Current Affairs – 2 March 2024
Current Affairs – 2 March 2024
Network Planning Group

- It is an Integrated Multimodal Network Planning Group (NPG) with heads of Network Planning Division of all connectivity infrastructure Ministries & Departments.
- It is responsible for unified planning and integration of the proposals and assist the Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS) in respect of its mandate.
- It facilitates regular interactions between the stakeholders.
- It will guide all the Departments/ Ministries responsible for creation of economic zones and connectivity infrastructure during the planning phase itself.
- The parameters/prescribed norms of the overall National Master Plan will be the overarching objective of the NPG for examining and sanctioning future projects thus leading to minimising of disruptions and strive for the creation of an ideal & efficient operating system for all infrastructure projects in the country.
- Its role is to ensure:
- integration of networks;
- enhance optimization through modification/expansion/new network creation;
- avoid duplication of works for holistic development of any region;
- reduction logistics costs through micro-plan detailing.
What is PM GatiShakti?
- It is an approach for growth accelerating trustworthy infrastructure through synchronized, holistic, integrated and comprehensive planning based on knowledge, technology and innovation.
- PM GatiShakti National Master Plan provides comprehensive database of the ongoing & future projects of various Ministries i.e. Infrastructure Ministries & Ministries and States involved in development of Economic Zones, integrated with 200+ GIS layers thereby facilitating planning, designing and execution of the infrastructure projects with a common vision.
Exercise Samudra Laksamana

- It is a joint naval exercise between the Indian Navy and Royal Malaysian Navy.
- It is the 3rd edition of this exercise.
- Indian Naval Ship Kiltan and Royal Malaysian Ship KD Lekir are participating in this exercise which has harbour professional interactions followed by the operational phase at sea.
- At harbour, crew of both ships will have various professional interactions, Subject Matter Expert Exchange on topics of mutual interest, sports fixtures, and other interactions.
- These interactions are aimed to enhance knowledge base, share best practices and further cooperation on maritime aspects. The exercise aims to strengthen bonds and enhance interoperability between the Indian and Royal Malaysian Navy.
Key points about INS Kiltan
- It is an indigenously-built anti-submarine warfare stealth corvette
- This is the third of the four Kamorta-class corvettes being built under Project 28.
- The ship derives its name from one of the islands in Aminidivi group of the strategically located Lakshadweep and Minicoy group of islands.
- It is designed by the Indian Navy’s in-house organisation Directorate of Naval Design and built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
Semiconductor fabrication
- A semiconductor fab — short for fabrication — is a manufacturing plant in which raw silicon wafers are turned into integrated circuits (ICs).
- The process includes creating intricate patterns on the wafer using light and chemicals, depositing different materials to form components, and etching away unwanted materials.
- This results in the formation of transistors, interconnects, and other elements that make up a semiconductor device.
- A semiconductor fab facility always includes a clean room because its environment is carefully controlled to eliminate dust and vibrations and to keep the temperature and humidity within a specific narrow range.
What kind of technology is used in fabs?
- Photolithography:
- It is a crucial step in semiconductor fabrication where patterns are transferred onto silicon wafers.
- A photosensitive material, called photoresist, is applied to the wafer and exposed to light through a mask.
- The exposed areas are chemically etched, creating the desired pattern. This process enables the precise definition of features on the wafer, enabling the creation of intricate circuitry.
- Deposition techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical vapor deposition (PVD) to add thin layers of materials; etching processes to remove unwanted materials; and various metrology tools for inspection and measurement.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency

