Current Affairs – 14th Feb 2024
Current Affairs – 14th Feb 2024
Market Capitalisation
Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) became the first Indian company to surpass Rs 20 lakh crore in market capitalisation.

About Market Capitalisation:
- Market Capitalization, or Market Cap, is a term used to represent the market value of a company based on its current share price and the total number of its outstanding shares.
- It can be calculated by multiplying the number of outstanding shares of a company by the current price of its shares.
- It represents the market’s perception of a company’s worth and indicates its size and significance in the financial markets.
- On the basis of market cap, companies may be classified as large-cap, mid-cap, or small-cap companies.
- Large-cap companies are usually stable, reputable, and well-established businesses that have a significant market share. They have market caps of INR 20,000 crore or more.
- Mid-cap companies have a market cap ranging from INR 5,000 crore to INR 20,000 crore.
- Small-cap companies operate at a smaller scale than large-cap and mid-cap companies. Consequently, their market cap is also lower (less than INR 5,000 crore).
- Why is market capitalization important?
- It allows potential investors to understand the true value of companies and the size of one company in relation to another.
- It helps investors predict the future performance of the stock of a company because it reflects what the market is willing to pay for the stock.
What is Free float market capitalisation?
- While calculating the total market capitalization of a company, all the shares, including the ones publicly traded as well as those held by promoters, government, or other private parties, are multiplied by the stock price.
- But in the free-float market capitalisation, we exclude shares held by private parties like promoters, trusts, or the government.
- We only consider shares held and traded by the public and multiply them by the share price to arrive at the free-float market capitalisation of a company.
Swachhata Green Leaf Rating
Swachhata Green Leaf Rating system for the hospitality sector is yet to take off as there has been no response from States despite the Union Tourism Ministry sending three communiques so far.
/bnn/media/media_files/b4d93356a374de7b5db34e6f58eb38bde71e2eeea7ad6d36f481df3bba404a48.jpg)
About Swachhata Green Leaf Rating:
- A government-initiated rating system for the hospitality sector which aims to ensure world-class hygiene and sanitation in hotels, resorts and homestays has become a non-starter with no State opting for it as of now.
- Objective: The objective is to prevent pollution in water bodies and keep the environment clean.
- Target group: The target groups are hotels, lodges, homestays, ‘Dharamshalas’ and camps which have portable toilets. The rating will be based on compliance with the safe sanitation practices outlined in the guidelines.
- The ranking scheme was launched in November 2023 by the Union Tourism Ministry in collaboration with the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- As part of the initiative, the State teams of Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin (rural) and the tourism department will organise workshops on the concept, process and desired outcomes for the stakeholders.
- Implementation: A three-tiered committee system has been proposed for implementation, beginning with a Verification Sub-Committee formed by the Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM) for the on-ground verification, followed by a District Committee, which the District Collector will chair and then a State-level committee, headed by the Chief Secretary of the State.
Cuscuta dodder
An invasive weed Cuscuta dodder is slowly choking the Chengalpet forests and Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary, threatening the local vegetation, ecology and habitat of migratory birds.

About Cuscuta Dodder:
- It is native to North America.
- It is a parasitic vine without roots, has already infested acres of trees in the reserve forests and has begun to spread inside India’s oldest bird sanctuary.
- It is the holoparasitic plant that builds a canopy on the host plant and casts thousands of tendrils to form a dense spectacle before it strangles and eventually kills it.
- As per a technical paper published by the National Research Centre for Weed Science, in India, Cuscuta poses a serious problem in oilseeds, pulses and fodder crops in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Orissa, West Bengal and parts of Madhya Pradesh under rain fed as well as irrigated conditions.
- Legislation in 25 countries has listed the dodder as a ‘declared noxious weed’ with seeds and plant material denied entrance. In the United States, it is the only weed seed whose movement is prohibited in every state.
- The seeds of Cuscuta are spheroid and have a hard coat, which aids them to survive up to 50 years in dry storage and at least 10 years in the field.
- Unlike root parasites, Cuscuta seeds do not require a specific stimulant to induce germination.
World Government Summit (WGS) 2024
The Indian Prime Minister will attend the World Government Summit 2024 as a guest of honour in the UAE.

About World Government Summit (WGS):
- It is an annual global gathering that brings together world leaders, policymakers, experts, and thought leaders from various fields to discuss and address pressing global issues.
- It was established in 2013 under the leadership of the Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE.
