Current Affairs – 5th Feb 2024
PM congratulates France for formal launch of UPI
India is internationalising UPI with France being latest country to adopt it for payments.
Background
- UPI is an instant payment system that allows users to transfer money between bank accounts using a single mobile app. It was developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) in 2016 and is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- As of November 2022, the platform had over 300 million monthly active users in India. The proportion of UPI transactions in total volume of digital transactions grew from 23% in 2018–19 to 55% in 2020–21 with an average value of ?1,849 per transaction. It enabled over 2,348 transactions every second in 2022. In Aug 2023, UPI crossed 10 billion transactions with a value of ?15.7 lakh crore. In FY 2023, the value of annual transactions reached $1.7 trillion, out of which $380 billion is in merchant payments.
Partnership, merchant adoption and benefits for Indian tourists
- The launch of UPI in France was facilitated by a partnership between NPCI International Payments (NIPL), a subsidiary of NPCI, and Lyra, a French e-commerce and proximity payments company.
- Indian tourists visiting the Eiffel Tower can now purchase entry tickets online using UPI by scanning a QR code generated on the merchant’s website and initiating a payment. Eiffel Tower is the first merchant to offer UPI payments in France, and the service will soon be extended to other merchants in the tourism and retail space across France and Europe.
Significance for India-France relations
- The launch of UPI in France is a significant step towards taking UPI global, as envisioned by Prime Minister Modi. It is also a testament to the strong bilateral relations between India and France, which have been enhanced by the recent visit of French President Emmanuel Macron as the chief guest for the 75th Republic Day celebrations in New Delhi on January 26.
Global vision for UPI
- UPI is a transformative force in the global payment landscape making payments instantaneous and low cost.
- It has potential for offering a simple, secure, and interoperable solution for cross-border transactions.
- UPI is now being pitched as a standard for global public infrastructure in payments as outlined during recent G20 summit.
Conclusion
UPI is a shining example of India’s innovation and leadership in the digital payment space. It has the potential to transform the global payment landscape by offering a simple, secure, and interoperable solution for cross-border transactions. UPI is not just a payment system, but a symbol of India’s digital empowerment and global integration.
Hydrothermal Systems
New maps have revealed a hidden hydrothermal system beneath Lake Rotorua, which sits at the heart of a dormant volcano in New Zealand.
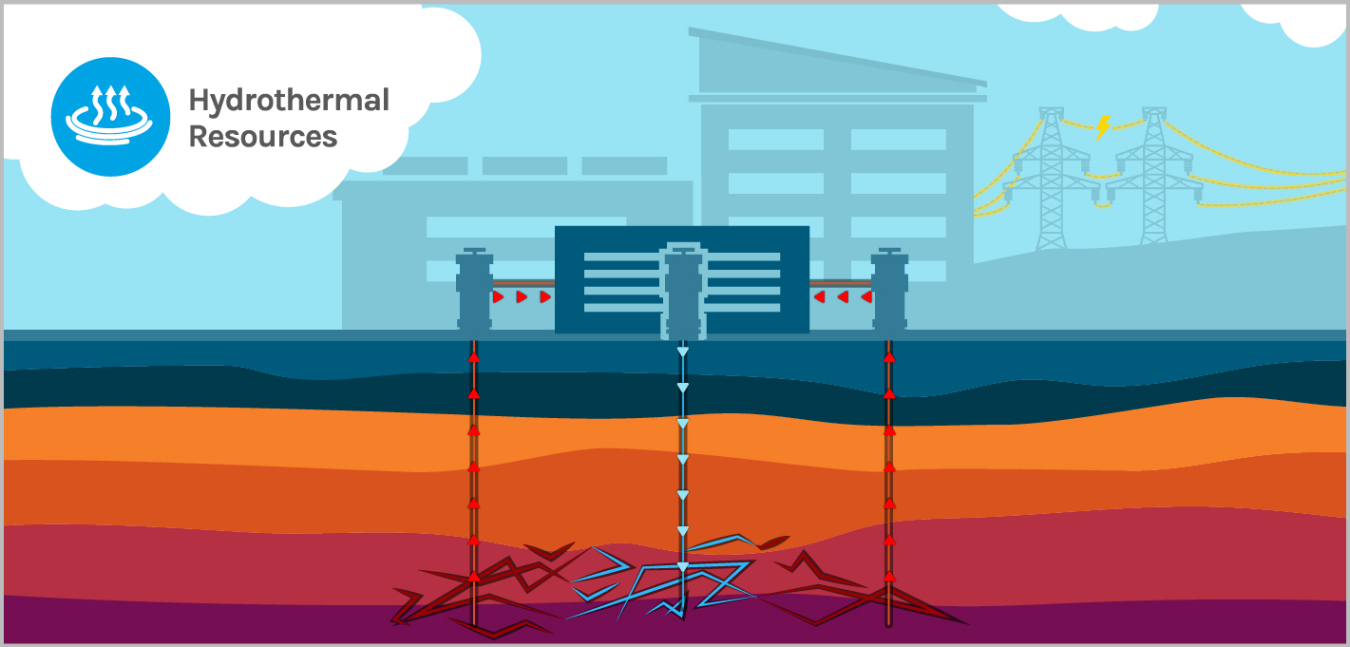
About Hydrothermal Systems:
- Hydrothermal systems occur in areas with high heat fluxes, both on continents, near convergent plate boundaries, and on the ocean floor, near the mid-ocean ridges.