- It was established in 2002 under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Objective: The primary objective of BEE is to reduce energy intensity in the Indian economy.
- Function and Duties
- It co-ordinates with designated consumers, designated agencies and other organizations; recognizes, identifies and utilizes the existing resources and infrastructure, in performing the functions assigned to it under the Energy Conservation Act.
- Regulatory functions
- Develop minimum energy performance standards for equipment and appliances under Standards and Labelling
- Develop minimum energy performance standards for Commercial Buildings
- Develop Energy Consumption Norms for Designated Consumers
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Power
State Energy Efficiency Index 2023
- It is the fifth edition of The State Energy Efficiency Index (SEEI), initiated by Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), in association with Alliance for an Energy Efficient Economy.
- It is to evaluate the annual progress of energy efficiency implementation in the states.
- It assesses the performance of 36 states and UTs using 65 qualitative, quantitative, and outcome-based indicators measures distributed across seven demand sectors: buildings, industry, municipal services, transport, agriculture, electricity distribution companies (DISCOMs), and cross-sector initiatives.
- In SEEI 2023, the states and UTs are categorized as ‘Front runner’ (>=60), ‘Achiever’ (50-59.75), ‘Contender’ (30-49.75), and ‘Aspirant’ (<30) based on their total scores.
- Furthermore, to enable peer-to-peer comparison of performance, all the states and UTs are classified into four groups based on their total final energy consumption (TFEC): Group 1 (>15 million tonnes of oil equivalent (MTOE)), Group 2 (5-15 MTOE), Group 3 (1-5 MTOE), and Group 4 (<1 MTOE).
- The top-performing states in each group are Karnataka (Group 1), Andhra Pradesh (Group 2), Assam (Group 3), and Chandigarh (Group 4).
Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)

- IED is a type of unconventional explosive weapon that can take any form and be activated in a variety of ways.
- An IED is basically a home-made bomb because they are improvised.
- IEDs can come in many forms, ranging from a small pipe bomb to a sophisticated device capable of causing massive damage and loss of life.
- They can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- While they have been in used for over a century, the term “IED” first entered common usage during the United States’ Iraq invasion (beginning in 2003), where such bombs were commonly used against US forces.
- Components
- Each IED comprises a few basic components, which can come in various forms, depending on resources available to the bomb-maker.
- These include an initiator or a triggering mechanism, (which sets the explosion off), a switch (which arms the explosive), a main charge (which causes the explosion), a power source (since most IEDs contain an electric initiator, they require an electronic power source), and a container.
- Additionally, IEDs may be packed with additional materials or “enhancements” such as nails, glass, or metal fragments designed to increase the amount of shrapnel released by the explosion — and thus the damage it causes.
- Enhancement may also include hazardous materials such as toxic chemicals, or radio-active circumstances — an IED packed with, say, depleted Uranium will be colloquially called a “dirty bomb”
- Some common materials used to build IEDs include fertilisers such as ammonium nitrate and urea nitrate, gunpowder, and hydrogen peroxide.
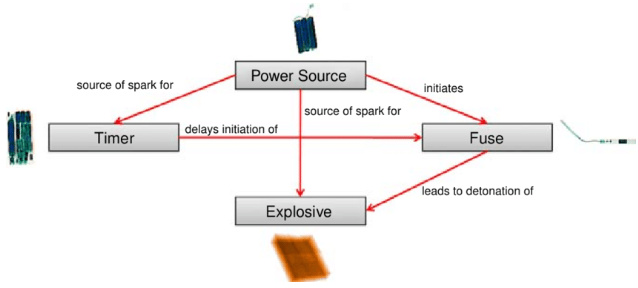
- Enhancements – Nails, glass, or metal fragments to increase the amount of shrapnel released and thus the damage it causes.
- It may also include hazardous toxic chemicals, or radio-active substances.
The colloquial name of an IED packed with depleted Uranium is dirty bomb.
- Materials used – It include fertilisers such as ammonium nitrate and urea nitrate, gunpowder, and hydrogen peroxide.
- Damages – The extent of damage depends on its size, construction and placement.
Notable instances of IEDs usage in India include the 1993 Mumbai serial blasts, the 2008 Jaipur blasts, the 2006 Jama Masjid bombings, and the 2013 Bodh Gaya bombings. It have also been commonly used by Maoist insurgents, and Kashmiri militants.
MILAN 2024
The 12th edition of Milan exercise held recently in Visakhapatnam, the city of Destiny in 2024.