- It is annually held in Dubai, UAE.
- The Summit, in its various activities, explores the agenda of the next generation of governments, focusing on harnessing innovation and technology to solve universal challenges facing humanity.
- Since its inception, the Summit has championed the mission of shaping future governments and creating a better future for humanity.
- World Government Summit (WGS) 2024:
- Theme: “Shaping Future Governments”
- It will focus on six main themes:
- Government Acceleration and Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence and the Next Frontiers
- Reimagining Development and Future Economies
- Future Societies and Education
- Sustainability and The New Global Shifts
- Urbanisation and Global Health Priorities
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
Prime Minister of India launched PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana to provide free electricity to its beneficiaries.

About PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana:
- In this scheme, the central government will provide 300 units of free electricity per month to its beneficiaries by investing worth ₹75,000 crores.
- The free electricity scheme was earlier announced by the Finance Minister in an interim budget speech.
- Target: It aims to light up 1 crore households.
- Under the scheme, Urban Local Bodies and Panchayats shall be incentivised to promote rooftop solar systems in their jurisdictions.
- The Central Government will guarantee no financial burden on the people by providing significant subsidies directly to their bank accounts and offering highly concessional bank loans.
- Expected benefits:
- Savings of up to fifteen to eighteen thousand rupees annually for households from free solar electricity and selling the surplus to the distribution companies;
- Charging of electric vehicles;
- Entrepreneurship opportunities for a large number of vendors for supply and installation;
- Employment opportunities for the youth with technical skills in manufacturing, installation and maintenance.
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species
The Fourteenth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (COP14) will be hosted by the Government of Uzbekistan, in Samarkand from 12-17 February 2024.

About the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species:
- It also known as the Bonn Convention, is an environmental treaty under the aegis of the United Nations Environment Programme.
- It provides a global platform for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats.
- It was signed in Bonn, Germany, on 23 June 1979.
- It is the only global and UN-based intergovernmental organisation established exclusively for the conservation and management of terrestrial, aquatic and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- The parties to the convention acknowledge the importance of conserving migratory species, and the need to pay special attention to species whose conservation status is unfavourable.
- Activities by CMS Parties may range from legally binding treaties(called Agreements) to less formal instruments, such as Memoranda of Understanding.
- The Conference of Parties (COP) is the decision-making organ of this convention.
- It has two Appendices.
- Appendix I lists endangered migratory species and includes prohibitions regarding the take of these species.
- Appendix II lists species that have an ‘unfavourable conservation status’ (as per the conditions set out in the Convention) and encourages range states to draft range-wide agreements for the conservation and management of these species.
e-Jagriti Portal
The Consumer Affairs Secretary recently asserted that integration of artificial intelligence in the ‘e-Jagriti’ portal will help reduce the number of pending cases in consumer courts.

About e-Jagriti Portal:
- It is an initiative of the Department of Consumer Affairs, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.
- It is a portal for consumer commissions.
- This portal has been designed to further improve the customer experience.
- It provides a simple, fast, and cost-effective consumer dispute redressal software solution at all levels.
- It is envisaged to integrate consumer grievance platforms, namely, the Online Case Monitoring System (OCMS), E-Daakhil, the National Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission (NCDRC) Case Monitoring System, CONFONET website, mediation application, on a single platform.
- The e-Jagriti platform has case filing, online fee payment, case monitoring modules for seamless disposal of cases by all the Commissions, has Smart search facility on archived consumer complaints/cases/judgements using AI technology for metadata and keyword creation, and Voice-to-text conversion of judgements, case history and other details using AI / ML technology.
- The portal will integrate a Virtual court facility for a convenient and accessible resolution of consumer complaints, reducing the time of disposal, multiple hearings, and physical court appearances, bringing effective and fast decisions & disposals in all Consumer Commissions.
Key Facts about the National Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission (NCDRC):
- It is a quasi-judicial commission in India which was set up in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- Its head office is in New Delhi.
- The Commission is headed by a sitting or retired Judge of the Supreme Court of India or a sitting or retired Chief Justice of the High Court.
- Section 21 of the Consumer Protection Act, 1986, posits that the National Commission shall have jurisdiction to entertain a complaint valued at more than two crores and also have appellate and revisional jurisdiction from the orders of State Commissions or the District, as the case may be.
- Any person aggrieved by an order of NCDRC may prefer an appeal against such an order to the Supreme Court of India within 30 days.