- Their formation requires the existence of three important components: fluids, heat, and permeability through rocks so that fluids can circulate.
- These systems are often found near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge and new seafloor is created.
- How do hydrothermal systems work:
- Hydrothermal systems occur when seawater percolates down through fractures in the oceanic crust, heating up as it nears the earth’s hot interior.
- Descending seawater interacts with the oceanic crust, removing chemicals from the rocks as it heats to 350-400 degrees Celsius, about four times hotter than boiling water (the extreme pressure in the ocean’s depths prevents fluids from boiling).
- This interaction of seawater and crust produces hydrothermal fluid, a chemically modified slurry of gases and dissolved elements, including metals.
- The superheated fluid is then ejected back up to the seafloor and promptly chilled by near-freezing ocean bottom waters.
- Chemicals dissolved in the fluid precipitate at the vent, forming chimney-like deposits.
- These deposits support deep-sea chemosynthetic communities—organisms that rely on chemicals rather than photosynthesis to fuel their metabolism.
Corbett Tiger Reserve
Five people have been killed near Uttarakhand’s Corbett Tiger Reserve in the past two months.

About Corbett Tiger Reserve:
- Location:
- It is located on the foothills of the Himalayas in Uttarakhand.
- By and large, the reserve is spread over the Bhabar and lower Shivalik regions with a deep-water table.
- Corbett was the first national park in India and was established in 1936. It was named Hailey National Park then. In 1957, the park was rechristened Corbett National Park in memory of the late Jim Corbett, a great naturalist and eminent conservationist.
- Today, after the addition of areas to the originally declared National Park, the total area of Tiger Reserve extends to 1288.31 sq. km.
- Vegetation: In general, the vegetation comprises sal and mixed forests, interspersed with grasslands and riparian vegetation.
- The terrain is undulating, with several valleys. The rivers Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi flow through the valleys.
- The habitat is characterised by open meadows (chaurs) interspersed with sal and moist, mixed deciduous forests.
- The grasslands are locally known as ‘Chaur’, which are an outcome of abandoned settlements or past clearings.
- Flora: It consists of evergreen Sal and its combined trees, the Sheesham, and the Kanju found extensively on the ridges.
- Fauna: Tiger and elephant are the charismatic mammals, besides a large array of co-predators (leopard, small carnivores), ungulates (sambar, hog deer, spotted deer), birds, reptiles (gharial, crocodile) and fishes.
GRAPES-3 experiment
The GRAPES-3 experiment discovered a new feature in the cosmic-ray proton spectrum at about 166 tera-electron-volt (TeV) energy while measuring the spectrum spanning from 50 TeV to a little over 1 peta-electron-volt (PeV).

About the GRAPES-3 experiment:
- Gamma Ray Astronomy PeV EnergieS phase-3 (GRAPES-3) is designed to study cosmic rays with an array of air shower detectors and a large area muon detector.
- Location: It is located in Ooty, India.
- It is operated by the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research.
- It aims to probe the acceleration of cosmic rays in different astrophysical settings.
- Its objectives are to study:
- The origin, acceleration and propagation of >1014 eV cosmic rays in the galaxy and beyond.
- Existence of “Knee” in the energy spectrum of cosmic rays.
- Production and/or acceleration of the highest energy (~1020 eV) cosmic rays in the universe.
- Astronomy of multi-TeV γ-rays from neutron stars and other compact objects.
Key facts about Cosmic rays:
- These rays were discovered more than a century ago.
- They are considered to be the most energetic particles in the universe.
- Our planet is constantly bombarded by them from outer space almost uniformly from all directions at a constant rate.
- They enter into Earth’s atmosphere and induce a shower of particles that travel to the ground almost at the speed of light.
- The shower particles constitute electrons, photons, muons, protons, neutrons etc.
- They have been observed over a remarkably wide energy range (108 to 1020 eV).
Dusted Apollo
Recently, Dusted Apollo (Parnassius stenosemus), a rare high-altitude butterfly, has been sighted and photographed for the first time in Himachal Pradesh.

About Dusted Apollo:
- It is an extremely rare butterfly and has never been photographed before in Himachal Pradesh.
- Distribution range: It is found from Ladakh to West Nepal and it flies between 3,500 to 4,800 metres in the inner Himalayas.
- Appearance
- It closely resembles Ladakh Banded Apollo (Parnnasius stoliczkanus) but the discal band on the upper fore wing in dusted Apollo is complete and extends from costa to vein one while this discal band is incomplete and extends only up to vein four in Ladakh Banded Apollo.
- Moreover, the Dark marginal band on the hind wings is much narrower in Dusted Apollo while it is broad in Ladakh Banded Apollo.
- Another rare species Regal Apollo (Parnnasius charltonius) was also photographed at Manimahesh, which is protected under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- There are 11 Apollo species recorded from Himachal Pradesh and five of them are declared as Scheduled species.
- It is an encouraging indication of the flourishing diversity of Apollo butterflies in the region.
- Threats: Apollos are considered commercially important butterflies and they fetch high prices in the poaching industry.
- Most of the Apollo butterflies are now endangered and need immediate attention for their conservation and protection.
- Conservation measures:
- Community awareness about poaching and the importance of these species may play an important role in their conservation.
- Also, establishing butterfly parks and conservation reserves in the State should be on the priority list of the government.