| MILAN |
|
- Aim – To enhance professional interaction between friendly navies and gain experience in multilateral large force operations at sea.
- Theme – ‘Camaraderie, Cohesion, and Collaboration’.
- The Harbour Phase – It will have Table Top Exercise, Interactions of Young Officers, Outstation Cultural visits and International City Parade.
- The Sea Phase – Indian Navy ships, aircraft and submarines led by Indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant and 20-25 Foreign Naval Units will participate.
- It includes advanced air defence operations, Anti-Submarine warfare, Anti Surface warfare operation and War at Sea.
- Significance – An opportunity to share operational insights in harbour, hone skills at sea, enhance camaraderie on the sports fields, and gain an exposure to Indian culture.
- Strengthens Southeast Asian countries – Security of vital sea lines of communication (SLOCs) in the Indian Ocean is important for energy and trade interests.
- It helps to expand their naval engagements beyond their traditional geographical neighbourhood.
- Singapore, Indonesia, and Thailand since 1995, Malaysia in 1997, Myanmar in 2003, and Brunei, Cambodia, the Philippines, and Vietnam in 2012.
Malacca Strait links the Andaman Sea of the Eastern Indian Ocean to the South China Sea and serves as a transit for over 40% of global commodities.The Philippines and Indonesia are the largest and 3rd largest suppliers of seafarers, respectively.
Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport
The Rohini Sounding Rocket was launched from the mobile launch pad to mark the commencement of physical work on the Kulasekarapattinam spaceport.

- Geographical location – Thoothukudi district of Tamil Nadu.
Kulasekaranpattinam, better known for its Dussehra celebrations at Sri Mutharamman Temple.
- Role – It is ISRO’s 2nd satellite launch facility, would be completed within 2 years to launch SSLVs in order.
- It would have the capacity to launch 24 satellites per year.
- Need – The rockets launched from ISRO’s Sriharikota facility in Andhra Pradesh 1st heads east, and then turn south to avoid the Sri Lanka’s airspace, costing more fuel and reduce payload’s capacity.
- Geographical advantages – It can head straight in the southern direction without a dogleg manoeuvre and closer to equator than Sriharikota thereby reducing time and fuel wastage.
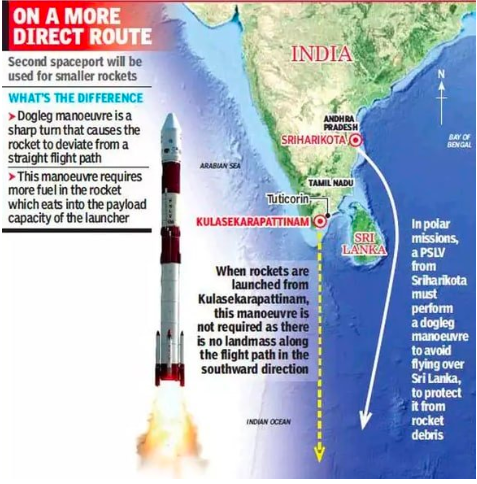
- Economic significance– It is relatively closer to the ISRO Propulsion Research Complex located in Mahendragiri, in Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu.
- It makes it easier to transport the rocket components safely in shorter time, thus reducing the costs involved.
- Safety considerations – Proximity to the eastern coastline of India are safer, as any failure of launches allow the debris to fall harmlessly in Bay of Bengal or Indian Ocean.
- Promotes development – A number of allied industries will come up in the neighbourhood that will create 1000s of jobs.
- Geo-stationary satellites – They are usually communication satellites or satellites used for scientific research such as the International Space Station which are placed in the orbit that are parallel to equator.
- Launching these satellites from the sites near the equator towards the east direction will get an initial boost equal to the velocity of the Earth surface.
- Polar satellites – They are placed in polar orbits moving across the equator in north south direction and are generally launched in southward or northward direction.
- Therefore, they cannot take advantage of the Earth’s rotation.
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs) – They are designed to launch light-weight satellites less than 500 kg into the lower earth orbit at low costs.
Bitcoin Halving
Crypto traders and Bitcoin miners are preparing for Bitcoin halving that is predicted to happen in April 2024.