Olive Ridley Turtles
The Andhra Pradesh government recently imposed a month-long ban on fishing in the 5-km radius of Hope Island to prevent the death of Olive Ridley turtles off the Kakinada coast.
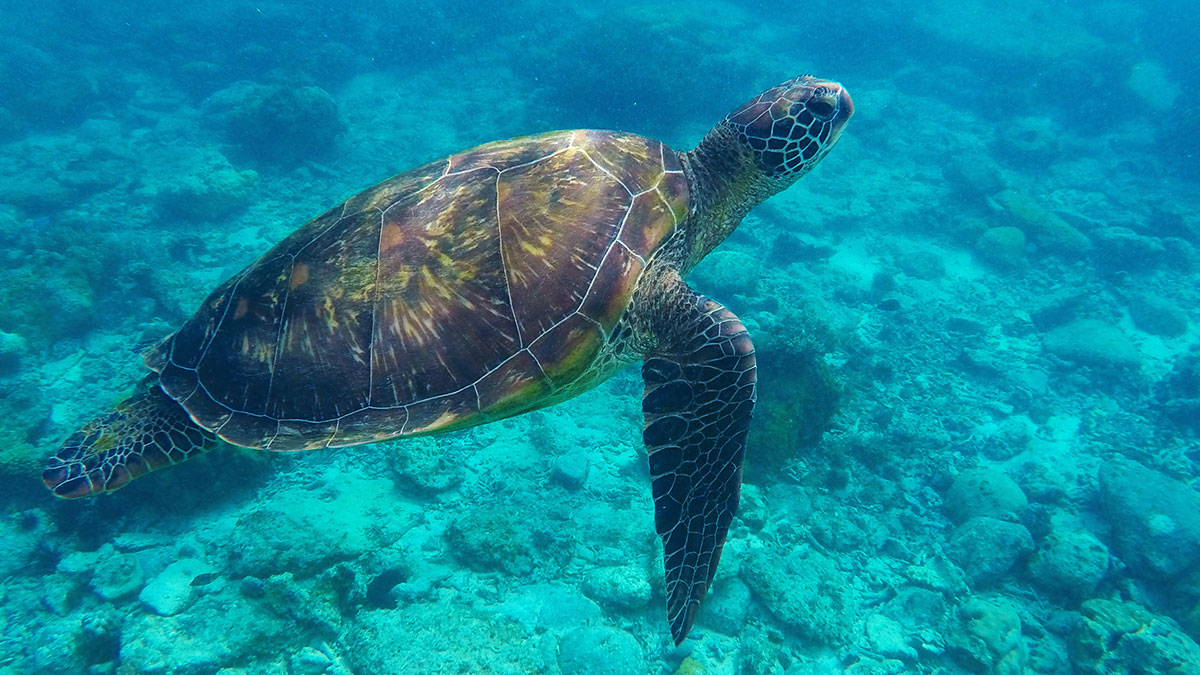

About Olive Ridley Turtles:
- They are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in the world.
- It gets its name from the olive-green colouration of its carapace (shell).
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- They are best known for their unique mass nesting, called Arribada, where thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.
- Distribution:
- They are mainly found in the warm waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans.
- Odisha’s Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary is known as the world’s largest rookery (a colony of breeding animals) of sea turtles.
- Features:
- An adult typically measures between 62 and 70 cm in length and weighs about 35-45 kg.
- They have one to two visible claws on each of their paddle-like flippers.
- They are omnivorous, meaning they feed on both plants and animals.
- They are solitary, preferring the open ocean.
- These turtles spend their entire lives in the ocean and migrate thousands of kilometres between feeding and mating grounds in the course of a year.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- CITES: Appendix I
Key Facts about Hope Island:
- It is a tadpole-shaped island, located off the coast of Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh, in the Bay of Bengal.
- Hope Island is so named for providing a natural haven to sailors against the forces of wind and tide against the weary traveller.
- This island is young, as it was formed in the late 18th century, by the waters of the Koringa River, which is a distributary of the River Godavari.
- The area between Kakinada coast and Hope Island is known as Kakinada Bay.
- It acts as a natural barrier from storm surges and is a natural breakwater for the Kakinada coast.
Bubonic Plague
Officials in the US state of Oregon recently said they are dealing with a rare human case of bubonic plague that was likely transmitted by a pet cat.