National Agriculture Market (eNAM)
With more states facilitating the trade of agricultural commodities on the eNAM, a spurt in trading among various markets within the state as well as at the inter-state level is being witnessed.
About eNAM:
- It is an online trading platform for agricultural commodities in India.
- It was launched on April 14, 2016, and is completely funded by the Government of India.
- The Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC) acts as the lead agency for implementing e-Nam under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It aims to create better marketing opportunities for the farmers to sell their products through a competitive and transparent price discovery system, along with an online payment facility for the buyers.
- The NAM portal networks the existing APMC (Agriculture Produce Marketing Committee) / Regulated Marketing Committee (RMC) market yards, sub-market yards, private markets, and other unregulated markets to unify all the nationwide agricultural markets by creating a central online platform for agricultural commodity price discovery.
- Features:
- It will enable farmers to showcase their products through their nearby markets and facilitate traders from anywhere to quote prices.
- It provides single-window services for all APMC-related services and information. This includes commodity arrivals, quality and prices, buy-and-sell offers, and e-payment settlements directly into farmer’s accounts, among other services.
- Using the eNAM service, licences for traders, buyers, and commission agents can be obtained from state-level authorities without any pre-condition of the physical presence or possession of a shop or premises in the market yard.
- Harmonisation of quality standards of agricultural products and infrastructure for quality testing are made available in every market.
- Provision of Soil Testing Laboratories is provided for the selected mandi (market) in order to facilitate the farmers visiting the mandi.
- e-NAM is designed and implemented to benefit all the stakeholders: farmers, mandis, traders, buyers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and exporters.
- The benefits to stakeholders include:
- Transparent online trading with enhanced accessibility to the market.
- Real-time price discovery for better and more stable price realisation for producers.
- Reduced transaction costs for buyers.
- Availability of information on the e-NAM mobile app about commodity prices.
- The details of the price of the commodity sold, along with the quantity, are received through SMS.
- Quality certification.
- More efficient supply chain and warehouse-based sales.
- Online payment directly to the bank accounts of the farmers.
InTranSE Program
During the launch event of “Digital India FutureLABS Summit 2024” held at IIIT- Delhi, three Indigenous Technologies – Thermal camera, CMOS camera and Fleet Management System designed and developed by CDAC Thiruvananthapuram under InTranSE Program of MeitY were transferred to 12 Industries.

About InTranSE Program:
- The Intelligent Transportation System Endeavor (InTranSE) is a revolutionary collaborative research and development programme.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- Purpose: To synergize the transformation in Intelligent Transportation Systems the Ministry of Electronics & IT took early steps by bringing together premier academic institutes like the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Indian Institute of Management (IIM) etc. and Premier R&D Centre like C-DAC under one umbrella.
- This initiative formulated the Collaborative Intelligent Transportation Systems Endeavor for Indian Cities (InTranSE) during the year 2009-2012 (Phase-I) that witnessed IIT Bombay, IIT Madras, IIM Calcutta and C-DAC Thiruvananthapuram collaboratively developing, implementing, demonstrating and knowledge transfer of ITS products and solutions.
- The InTranSE Phase-II program (2019-2021) is aiming at undertaking R&D projects collaboratively with IIT Bombay, IIT Madras, IISc Bangalore and C-DAC Thiruvananthapuram
- Significance: It will achieve traffic efficiency by minimising traffic problems, prompting efficient infrastructure usage, enriching users with prior information about traffic and reducing travel time as well as enhancing the safety and comfort of commuters.
Candida auris (C. auris)
A deadly fungal infection called Candida auris has been spreading rapidly in the United States recently.
About Candida auris (C. auris):
- It is an emerging multidrug-resistant yeast (fungus) that represents a global health threat.
- It is capable of causing invasive infections in the human body. It can cause severe illness in people with weakened immune systems.
- Scientists first discovered C. auris in Japan in 2009. Since then, it has spread quickly to other countries.
- Transmission:
- It is primarily contracted in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
- It can also live on the skin or other body parts without making a person sick. This is called being “colonised.”
- The fungus can either colonise a specific region of the body, such as the skin, rectum, or mouth, without causing symptoms or it can cause severe invasive infections by entering the bloodstream or wounds.
- It can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment, or from physical contact with a person who is infected or colonised.
- Symptoms:
- It can cause infections in different parts of the body, such as the bloodstream, open wounds, and ears.
- The symptoms depend on the location and severity of the C. auris infection.
- Symptoms may be similar to those of an infection caused by bacteria. There is not a common set of symptoms specific to C. auris infections.
- A high fever with chills that do not get better after taking antibiotics may be a sign of a C. auris infection.
- Treatment:
- Most C. auris infections are treatable with antifungal drugs.
- However, some C. auris infections have been resistant to all three main classes of antifungal medications, making them more difficult to treat and often requiring the use of combination therapies.
Mekong River
A multibillion-dollar dam project underway across the Mekong River in Laos has prompted concerns that it could result in Luang Prabang City losing its UNESCO World Heritage Site status.

About the Mekong River:
- It is the longest river in Southeast Asia, the 7th longest in Asia, and the 12th longest in the world.
- It has a length of about 2,700 miles (4,350 km).
- Course:
-
- It rises in southeastern Qinghai Province, China.
- It originates from the Sanjianyuang in the Tibetan Plateau, with the area designated a national nature reserve to protect the headwaters of the Yangtze, Yellow, and Mekong Rivers.
- The river drains approximately 795,000 square kilometres and flows through six Asian countries: China, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia, where it is referred to by different names.