| Bitcoin (BTC) |
|
Bitcoin (BTC) can only ever be 21 million BTC in the world, over 19 million have already been “mined” or released.
- Reward for mining – It is given to the person who solves the puzzles 1st which is currently set at 6.25 Bitcoin (BTC).
- While the reward is set, the true value of this prize fluctuates based on BTC prices in the market, and when the owner chooses to sell.
- Bitcoin Halving – It refers to the 50% reduction in the reward paid to Bitcoin miners who successfully process other people’s cryptocurrency transactions.
- Occurrence – It takes place after 2,10,000 blocks are mined, and has happened so far in 2012, 2016, and 2020, every 4 years.
- Need – This saved reward will be added to the public digital ledger known as the blockchain.
- Significance – Bitcoin mining increases the supply of BTC in circulation while the Bitcoin Halving reduces the rate at which these coins are released, making the asset scarcer.
- Scarcity is seen as pushing up prices, as is the case with gold.
- Impact on investors – It depends on the investor in question, and the extent of their involvement with Bitcoin and its ecosystem.
- For example, a corporate-level miner will probably be desperate to earn their block reward in these last days.
- A new trader who has invested a small sum of money might not even react to the news of the halving.
- A more experienced trader might try increasing their Bitcoin investment hoping to profit from a possible price crash.
- Impact on crypto market – It varies as every halving in Bitcoin’s history has been wildly different.
- It depends on varied factors like blockchain-related factors, diverse geopolitical events or economic shocks, among others.
PM Modi Inaugurates Rs 7,200 Crore Projects In West Bengal

Empowerment through Development
- The Prime Minister expressed confidence in the resolutions of Viksit Bharat being accomplished with the contributions of the people of West Bengal.
- PM Modi praised India’s achievements in environmental harmony, citing the example of the Haldia Barauni crude pipeline which promotes safe and environmentally friendly transportation of crude oil.
Key Projects Inaugurated
1.Indian Oil’s Haldia-Barauni Crude Oil Pipeline
- This pipeline, spanning 518 kilometers, was inaugurated at a cost of about Rs 2,790 crore.
- It passes through Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal, supplying crude oil to Barauni Refinery, Bongaigaon Refinery, and Guwahati Refinery.
- The pipeline ensures safe, cost-efficient, and environment-friendly transportation of crude oil, contributing to the energy security of the region.
2.Indian Oil’s LPG Bottling Plant at Vidyasagar Industrial Park, Kharagpur
- Developed at a cost of more than Rs 200 crore, this LPG bottling plant is the first of its kind in the region.
- With a capacity of 120 TMTPA, it will supply LPG to about 14.5 lakh customers in West Bengal, addressing the growing demand for clean cooking fuel in the area.
3.Infrastructure Strengthening at Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port, Kolkata
- Projects worth about Rs 1000 crore were dedicated to strengthening the infrastructure at the port.
- This includes the reconstruction of Berth No. 8 NSD and the mechanization of berth no. 7 & 8 NSD of Kolkata Dock System.
- Additionally, augmentation of the firefighting system at oil jetties of Haldia Dock Complex was inaugurated, equipped with state-of-the-art automated facilities for immediate hazard detection.
- The third Rail Mounted Quay Crane (RMQC) of Haldia Dock Complex, with a lifting capacity of 40 Tonnes, was also dedicated, aimed at boosting the productivity of the port substantially.
4.Rail Projects
- Inauguration of the third rail line connecting Jhargram – Salgajhari, spanning 90 kilometers.
- Doubling of Sondalia – Champapukur rail line covering 24 kilometers.
- Doubling of Dankuni – Bhattanagar – Baltikuri rail line, covering 9 kilometers.
- These projects expand rail transport facilities in the region, improving mobility and facilitating seamless service of freight traffic, thereby fostering economic and industrial growth.
5.Wastewater Treatment and Sewerage Projects
- Inauguration of projects related to wastewater treatment and sewerage in West Bengal, developed at a cost of about Rs 600 crore, funded by the World Bank.
- Includes Interception and Diversion (I&D) works and Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) at Howrah, Bally, Kamarhati & Baranagar, addressing environmental concerns and improving sanitation facilities in the region.
Driving Comprehensive Development in West Bengal
- Inauguration and foundation laying signify a significant stride in West Bengal’s comprehensive development.
- Initiatives prioritize infrastructure, environmental sustainability, and empowerment for enhanced economic growth and better quality of life.
Dharmendra Pradhan Launches Project ODISERV For Odisha’s Graduates

