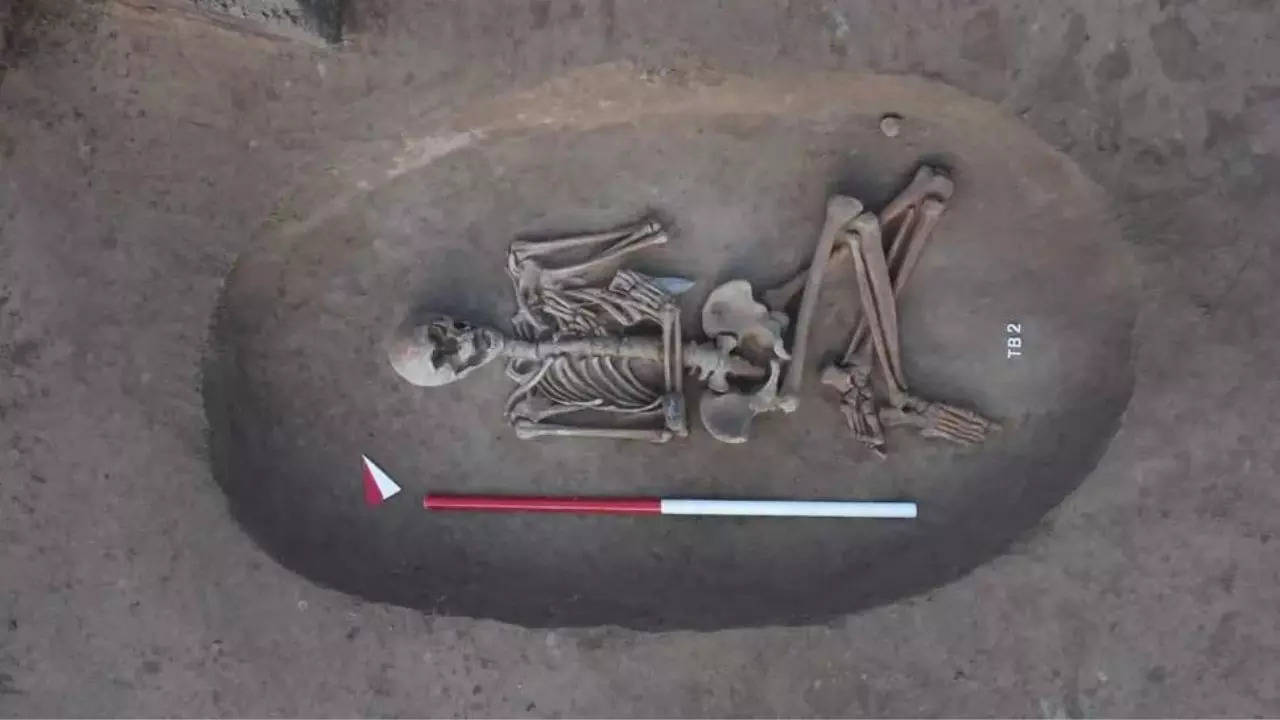

About Copper Age:
- The Copper Age, or Chalcolithic time period, is a period that spans from about 5,000 to 2,000 years ago, depending on the region.
- It was a transitional phase from the Neolithic period (the New Stone Age) to the Bronze Age.
- Features:
- It is characterized by the emergence of metallurgy, especially the use of copper, along with stone tools.
- It coincides with the beginnings of craft specialization, the development of agriculture, long-distance trade, and increased sociopolitical complexity.
- Farmers typically raised domestic animals such as sheep-goats, cattle, and pigs, a diet supplemented by hunting and fishing.
- Crops grown by Chalcolithic farmers included barley, wheat and pulses.
- A main identifying characteristic of the Chalcolithic period is polychrome painted pottery.
- Houses built by Chalcolithic farmers were constructed of stone or mudbrick.
- One characteristic pattern is a chain building, a row of rectangular houses connected to one another by shared party walls on the short ends.
- Another pattern, seen in larger settlements, is a set of rooms around a central courtyard, which may have facilitated the same sort of social arrangement.
- In archaeology, the first signs of massacres, battles and warrior burials begin appearing with the rise of the Copper Age.
- By the end of the Copper Age, people discovered that by adding tin to copper, a stronger and more durable metal could be created: bronze. From that point on, the Bronze Age begins.
Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor
Recently, the Prime Minister of India witnessed the start of the process of core-loading the indigenous prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) at Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
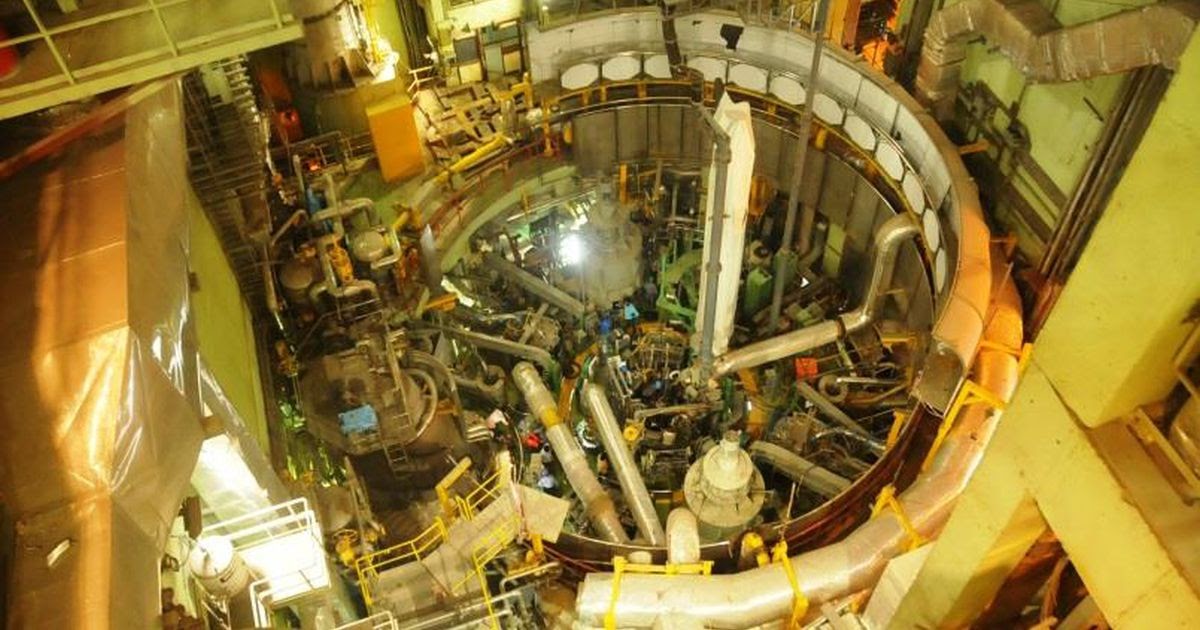

About Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor:
- It is a machine that produces more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- Fuel: The Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) will initially use the Uranium-Plutonium Mixed Oxide (MOX) fuel.
- The Uranium-238 “blanket” surrounding the fuel core will undergo nuclear transmutation to produce more fuel, thus earning the name ‘Breeder’.
- The use of Throium-232, which in itself is not a fissile material, as a blanket is also envisaged in this stage.
- By transmutation, Thorium will create fissile Uranium-233 which will be used as fuel in the third stage.
- Coolant: It uses liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as coolant in two circuits. Coolant in the first circuit enters the reactor and leaves with (heat) energy and radioactivity. Via heat-exchangers, it transfers only the heat to the coolant in a secondary circuit. The latter transfers the heat to generators to produce electricity.
- It has been fully designed and constructed indigenously by Bhartiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd (BHAVINI).
- In terms of safety, the PFBR is an advanced third generation reactor with inherent passive safety features ensuring a prompt and safe shut down of the plant in the event of an emergency.
- Significance:
- Since it uses the spent fuel from the first stage, FBR also offers great advantage in terms of significant reduction in nuclear waste generated, thereby avoiding the need for large geological disposal facilities.
- Once commissioned, India will only be the second country after Russia to have commercial operating Fast Breeder Reactor.
- FBR is thus a stepping stone for the third stage of the program paving the way for the eventual full utilization of India’s abundant thorium reserves.
Gangetic River Dolphin
Recently, National Dolphin Research Centre (NDRC) was inaugurated in Patna in Bihar.