- Vientiane(Viangchan), the capital of Laos, and Phnom Penh, the capital of Cambodia, both stand on its banks.
- The river drains into the South China Sea south of Ho Chi Minh City (Vietnam).
- Tributaries: The left-bank tributaries (draining high rainfall areas) include Nam Ou, Tha, and Nam Khan, while the right-bank tributaries (draining the lower relief region) are Ruak, Kok, Tonle Sap, and Mun.
- Its biodiversity is only second to the Amazon River Basin and contains about 20,000 plant species, 1,200 birds, 430 mammals, 800 amphibians and reptiles, and 850 fish species.
- It is the river with the largest fish species, including giant freshwater stingrays, giant pangasius, Mekong giant catfish, and giant barb.
- The Mekong creates a huge delta, or triangular piece of land, in southern Vietnam. The delta has rich soil and is one of the world’s great producers of rice.
Directorate General of GST Intelligence
The Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) is investigating Mahadev Online Book, an allegedly illegal betting application, and its promoters for suspected violation of GST rules and non-payment of tax.

About Directorate General of GST Intelligence:
- The Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence (DGCEI) is now renamed as Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI).
- It is an apex intelligence organisation functioning under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, Department of Revenue, and Ministry of Finance.
- It is entrusted with the task of collection, collation, and dissemination of intelligence relating to the evasion of Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the duties of Central Excise and Service Tax on an all-India basis.
- Functions of DGGI:
- Intelligence gathering: It is responsible for gathering intelligence about potential violations of the GST law. This includes collecting information from various sources, such as GST returns, financial statements, and other documents.
- It develops intelligence, especially in new areas of tax evasion through its intelligence network across the country and disseminates such information, by issuing Modus Operandi Circulars and Alert Circulars to sensitise the field formations about the latest trends in duty evasion.
- Investigation: It has the power to conduct investigations into suspected cases of GST evasion or non-compliance. This may involve summoning persons, examining records, and carrying out searches and seizures.
- Enforcement: It is responsible for enforcing the provisions of the GST law. This includes taking legal action against offenders, imposing penalties, and recovering any taxes or duties due.
Thrips parvispinus
The recent study states that ‘new invasive species of Thrips Parvispinus in Florida is tiny but deadly to landscapes and crops’.
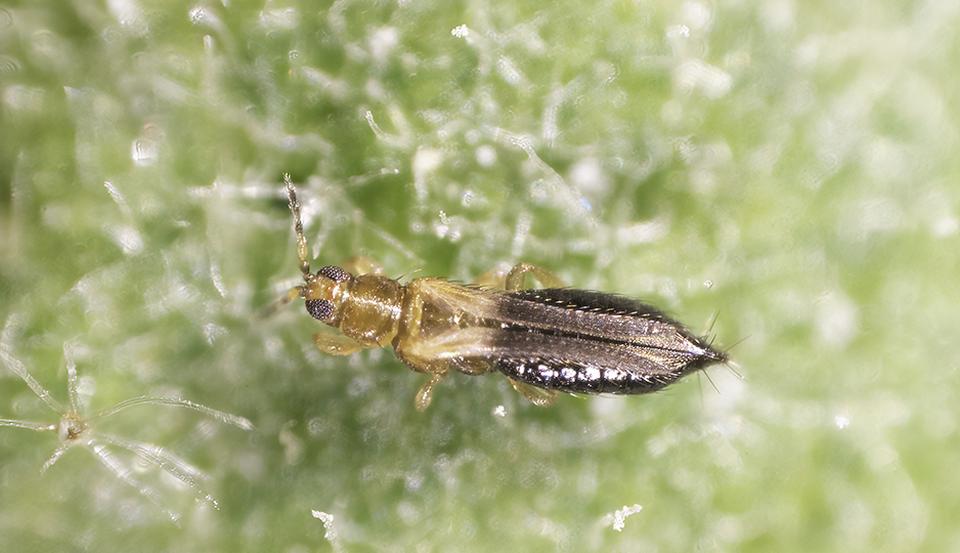

Thrips are important group of sucking pests which cause significant economic losses both as pests and vectors of serious plant viruses in several horticultural crops.
- Common name – Karny, an invasive pest species.
- Size – The adult female is smaller than a pencil tip but visible to naked eye and their larvae are transparent.
- Life cycle – About 2 weeks, the female is fertile within 9 days, laying about 15 eggs in a clutch.
- Feed – It is a polyphagous species, infesting beans, eggplant, papaya, chilli, pepper, potato, strawberry, tobacco and also it inflicts injury to ornamentals plants like Chrysanthemum.
- Infestations – Adults mainly colonize on flowers and underside of leaves whereas larvae suck sap from under surface.
- It also scratches the flesh, leading to curling leaves, stippling, scabbing and stunted growth, heavy flower drop and thereby reducing fruit production.
- Spread – They are present in at least 17 countries, including India, Indonesia, Japan, Taiwan, Singapore and Thailand.
- In India – It was 1st reported on Papaya from Bengaluru in 2015.
- During Rabi season of 2021-22, they were reported in chilli growing areas of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka.
- Its infestation increased during heavy rainfall of North East monsoon in contrast to other thrips species.
- Control measures – Promotion of cultural practices like deep summer ploughing, intercropping, clean cultivation, balanced use of fertilisers, uprooting and destruction of plant debris and Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies for pest control.
