Current Affairs – 10 May 2024
Current Affairs – 10 May 2024
United Nations Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund
Recently, India contributed $5,00,000 to UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund, reaffirming unwavering commitment to global fight against terrorism.

About United Nations Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund:
- It was established in 2009 and transferred to UN Office of Counter- Terrorism (UNOCT) in 2017.
- Who can contribute? The Fund accepts contributions from Governments, inter-governmental and non-governmental organizations, private institutions and individuals.
- Contributions may be unearmarked or earmarked for one of UNOCT’s global programmes or specific initiatives.
- India’s contribution would support UNOCT’s global programmes — mainly Countering Financing of Terrorism (CFT) and Countering Terrorist Travel Programme (CTTP).
- They are aimed at building capacities of the member states of eastern and southern Africa to combat the critical issues of financing of terrorism and prevent the movement and travel of terrorists.
Key facts about UN Office of Counter- Terrorism:
- It was established on 15 June 2017 through the adoption of UN General Assembly
- Functions
- Provide leadership on the General Assembly counter-terrorism mandates entrusted to the Secretary-General from across the United Nations system.
- Enhance coordination and coherence across the Global Counter-Terrorism Coordination Compact entities to ensure the balanced implementation of the four pillars of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy.
- Strengthen the delivery of United Nations counter-terrorism capacity-building assistance to Member States.
- Improve visibility, advocacy and resource mobilization for United Nations counter-terrorism efforts.
- Ensure that due priority is given to counterterrorism across the United Nations system and that the important work on preventing violent extremism is firmly rooted in the Strategy.
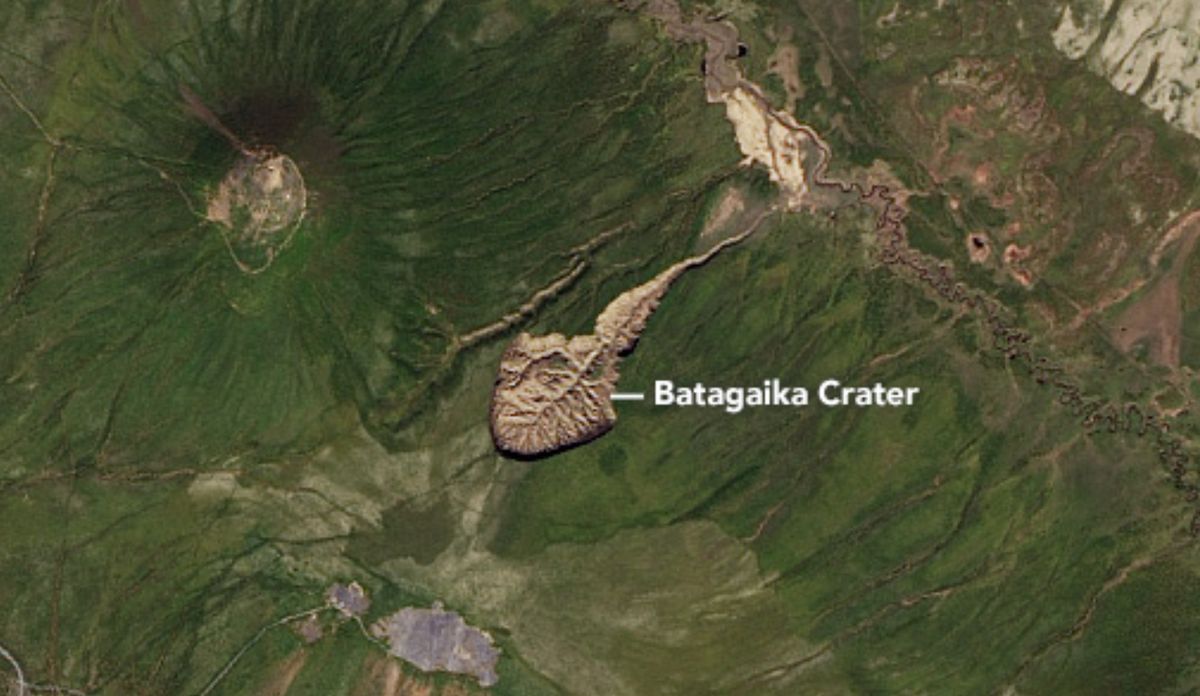
Batagay Crater
According to a new study a huge crater in Siberia’s permafrost, is growing by 35 million cubic feet every year as the frozen ground melts.
Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA)
The Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) has adopted a work plan focused on assessing country landscapes, drafting policy frameworks, and conducting biofuel workshops.