Bridge Between Education and Skilling
- Shri Pradhan emphasized the pivotal role of Project ODISERV in bridging the gap between education and skilling.
- Highlighted the transformative impact of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 in fostering synergies between academic knowledge and job-ready skills.
Training and Employment
- 1100 students in Odisha have already undergone training under Project ODISERV, with several of them securing job offers on the same day.
- Shri Pradhan extended congratulations to the successful candidates and expressed gratitude to Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi for his vision of nurturing India’s youth into future-ready professionals.
Skill Enhancement for Future-Ready Workforce
- The 100-hour training program under Project ODISERV aims to equip Odisha’s youth with essential skills for the banking, finance, and insurance industries.
- Emphasized that this initiative would not only enhance competencies but also significantly increase the employability of the youth.
Industry Perspective
- Shri Sanjiv Bajaj, Chairman & Managing Director of Bajaj Finserv, underscored the importance of skilling and employment generation for harnessing India’s demographic dividend.
- Highlighted Bajaj Finserv’s commitment to social impact through initiatives like the Certificate Programme for Banking Finance & Insurance (CPBFI).
NSDC and Bajaj Finserv Partnership
- The collaboration between the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and Bajaj Finserv aims to revolutionize skill development in Odisha and across India.
- With plans to launch CPBFI in 60 colleges across Odisha, the initiative is poised to transform the skill landscape of the state.
Scaling Up Nationwide
- Under the partnership, CPBFI will be introduced in 22 states, covering over 400 colleges, with an initial target of skilling 20,000 candidates.
- The program’s curriculum, developed in collaboration with industry experts, will adapt to the dynamic landscape of finance, banking, and insurance.
Paving the Way for a Skilled Workforce
- Project ODISERV stands as a testament to the commitment of the government, industry, and educational institutions towards nurturing a skilled workforce.
- Through collaborative efforts and innovative initiatives like Project ODISERV, India is poised to harness its demographic dividend and emerge as a global economic powerhouse.
Veteran Congress Leader and Former UP Governor Aziz Qureshi Passes Away
 Early Life and Political Ascent
Early Life and Political Ascent
- Born on April 24, 1941, in Bhopal, Aziz Qureshi embarked on his political journey with a strong foundation rooted in his dedication to public service. His early foray into politics saw him being elected as an MLA from the Sehore seat in Madhya Pradesh in 1972, marking the beginning of a long and illustrious career.
Contributions and Leadership
- Aziz Qureshi’s political acumen led him to serve in various high-profile roles across the Indian states. Notably, he held the gubernatorial positions in Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh (additional charge), and Mizoram, where his leadership and vision contributed significantly to the states’ governance.In addition to his role as a governor, Qureshi also made his mark as a cabinet minister in Madhya Pradesh in 1973, further solidifying his reputation as a dedicated public servant. His political journey also saw him winning the Lok Sabha elections from the Satna constituency of Madhya Pradesh in 1984, showcasing his widespread appeal and commitment to the nation.
Legacy and Later Years
- Beyond his political roles, Aziz Qureshi was appointed the President of the Madhya Pradesh Urdu Academy by the then Kamal Nath government on January 24, 2020. This position allowed him to contribute to the promotion of Urdu language and literature, reflecting his diverse interests and commitment to cultural preservation.
Anurag Agarwal Appointed as Head of Parliament Security
In a significant move to bolster the security of India’s parliamentary complex, IPS officer Anurag Agarwal has been appointed as the new head of Parliament security. This decision comes at a crucial juncture, following recent security breaches that have underscored the need for stringent protective measures within one of the nation’s most critical infrastructures.