In India, Thrips Parvispinus might have dominated or even replaced the native chilli thrips known as scirtothrips dorsalis.
Seabed Curtain project
Scientists are working on an unusual plan to prevent Antarctic glaciers from melting through seabed curtain project.

- Aim – To build a set of giant underwater curtains in front of ice sheets to protect them from being eroded by warm sea water.
- Need – Ice in Polar Regions is now disappearing at record rates as global warming intensifies.
- Warmer air melts the surface of glaciers, while they are also eroded at their bases by warm seawater.
Loss of the Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers could be enough to raise sea levels round the world by 3 metres if they melted.
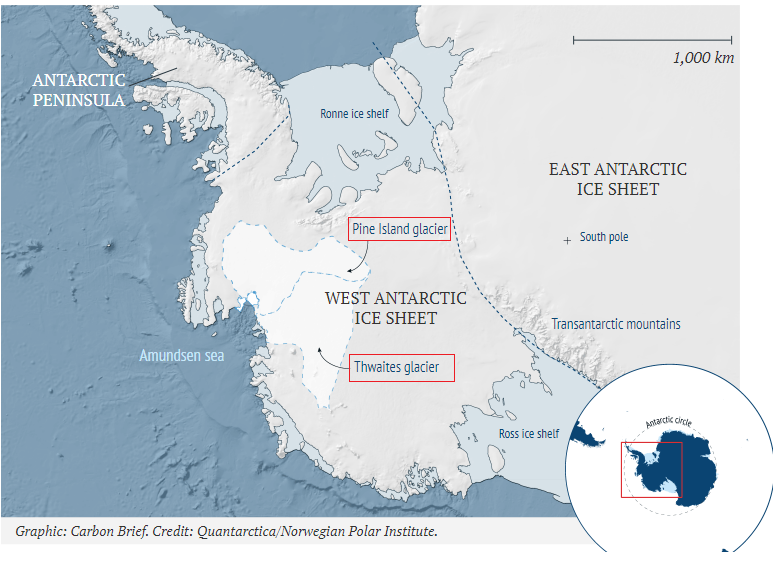
- Proposal – To construct a 100km-long curtain attached to the bed of the Amundsen Sea and would rise by about 200 metres.
- Curtain – It would stretch along the seabed opposite the Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers to act as plugs that prevent the giant ice sheets behind them from sliding into the ocean.
- Working – It would partially restrict the inflow of relatively warm water that laps at the bases of coastal Antarctic glaciers and undermines them.
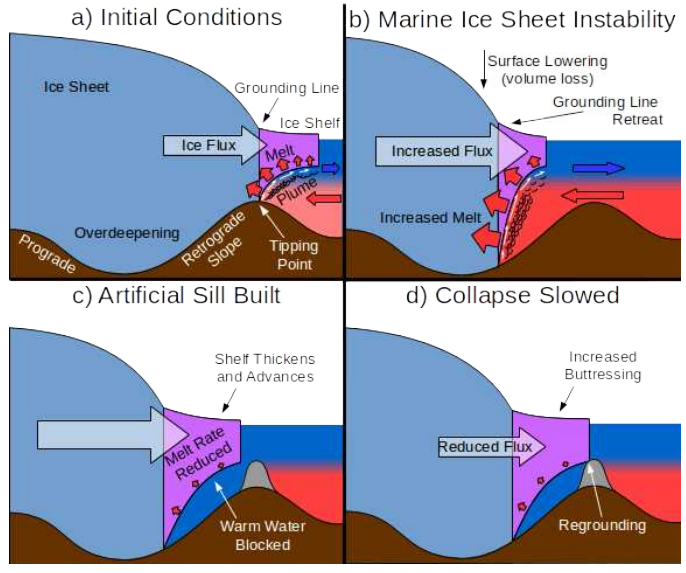
The Seabed Curtain project, if implemented, would be one of the biggest geo-engineering programmes ever undertaken
Interim Budget 2024-2025
Why in News?
- Recently, the Interim Budget 2024-25 was tabled in the parliament. It envisions ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047, with all-round, all-pervasive, and all-inclusive development.

What is an Interim Budget?
- An Interim Budget is presented by a government that is going through a transition period or is in its last year in office ahead of general elections.
- The purpose of the interim budget is to ensure the continuity of government expenditure and essential services until the new government can present a full-fledged budget after taking office.
What is the Difference Between Interim Budget and Vote on Account?
| Feature | Interim Budget | Vote on Account |
| Constitutional Provision | Article 112 | Article 116 |
| Purpose | Financial Statement presented by the government ahead of general elections. | To meet essential government expenditures for a limited period until the budget is approved. |
| Duration of Expenditure | Covers a specific period, usually a few months until a new government is formed and a full budget is presented. | It is generally granted for two months for an amount equivalent to one-sixth of the total estimation. |
| Policy changes | Can propose changes in the tax regime | Cannot change the tax regime under any circumstances |
| Impact on Governance | Provides continuity in governance during the transition period between two governments. | Ensures the smooth functioning of the government and public services until the regular budget is approved. |
Highlights of Union Budget 2024-25

What are the Major Highlights of the Interim Budget 2024-25?
- Capital Expenditure: An 11.1% increase in the capital expenditure outlay for 2024-2025 was announced.
- The capital expenditure is set at Rs 11,11,111 crore, constituting 3.4% of the GDP.
- Economic Growth Projections: The GDP growth for FY 2023-24 real GDP growth is projected at 7.3%, aligning with the RBI’s revised growth projection.