About the Bubonic Plague:
- Plague is an infectious disease caused by a specific type of bacterium called Yersinia pestis, a zoonotic bacterium usually found in small mammals and their fleas.
- pestis can affect humans and animals and is spread mainly by fleas.
- Bubonic plague is one type of plague. It gets its name from the swollen lymph nodes (buboes) caused by the disease.
- Called the Black Death, it killed millions of Europeans during the Middle Ages.
- The other types of plague are:
- Septicemic plague, which happens when the infection goes all through the body.
- Pneumonic plague, which happens when the lungs are infected.
- Plague can be a very severe disease in people, with a case-fatality ratio of 30% to 60% for the bubonic type, and is always fatal for the pneumonic kind when left untreated.
- Symptoms: Bubonic plague symptoms include
- Sudden high fever and chills.
- Pain in the areas of the abdomen, arms, and legs.
- Headaches.
- Large and swollen lumps in the lymph nodes(buboes) that develop and leak pus.
- Transmission:
- pestis is spread mostly by fleas on rodents and other animals.
- It is transmitted between animals and humans by the bite of infected fleas, direct contact with infected tissues, and inhalation of infected respiratory droplets.
- The incubation period of bubonic plague is usually 2 to 8 days.
- Treatment:
- It can be treated and cured with antibiotics.
- Antibiotics that treat bubonic plague include Ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, Gentamicin and Doxycycline.
- It can be fatal if it’s not treated.
J&K Bills on Local Bodies and SC/ST lists
Recently, the Rajya Sabha has passed 3 bills related to reservation for Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and modification of the lists of SC and ST in Jammu & Kashmir.

- Since Lok Sabha had previously passed them, all 3 bills are deemed to be passed by the Parliament to become an Act.
- J&K Local Bodies Laws (Amendment) Bill 2024 – It seeks to amend certain provisions of the
- Jammu and Kashmir Panchayati Raj Act, 1989
- Jammu and Kashmir Municipal Act, 2000
- Jammu and Kashmir Municipal Corporation Act, 2000
- It seeks to provide reservation to the OBC in the Panchayats and the Municipalities and will empower State Election Commission of J&K to conduct local body polls.
- The removal of state election commissioner shall be similar to those of a judge of a high court as enshrined in the Constitution of India.
J&K Bills on SC/ST List
- The Constitution (J&K) SCs Order (Amendment) Bill – It seeks to amend the Constitution (J&K) SCs Order of 1956, which lists the castes deemed to be SC in J&K and Ladakh.
- It adds Valmiki community as a synonym of Chura, Balmiki, Bhangi, and Mehtar communities.
- The Constitution (J&K) STs Order (Amendment) Bill – It seeks to amend the Constitution (J&K) STs Order, 1989.
- It proposes the creation of separate lists of STs for the UTs of J&K and Ladakh.
- It also adds Gadda Brahmin, Koli, Paddari Tribe, and Pahari Ethnic Group communities in the list of STs in Jammu & Kashmir.
NATO & its Funding
Former US President Donald Trump has once again attacked NATO with respect to member nation’s lack of funding to the organisation.

- NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, was conceived to provide collective security against the erstwhile USSR.
- Launched in – 1949, with the passage of Washington Treaty.
- Headquarters – In Brussels, Belgium since 1967.
- Aim – To guarantee the freedom and security of its members through political and military means.
- Political – To solve problems, build trust and, in the long run, prevent conflict in defence & security-related issues.
- Military – For peaceful resolution of disputes, if failed then using military power for crisis-management operations.
- Membership – 31 (most of European nations, US and Canada).
- It is open to any other European state that accepts this Treaty and accepts to contribute to the security of the North Atlantic area.
The newest member is Finland in 2023. Sweden has applied but is waiting for Hungary to ratify its application as the final major step before membership.
- Decision making – It is by consensus.
- Collective defence – An attack on 1 member is considered an attack on all of them as per Article 5 of the treaty.
NATO derives its authority from Article 51 of the United Nations Charter, which reaffirms the inherent right of independent states to individual or collective defence.
- Limitation – Article 5 failed to commit automatic military response to help an ally under attack.
- It depends on clear statements from political leaders that it will be backed up by action.
NATO’s Funding Mechanism
- It has some common funds, to which all members contribute.
- But it majorly depends on members’ own national defence spending to maintain forces and buy arms that can also be used by NATO.
- Funding commitment – To spend at least 2% of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP) every year on defence.
- Issues – Most of the members did not meet their funding commitments in 2023.