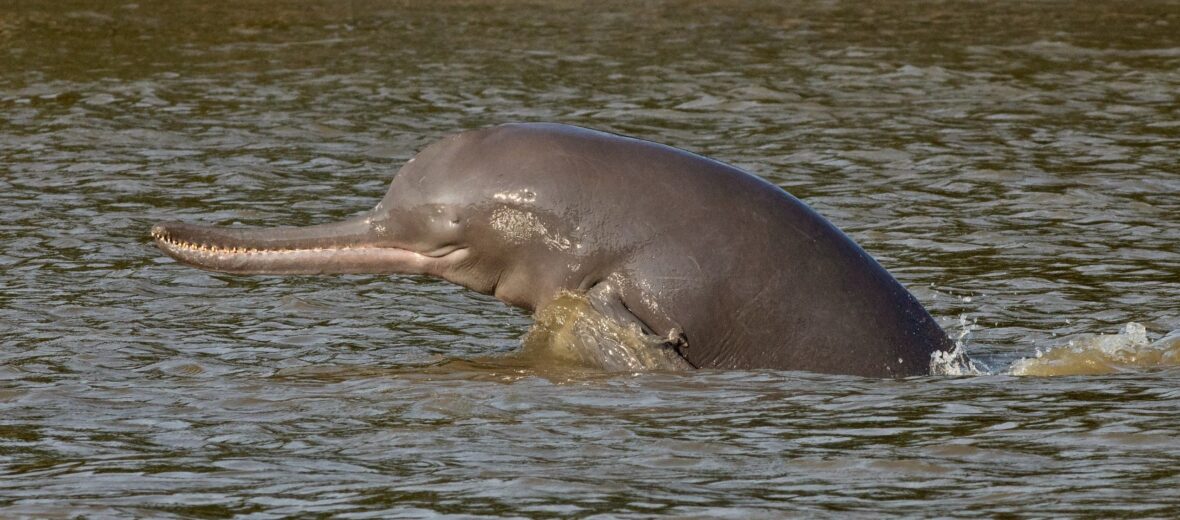

- It is India’s 1st centre for research on conserving the Gangetic river dolphin.
- Scientific name – Platanista gangetica gangetica
- Common name – Susu, Shushak, Side-swimming Dolphin
- Distribution – They are endemic to River Ganga.
- Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
Bihar has around 50% of the estimated 3,000 Gangetic dolphins in India.
- Habitat – Only freshwater and prefer deep water, live in a zone of little or no current.
The Gangetic river dolphin is one of 4 freshwater dolphin species in the world. The other 3 are found in the Yangtze River in China (now extinct), the Indus River in Pakistan and the Amazon River in South America.
- Features – It is functionally blind and finds its way and prey in river waters through echolocation.
- Being a mammal, it cannot breathe in water so it surfaces above the water every 30-40 seconds to breathe with a slit similar to a blowhole on top of its head acts as a nostril.
- They are frequently found alone or in small groups, and generally a mother and calf travel together.
- Calves are chocolate brown at birth and then have grey-brown smooth, hairless skin as adults.
- Females are larger than males.
- Major Threats – Unintentional killing through entanglement in fishing gear, pollution and overexploitation of prey.
- Poaching for dolphin oil, used for medicinal purposes.
- Habitat destruction due to development projects like dams.
- Protection status
- IUCN – Endangered
- Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 – Schedule I
- CITES – Appendix I
Quick Facts
- Gangetic River Dolphin – It is India’s national aquatic animal.
- It is state aquatic animal of Uttar Pradesh.
- It was recently rescued in Jalaka River of Odisha, which indicates that there is presence of more freshwater dolphins in the river.
- Project Gangetic Dolphin was launched in 2016 for conserving it.
Volcanic winter
Researchers from NASA used advanced computer modelling to simulate super-eruptions like the Toba event and found that volcanic winter would probably not exceed 1.5 degrees Celsius.

To qualify as a super eruption, a volcano must release more than 1,000 cubic kms of magma. These eruptions are extremely powerful and rare. The most recent one was around 22,000 years ago in New Zealand.
- Volcanic winter – A climatic cooling effect caused by large-scale volcanic eruptions.
- Previous studies agreed that some planet-wide cooling would occur and estimates have ranged from 2 to 8 degrees Celsius.