- The International Monetary Fund upgraded India’s growth projection to 6.3% for FY 2023-24. It also anticipates India becoming the third-largest economy in 2027.
- Revenue and Expenditure Estimates (2024-25):
- Total Receipts: Estimated at Rs 30.80 lakh crore, excluding borrowings.
- Total Expenditure: Projected at Rs 47.66 lakh crore.
- Tax Receipts: Estimated at Rs 26.02 lakh crore.
- GST Collections: Reached ₹1.65 lakh crore in December 2023, crossing the ₹1.6 lakh crore benchmark for the seventh time.
- Fiscal Deficit and Market Borrowing: Fiscal deficit is estimated at 5.1% of GDP in 2024-25, aligning with the goal of reducing it below 4.5% by 2025-26 (announced in budget 2021-22).
- Gross and net market borrowings through dated securities in 2024-25 are estimated at Rs 14.13 and 11.75 lakh crore, respectively.
- Taxation: The Interim Budget maintains the existing rates for direct and indirect taxes, including import duties.
- For Corporate Taxes: 22% for existing domestic companies, 15% for certain new manufacturing companies.
- No tax liability for taxpayers with income up to ₹7 lakh under the new tax regime.
- Certain tax benefits for Start-Ups and investments extended by one year up to March 31, 2025.
- Priorities: Emphasizing the focus on the Poor, Women, Youth and Farmer.
- Poor: Successful movement of 25 crore people out of multidimensional poverty.
- Credit assistance was provided to 78 lakh street vendors under PM-SVANidhi.
- Women: Disbursement of 30 crore Mudra Yojana loans to women entrepreneurs.
- 43% of female enrolment in STEM courses.
- Assistance to 1 crore women through 83 lakh SHGs, fostering ‘Lakhpati Didis.’
- 28% increase in female enrolment in higher education over a decade.
- Youth: Training of 1.4 crore youth under the Skill India Mission.
- Fostering entrepreneurial aspirations with 43 crore loans sanctioned under PM Mudra Yojana.
- Farmers: Direct financial assistance was provided to 11.8 crore farmers under PM-KISAN.
- Crop insurance extended to 4 crore farmers through Fasal Bima Yojana.
- Integration of 1,361 mandis under eNAM for streamlined agricultural trade.
- Poor: Successful movement of 25 crore people out of multidimensional poverty.
- Major Development Plans:
- Infrastructure:
- Railways: Three major economic railway corridor programmes will be implemented- energy, mineral & cement corridors, port connectivity corridors, and high traffic density corridors.
- Forty thousand normal rail bogies will be converted to Vande Bharat standards for enhanced safety, convenience, and passenger comfort.
- Aviation: Expansion of existing airports and comprehensive development of new airports under the UDAN scheme.
- Urban Transport: Promotion of urban transformation via Metro rail and NaMo Bharat.
- Railways: Three major economic railway corridor programmes will be implemented- energy, mineral & cement corridors, port connectivity corridors, and high traffic density corridors.
- Clean Energy Sector:
- Viability gap funding for wind energy
- It will help in harnessing offshore wind energy potential, aiming for an initial capacity of 1 gigawatt.
- Establishment of coal gasification and liquefaction capacity of 100 million tonnes by 2030.
- Phased mandatory blending of CNG, PNG and compressed biogas
- Financial assistance for procurement of biomass aggregation machinery
- Rooftop solarization: 1 crore households will be enabled to obtain up to 300 units of free electricity per month
- Strengthening e-vehicle ecosystem by supporting manufacturing and charging
- New scheme of biomanufacturing and bio-foundry to be launched to support environment friendly alternatives
- Viability gap funding for wind energy
- Housing Sector: Government plans to subsidize the construction of 30 million affordable houses in rural areas.
- Housing for Middle Class scheme to be launched to promote middle class to buy/built their own houses
- Healthcare Sector: Encouraging Cervical Cancer Vaccination for girls (9-14 years).
- U-WIN platform for immunization efforts of Mission Indradhanush to be rolled out.
- Expanding the Ayushman Bharat scheme to include all ASHA workers, Anganwadi workers, and helpers.
- Agricultural Sector: Encouraging the use of ‘Nano DAP’ for various crops across all agro-climatic zones.
- Formulating policies to support dairy farmers and combat Foot and Mouth Disease.
- Strategizing for AtmaNirbharta (self-reliance) in oilseeds, covering research, procurement, value addition, and crop insurance.
- Fishery Sector: Establishing a new department, ‘Matsya Sampada,’ to address the needs of fishermen.
- For States Capex: The continuation of the fifty-year interest-free loan scheme for capital expenditure to states was announced.
- A total outlay of Rs 1.3 lakh crore, with a provision of Rs 75,000 crore for fifty-year interest-free loans to support state-led reforms.
- Special attention will be paid to the eastern region to make it a powerful driver of India’s growth.
- Others:
- Establishment of a corpus of Rs 1 lakh crore with a fifty-year interest-free loan to encourage research and innovation in sunrise domains.
- Also, aiming to boost private sector participation in research and innovation.
- To address rapid population growth and demographic shifts, the government will form a high-powered committee.
- The committee will provide comprehensive recommendations aligned with the goal of ‘Viksit Bharat.’
- Establishment of a corpus of Rs 1 lakh crore with a fifty-year interest-free loan to encourage research and innovation in sunrise domains.