BAPS Swaminarayan Temple
Prime Minister of India to inaugurate the BAPS Swaminarayan temple in Abu Dhabi in UAE, the 1st Hindu temple in the Gulf nation.
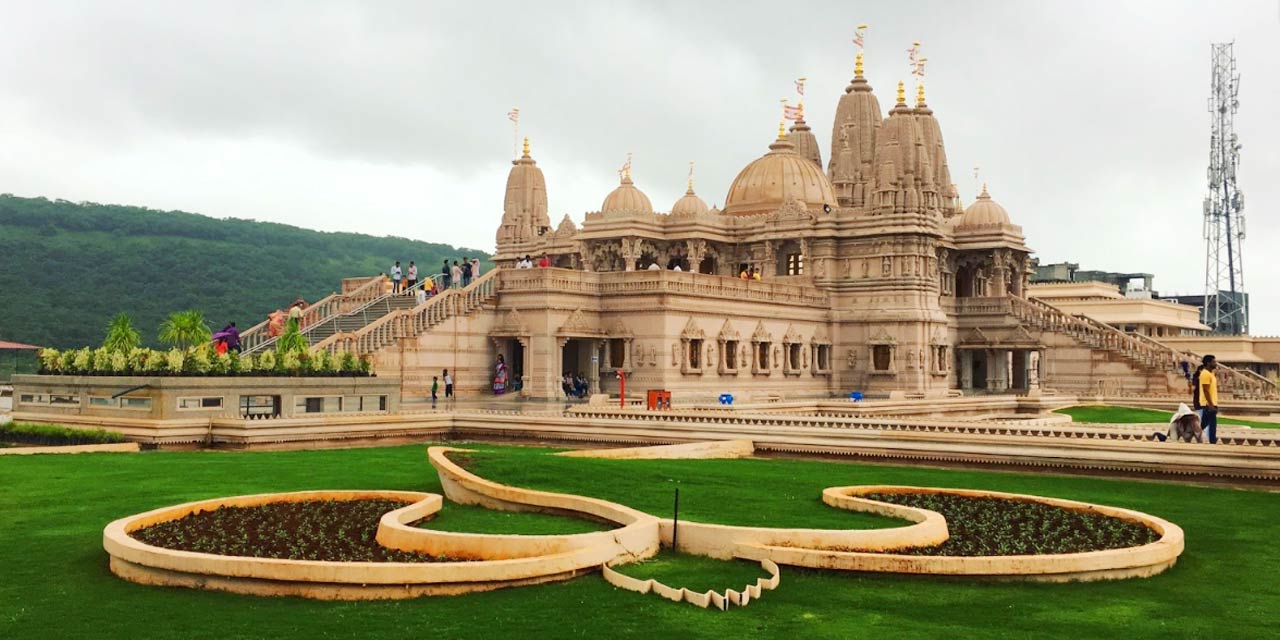

- A traditional 108 feet high Hindu temple.
- Built by – BAPS.
Bochasanwasi Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha (BAPS) is a denomination of the Swaminarayan Sampradaya (a Vaishnav sect of Hinduism). It has a network of around 1,550 temples across the world.
- Style – Nagara style.
- Construction material – Its external facade uses pink sandstone from Rajasthan, while the interior uses Italian marbles.
- 2 central domes – Dome of Harmony and Dome of Peace, emphasising human coexistence.
- A Wall of Harmony – 3D-printed wall, features a video showcasing key milestones of the temple’s construction.
- 7 shikhars (spires) – It represents of the 7 Emirates of the UAE.
- It also includes an assembly hall, a community centre, exhibitions, classrooms, and a majlis venue.
- Inter-faith harmony – It is open to everyone.
- A Muslim king donated land and it has participation of personalities from Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Parsi and from Jainism.
- Temple’s front panel depicts universal values, stories of harmony from different cultures, Hindu spiritual leaders and avatars.
The Indian diaspora is almost 3.3-million strong in UAE, a huge percentage of the country’s population. Of these, some 150 to 200 families are BAPS Swaminarayan devotees.
Key architectural features of BAPS Temple in UAE
- Conception scene – A stone carving of the scene of Pramukh Swami Maharaj envisioning the temple in Abu Dhabi in 1997.
- Pillars – Circular and hexagonal, a special pillar named Pillar of pillars which has around 1,400 small pillars carved into it.
