Current Affairs – 3 May 2024
Diplomatic Passport
Recently, suspect in a sex abuse case, one of the Member of Parliament (MP) fled to Germany on a diplomatic passport.

About Diplomatic Passport:
High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS)
Russia’s government recently published new footage claiming to show the targeting of two Ukrainian High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS).
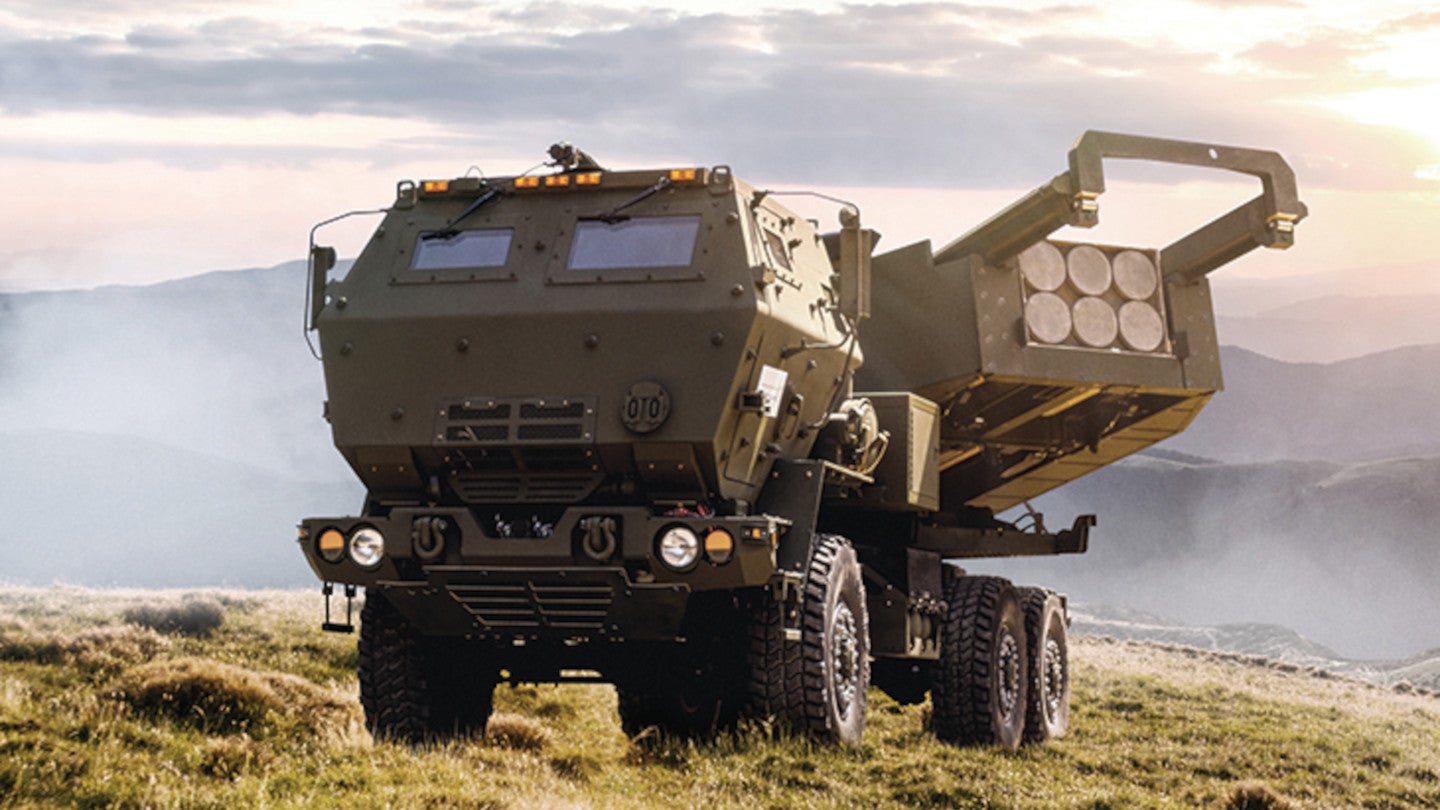

- IMARS is a light, multiple rocket launcher designed to engage and defeat various targets, including artillery, air defense concentrations, light armor, and personnel carriers.
- Manufactured by Lockheed Martin Corporation, it is intended for mobility and versatility in combat situations.
- The launcher is mounted on a 5-ton Family of Medium Tactical Vehicles (FMTV), making it air-transportable.
- It can carry either a launcher pod of six rockets or one MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) with a range of 300 km (186 miles).
- HIMARS requires less than 20 seconds to prepare for firing, and a full load of six rockets can be fired within 45 seconds.
- After firing, the system can quickly move away from the area to evade detection by enemy forces.
- The Increased Crew Protection cabin is equipped to shield the three-man operating crew from plume gases, rocket launch debris, and small arms fire, enhancing crew safety.
Five Eyes Intelligence-sharing Network
Recently, 4 countries on 3 continents, which are part of the Five Eyes intelligence-sharing network has been, accused India for running espionage operations.