- Infrastructure:
Note
Nano-DAP (Di-ammonium Phosphate) is a nanotechnology-based agri-input developed by the Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited (IFFCO). It helps in correcting the Nitrogen & Phosphorus deficiencies in standing crops.
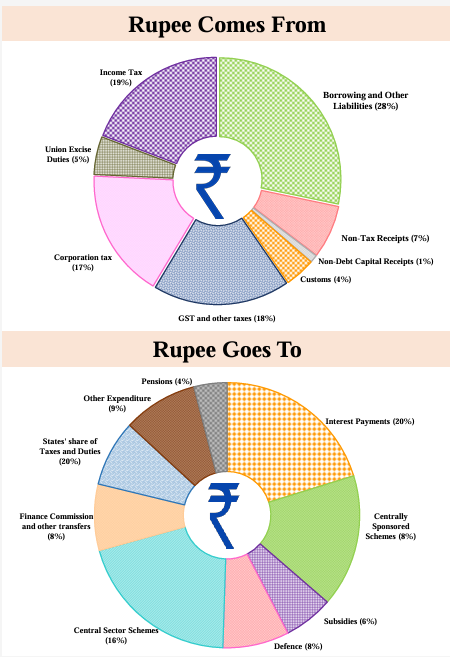
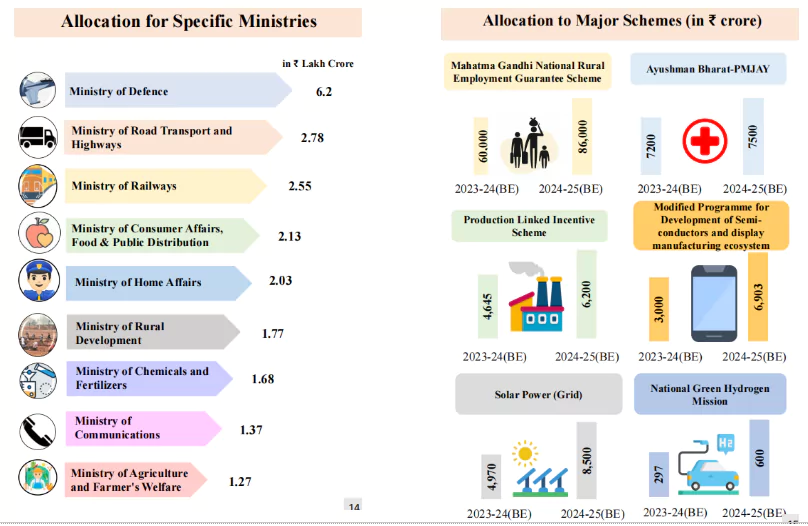
What are the Funds Related to the Budget in India?
- Consolidated Fund of India: Article 266 (1) of the Constitution consolidates all revenues, loans, and loan repayments received by the Union Government into a single fund known as the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Withdrawal needs parliament permission (except for Charged Expenditure like Judges’ salaries).
- Public Account of India: Under Article 266 (2), it includes incoming money from provident fund, small savings, postal deposit etc.
- Government acts similar to a banker transferring funds from here to there so parliament permission is not necessary.
- Contingency Fund of India: It is established under the Contingency Fund of India Act, 1950 and operates as an imprest in accordance with Article 267(1).
- It serves the purpose of offering advances to the government for unforeseen expenditures during the fiscal year, pending authorization by Parliament.
- Funds withdrawn from the Contingency Fund are replenished upon parliamentary approval through Supplementary Demands for Grants.

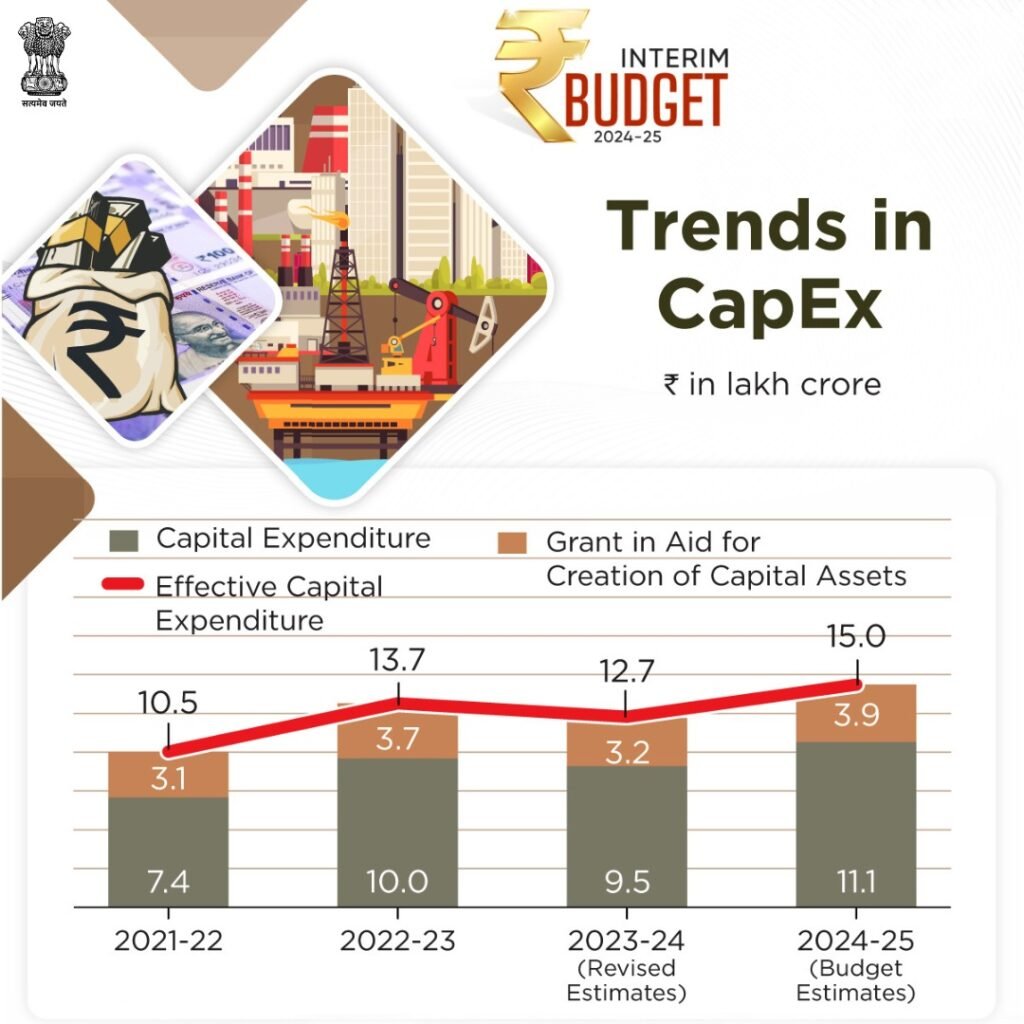