- Deities – It has deities from all 4 corners of India like Lord Ram, Shiv, Jagannath, Tirupati Balaji and Lord Ayappa.
- A ‘holy river’ – It surround the temple, has waters of River Ganga and Yamuna with Varanasi-like ghat, where the ‘Ganga’ passes.
- The river Saraswati has been depicted in the form of white light.
- Depiction of civilisations – It depicts stories of Indian, Mayan, Aztec, Egyptian, Arabic, European, Chinese and African civilisation.
- Other features – Its surrounding buildings are modern and monolithic, with their colour resembling sand dunes.
- It has 96 bells and gaumukhs around the path leading to the temple, a tribute to Pramukh Swami Maharaj’s 96 years of life.
- No ferrous material is used, thereby prevent corrosion.
- Nano tiles allows devotees to walk even in the hot weather.
The BAPS temple of UAE was judged the Best Mechanical Project of the Year 2019 at the MEP Middle East Awards, and the Best Interior Design Concept of the Year 2020.
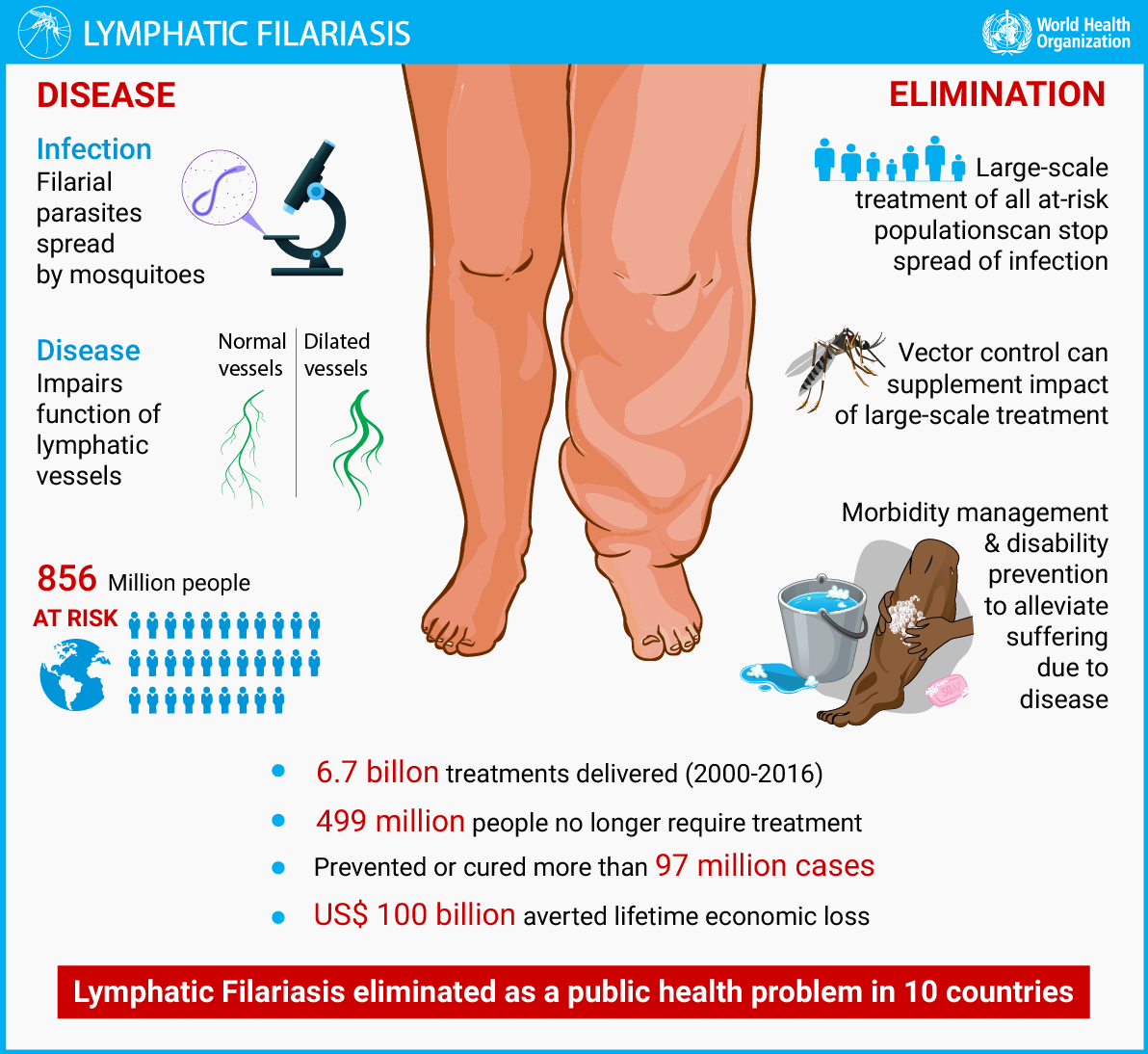
Lymphatic Filariasis
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare launched the first phase of the Bi-annual Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign for Lymphatic filariasis (LF) elimination.