Commission on Population and Development
The Permanent Mission of India to the United Nations and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, in collaboration with the United Nations Population Fund is organizing event titled “Localizing the SDGs: Women in Local Governance in India Lead the Way” during the 57th Session of the Commission on Population and Development (CPD57).
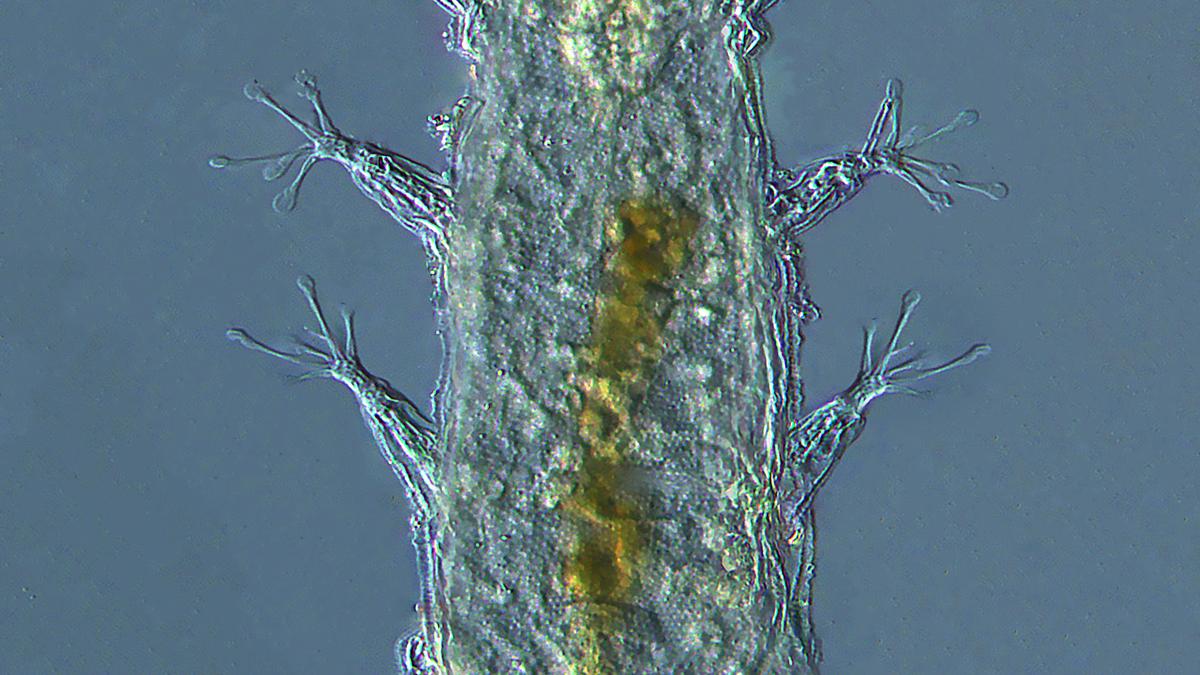
Batillipes chandrayaani
A new species of marine tardigrade discovered from the southeast coast of Tamil Nadu has been named Batillipes chandrayaani after the Chandrayaan-3.
Solomon Islands Elects Pro-China Leader Jeremiah Manele as New Prime Minister

Micron’s Venture in India: Rollout of First India-Made Chips
- Micron India’s Sanand unit gears up to unveil its inaugural batch of domestically manufactured semiconductor chips in 2025, with a focus on global exportation. Anand Ramamoorthy, the managing director, underscores the burgeoning global demand, strategic partnerships, and the diverse applications spanning various sectors, notably emphasizing agility and the scarcity of talent in niche domains such as cybersecurity.
Export Focus and Market Dynamics
- Ramamoorthy highlights the predominant emphasis on exports from the Sanand unit, aligning with the substantial global demand for semiconductors. While acknowledging the burgeoning domestic demand, he asserts that India’s market size for semiconductor chips remains modest compared to international demand.
Utilization and Application
- The chips packaged at the Sanand unit are slated for utilization across diverse sectors including data centers, smartphones, notebooks, IoT devices, and automotive applications.
Implications of Domestic Foundries
- The trajectory of India’s semiconductor demand is expected to be influenced by initiatives like the Tata Group’s collaboration with Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation, shaping the demand-supply dynamics in the semiconductor ecosystem.
Agility in Response to Market Dynamics
- Ramamoorthy underscores the necessity for agility and adaptability in responding to the evolving demands of various sectors, acknowledging the fluidity of product allocations driven by factors such as inventory, turnaround time, pricing, and customer requirements.
Investment and Employment Outlook
- Micron’s significant investment in the Sanand unit, totaling $2.75 billion, underscores its commitment to bolstering India’s semiconductor landscape. The expansion plans also aim to ramp up employment, with a target of increasing the India headcount to 5,000 and creating around 15,000 indirect jobs.
Talent Development and Global Training
- Highlighting the global talent shortage, particularly in niche sectors like cybersecurity and semiconductors, Ramamoorthy emphasizes Micron’s focus on continuous training and development, including global rotations and a significant proportion of fresh college graduates in its R&D workforce.