Resilient Performance of the Indian Economy
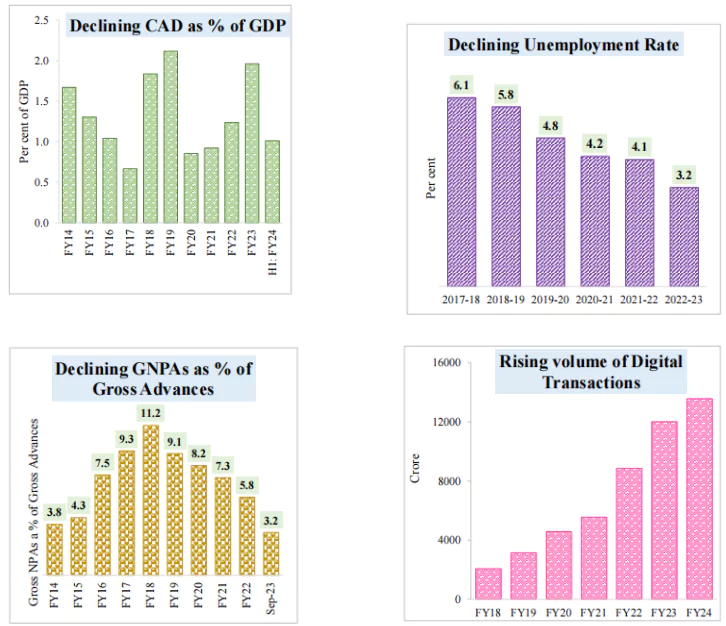
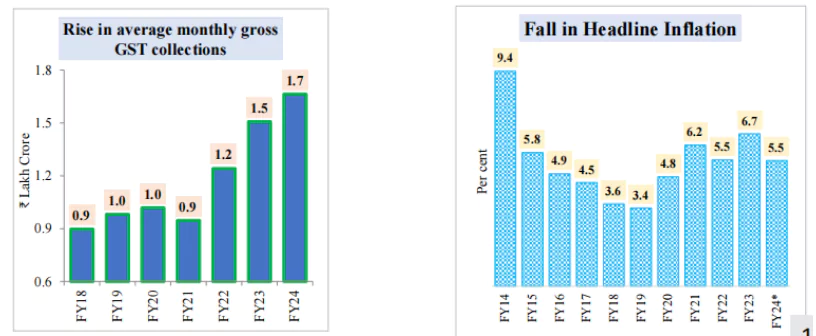
|
Other Important Topics |
||||||||||||
| Chamundi Hills | ||||||||||||
Chamundi Hill ropeway plan in Mysuru resurfaces, green activists maintain opposition.
|
||||||||||||
| Typbar | ||||||||||||
India-made typhoid vaccine efficacy lasts for four years.
|
||||||||||||
| Climbing Himalayan Treelines | ||||||||||||
Himalayan treelines might be climbing higher in response to climate change.
|
||||||||||||
| Patna Declaration | ||||||||||||
Bihar to bring ‘Patna declaration’ at international workshop to discuss bird conservation efforts.
|
||||||||||||
| Thangjing Hill | ||||||||||||
A cross has been installed atop the Thangjing hill by the Kuki community near Manipur’s Moirang town which was seen as destabilizing in the already violence-hit Manipur.
|
||||||||||||
| Pong Dam | ||||||||||||
Over 83000 migratory birds descend upon Pong wetland, count lower than last winter.
|
||||||||||||
| Pangolakha Wildlife Sanctuary | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| China’s Fifth Research Station | ||||||||||||
Helipad construction starts in China’s new Antarctic research station.
|
||||||||||||
| Red Sea Naval Mission | ||||||||||||
EU aiming to launch Red Sea naval mission by mid-Feb.
|
||||||||||||
| First Woman Chief Justice of Uttarakhand | ||||||||||||
First woman Chief Justice of Uttarakhand appointed.
|
||||||||||||