Note:
- The campaign aims to check disease transmission by providing free preventive medications to the residents in areas affected by the disease. The campaign will cover 92 districts across 11 states.
What is Lymphatic Filariasis?
- About:
- Lymphatic filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis, is a neglected tropical disease(NTD) caused by infection with filarial parasites transmitted through mosquitoes.
- Prevalence:
- In 2021, approximately 882.5 million people in 44 countries lived in areas requiring preventive chemotherapy to halt the spread of infection.
- LF is a serious public health problem in India. Currently, there are 345 lymphatic filariasis endemic districts in 20 states and union territories of the country.
- 75% of MDA districts are from 5 states Bihar, Jharkhand, UP, Odisha and Telangana.
- Lymphatic filariasis is more prevalent among the urban poor and affects all segments of the rural population.
- Impact:
- The infection starts in childhood and accumulates through adulthood, resulting in irreversible chronic disease conditions.
- The disease inflicts stigma, mental suffering, social deprivation and economic loss and is a major cause of poverty in the affected communities.
- The infection starts in childhood and accumulates through adulthood, resulting in irreversible chronic disease conditions.
- Cause and Transmission:
- Parasitic Infection:
- Lymphatic filariasis is caused by infection with parasites classified as nematodes (roundworms) of the family Filariodidea. There are 3 types of these thread-like filarial worms:
- Wuchereria bancrofti (responsible for 90% of the cases)
- Brugia malayi (causes most of the remainder of the cases)
- Brugia timori (which also causes the disease)
- Lymphatic filariasis is caused by infection with parasites classified as nematodes (roundworms) of the family Filariodidea. There are 3 types of these thread-like filarial worms:
- Transmission Cycle:
- Adult worms reside in the lymphatic vessels, producing microfilariae that circulate in the blood.
- Mosquitoes become infected by biting an infected host and transmit the larvae to humans, perpetuating the transmission cycle.
- Parasitic Infection:
- Symptoms and Complications:
- Asymptomatic and Chronic Conditions:
- The majority of infections are asymptomatic, but chronic conditions can lead to lymphoedema (swelling of the limbs), elephantiasis (thickening of the skin and tissues), and hydrocele (swelling of the scrotum), causing physical disfigurement and psychological distress.
- Acute Episodes:
- Acute inflammatory episodes often accompany chronic conditions, leading to debilitating symptoms and loss of productivity among affected individuals.
- Asymptomatic and Chronic Conditions:
- Treatment and Prevention:
- Preventive Chemotherapy:
- MDA with annual doses of medicines to the at-risk population is the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended strategy for eliminating lymphatic filariasis.
- MDA Regimens:
- Different drug regimens are recommended based on co-endemicity with other filarial diseases, aiming to reduce microfilariae density and interrupt transmission.
- Morbidity Management:
- Surgery, hygiene measures, and clinical care are essential for managing chronic manifestations and preventing disease progression.
- Vector Control:
- Supplemental strategies such as mosquito control help reduce transmission and complement preventive chemotherapy efforts.
- Preventive Chemotherapy:
- WHO Response and Goals:
- Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF):
- Launched in 2000, GPELF aims to eliminate lymphatic filariasis as a public health problem through preventive chemotherapy and morbidity management.
- In 2020, GPELF set the following goals for the new NTD Road Map (2021–2030):
- Validation: 80% of endemic countries (58) to validate elimination, maintaining low infection rates post-MDA.
- Surveillance: All endemic countries (72) to implement surveillance to prevent disease resurgence.
- MDA Reduction: Targeting zero population needing mass drug administration.
- Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF):
- India’s Initiatives:
- Mission Mode India Multi-drug administration (MDA) Campaign twice a year synchronized with National Deworming Day (10th Feb and 10th August)
- India is committed to eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis by 2027, three years before the global target.