- Occurrence – A massive volcanic eruption can deposit enormous amounts of ascending light coloured volcanic ash and sulphur aerosols above the troposphere and into the lower stratosphere.
- Global cooling – These erupted particles reflect incoming solar radiation, resulting in cooler temperatures on the earth below.
- They can remain there for 2 years causing global cooling.
- The air between the troposphere and the stratosphere eventually mixes causing these particles to fall into the troposphere and wash down on the earth through precipitation.
One of the most severe volcanic winters occurred between 74,000 and 71,000 years ago following the eruption of the Mount Toba volcano on the island of Sumatra.
- Challenges – The ash produced from the eruption of Mount Etna in 44 B.C. was described to have dimmed the Sun’s rays and the resulting cooling caused crops to shrivel and produce famine in ancient Rome and Egypt.
Stratospheric Aerosols Injection (SAI) involves spraying large quantities of tiny particles like Sulphur dioxides or finely powdered calcium carbonate into the earth’s stratosphere to reflect sunlight and thereby reducing Earth’s temperature.
Sub-Inspector Suman Kumari Makes History as BSF’s First Female Sniper
Sub-Inspector Suman Kumari has etched her name in history as the first woman sniper of the Border Security Force (BSF). Her recent completion of an eight-week intensive sniper course at the Central School of Weapons and Tactics (CSWT) in Indore not only showcases her exceptional abilities but also her pioneering spirit. Suman achieved the prestigious ‘instructor grade’, a testament to her proficiency and expertise.

A Determined Volunteer
- Suman’s journey to becoming a sniper began with her volunteering for the challenging course. Her decision was fueled by firsthand experiences of the sniper threat across the border while she was commanding a platoon in Punjab. Recognizing her determination and potential, her superiors green-lit her participation in the course. This marked the beginning of a grueling but fulfilling journey for Suman.
Standing Tall Among Peers
- The course, known for its rigorous physical and mental demands, saw Suman as the lone female among 56 male counterparts. This did not deter her; instead, it served as a motivation to excel and prove her mettle. Her hard work and dedication paid off, as she not only completed the course but did so with flying colors, earning her the right to be posted as a sniper instructor.
Inspiration for Many
- CSWT IG Bhaskar Singh Rawat hailed Suman’s achievement as a significant milestone, emphasizing the sniper course’s reputation as one of the toughest, second only to commando training. Suman’s success is seen as an inspiration for other female recruits, encouraging them to explore and excel in similar military roles.
A Humble Background
- Hailing from Mandi district in Himachal Pradesh, Suman comes from a humble background. Her father, an electrician, and her mother, a homemaker, have been her pillars of support throughout her journey. Joining the BSF in 2021, Suman has also demonstrated her prowess in unarmed combat, further highlighting her versatile skill set.
- Suman Kumari’s journey from a small town in Himachal Pradesh to becoming the BSF’s first woman sniper is a story of perseverance, skill, and breaking traditional barriers. Her achievements not only underscore the changing dynamics in defense roles for women but also pave the way for future female soldiers to follow in her footsteps.
Important takeaways for all Competitive Exams
- BSF Founder: Khusro Faramurz Rustamji;
- BSF Founded: 1 December 1965;
- BSF Director General: Nitin Agarwal, IPS.
|
Other Important Topics |
| Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) |
Minister of Communications recently launched the Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) and ‘Chakshu’ facility on Sanchar Saathi portal.
|
| PROJECT SEABIRD |
|
| Abortion in France |
|
| Single use plastics in Odisha |
|
| Eenthu Pana (Cycas circinalis) |
Eenthu Pana in Kerala is on the verge of extinction after being hit by an unknown and fast spreading plant disease.
|
| India’s 1st Green Hydrogen plant in stainless steel sector |
Union Minister for Steel and Civil Aviation recently inaugurated India’s 1st Green Hydrogen Plant in Stainless Steel Sector in Haryana.
|
| Carl Gustaf Weapon System |
Swedish defence company SAAB has announced its plans to manufacture the iconic Carl-Gustaf M4 weapon systems in Haryana.
|
| C4IR |
The World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Centre for the 4th Industrial Revolution (C4IR) was recently launched in Hyderabad.
|
| Serengeti ecosystem |
|
| Alaskapox virus |
The first known fatality from the recently discovered Alaska pox virus has been reported in Alaska.
|