Background of Anurag Agarwal
- Anurag Agarwal, a seasoned officer from the 1998 batch of the Assam-Meghalaya cadre, has been serving as an inspector general in the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF). With his extensive experience in law enforcement and internal security, Agarwal brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise to his new role as the joint secretary (security) of the Parliament House complex.
Appointment Details
- The appointment of Mr. Agarwal was officially confirmed through an order issued by the Lok Sabha Secretariat, marking the culmination of a search for a suitable candidate to fill the vacancy left since October 20. The position had been empty following the departure of the previous joint secretary, Raghubir Lal, who returned to his cadre. The role of JS (Security) is a pivotal one, traditionally occupied by an IPS officer, tasked with overseeing the comprehensive security framework of the Parliament.
Challenges and Responsibilities
- Mr. Agarwal assumes his responsibilities at a time when the security of the Parliament House complex is under scrutiny. This follows an incident on December 13, where two individuals managed to breach security protocols, entering the Lok Sabha chamber from the visitors’ gallery and releasing a can of yellow smoke. The event has highlighted the imperative for a thorough overhaul of security measures to prevent any such occurrences in the future.
Foreign Exchange Reserve
India’s foreign exchange reserves surged by $2.98 billion to $619.07 billion recently.

About Foreign Exchange Reserve:
- Foreign Exchange Reserves (also called Forex Reserves) are reserve assets held by a central bank in foreign currencies.
- Foreign assets comprise assets that are not denominated in the domestic currency of the country.
- These may include foreign currencies, bonds, treasury bills, and other government securities.
- Reserves are denominated and expressed in the US dollar, which is the international numeraire for the purpose.
- RBI is the custodian of the foreign exchange reserves in India.
- India’s foreign exchange reserves comprise of;
- Foreign currency assets (FCAs): These are maintained in currencies like the US dollar, euro, pound sterling, Australian dollar, and Japanese yen.
- Gold
- SDR (Special Drawing Rights): This is the reserve currency with the IMF.
- RTP (Reserve Tranche Position): This is the reserve capital with the IMF.
- The biggest contributor to India’s Forex reserves is foreign currency assets, followed by gold.
- Purpose:
- They are used to back liabilities on their own issued currency, support the exchange rate, and set monetary policy.
- To ensure that RBI has backup funds if their national currency rapidly devalues or becomes altogether insolvent.
- If the value of the Rupee decreases due to an increase in the demand for the foreign currency, then RBI sells the dollar in the Indian money market so that depreciation of the Indian currency can be checked.
- A country with a good stock of forex has a good image at the international level because the trading countries can be sure about their payments.
- A good forex reserve helps in attracting foreign trade and earns a good reputation with trading partners.
Genome India Project
The Genome India Project recently announced that it had finished sequencing 10,000 Indian genomes.

About Genome India Project:
- It is a pan-India initiative focused on the whole genome sequencing of representative populations across India.
- Goal: The goal is to start with and execute whole genome sequencing and subsequent data analysis of 10,000 individuals representing the country’s diverse population.
- This is a mission-mode, multi-institution consortium project, the first of its kind in India, supported and funded by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India.
- The specific aims of the project are:
- Create an exhaustive catalogue of genetic variations (common, low frequency, rare, single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs, and structural variations) in Indians.
- Create a reference haplotype structure for Indians. This reference panel can be used for imputing missing genetic variation in future studies.
- Design genome-wide arrays for research and diagnostics at an affordable cost.
- Establish a biobank for DNA and plasma collected for future use in research.
What is Genome?
- A genome is the complete set of genetic information in an organism.
- In living organisms, the genome is stored in long molecules of DNA called chromosomes.
- In humans, the genome consists of23 pairs of chromosomes located in the cell’s nucleus, as well as a small chromosome in the cell’s mitochondria.
- A genome contains all the information needed for an individual to develop and function.
Nano Urea
India plans to replace the consumption of 2.5 million tonnes (mt) of conventional urea with nano urea in FY24, Union Chemicals and Fertilizers Minister said at a press conference recently.

About Nano Urea:
- It is a nanotechnology-based revolutionary Agri-input that provides nitrogen to plants.
- It is developed and patented by the Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO).
- IFFCO Nano Urea is the only nano fertilizer approved by the Government of India and included in the Fertilizer Control Order (FCO).
- Features:
- Compared to conventional urea prill, Nano Urea has a desirable particle size of about 20-50 nm, and more surface area (10,000 times over 1 mm urea prill), and number of particles (55,000 nitrogen particles over 1 mm urea prill).
- It contains 4.0 % total nitrogen (w/v).
- Benefits:
- It is produced by an energy-efficient, environment-friendly production process with less carbon footprints.
- Increased availability to crops by more than 80%,resulting in higher nutrient use efficiency.
- It is expected to improve crop productivity, soil health, and nutritional quality of produce and address the “imbalanced and excessive use” of conventional fertilizer.
National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT
The National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) reported its highest-ever daily number of transactions at 4.10 crore recently.

About National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT):
- NEFT is a nation-wide electronic centralised payment system owned and operated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- It enables transferring funds from the account maintained with any bank to any other bank branch, provided the transaction is attempted between the banks that participate in the NEFT payment system.
- Organisations, companies and individuals can use it to transfer funds from one bank account to another.
- As per Reserve Bank of India (RBI) guidelines, the payments made via NEFT are processed and settled in half-hourly batches.
- Minimum Transfer Value: Rs. 1
- Maximum transfer value: No limit
- NEFT offers the following advantages for funds transfer or receipt:
- Round-the-clock availability on all days of the year.
- Near-real-time funds transfer to the beneficiary account and settlement in a secure manner.
- Pan-India coverage through large network of branches of all types of banks.
- The beneficiary need not visit a bank branch for depositing the paper instruments. Remitter can initiate the remittances from his / her home / place of work using internet banking, if his / her bank offers such a service.
- Penal interest provision for delay in credit or return of transactions.
- No levy of charges by RBI from banks.
- No charges to savings bank account customers for online NEFT transactions.
- The transaction charges have been capped by the RBI.
- NEFT system can be used for the payment of credit card dues to the card issuing banks, payment of loan EMIs, inward foreign exchange remittances, etc.
Amrabad Tiger Reserve
The leopard population increased considerably in Amrabad Tiger Reserve, according to the ‘Status of Leopards in India’ report released recently.

About Amrabad Tiger Reserve:
- Location: It is located in the Nagarkurnool and Nalgonda districts in the southern part of Telangana.
- It is one of the largest tiger reserves in India. It is the second-largest Tiger Reserve in terms of core area.
- Earlier, it was part of ‘Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, but post-state bifurcation, the northern part of the reserve was vested with Telangana state and renamed ‘Amrabad Tiger Reserve’. The southern portion continues to be ‘NSTR’ with Andhra Pradesh.
- ATR covers a part of the Nallamala Forest and is home to a variety of flora and fauna.
- Major reservoirs like the Srishailam Dam and Nagarjunsagar Dam are fed by the river Krishna and its several perennial streams that originate in the Tiger Reserve.
- Flora:
- Dense grass occurs in 30% of the area and is scattered in an additional 20%.
- Fauna:
- Major wild animals found are Tiger, Leopard, Wild dog, Indian Wolf, Indian fox, Rusty-spotted cat, Small Indian civet, Sloth bear, Honeybadger, Wild boar etc.
- Some important bird species include Eagles, Pigeons, Doves, Cuckoos, Woodpeckers, Drongos etc.