Current Affairs – 12 March 2024
Software Technology Parks of India
Recently, the Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) launched its Center of Entrepreneurship (CoE) – FinGlobe.

About Software Technology Parks of India:
- It is a premier autonomous Science and Technology organization under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is engaged in promoting IT/ITES Industry, innovation, R&D, start-ups, product/IP creation in the field of emerging technologies like IoT, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Computer Vision, Robotics and Robotics Process Automation (RPA) etc.
- Objectives
- To promote the development and export of software and software services including Information Technology (I.T.) Enabled Services / Bio-IT.
- To provide statutory and other promotional services to the exporters by implementing Software Technology Park/ Electronics and Hardware Technology Park Schemes and other such schemes this may be formulated and entrusted by the Government from time to time.
- To provide data communication services including value added services to IT / IT Enabled Services related industries.
- To promote micro, small and medium entrepreneurs by creating conducive environment for entrepreneurship in the field of IT / IT Enabled Services.
- Significance: These centres have been playing a pivotal role in boosting IT/ITeS/ESDM exports from the respective region, generating employment, and fostering startups to develop software products.
Mission Divyastra
Recently, the Prime Minister of India announced successful maiden flight test of Agni-5 missile with MIRV technology, code-named Mission Divyastra, boosting India’s defence capability.

About Mission Divyastra:
- The maiden flight test of the locally developed Agni-5 missile with multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicle (MIRV) technology and code named as Mission Divyastra.
- Key features of Agni-5 missile
- It uses a three-stage solid fuelled engine and has a range of more than 5,000km.
- Agni series has medium to Intercontinental versions of Agni missile systems 1 to 5 with a varying ranges — starting from 700 km for Agni-1 to 5000 km and above for Agni-5.
- In June 2021, DRDO successfully tested Agni P, a canisterised missile with a range capability between 1,000 and 2,000 km.
- This means that the missile can be launched from road and rail platforms, making it easier for it to be deployed and launched at a quicker pace.
What is MIRV technology?
- It can target multiple targets that can be hundreds of kilometers apart with a single missile.
- This Agni, capable of carrying nuclear warheads, has a range of more than 5,000 km, making it a long-range missile. These missiles can be launched from land or from sea from a submarine.
- In contrast to a traditional missile, which carries one warhead, MIRVs can carry multiple warheads. Warheads on MIRVed missiles can be released from the missile at different speeds and in different directions.”
- This has propelled India into an exclusive league of countries that have the capability to deploy MIRV missile systems, including the US, the UK, France, Russia and China.
Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019
Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) recently notified the Citizenship Amendment Rules, 2024.

About Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- The Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) amends the Citizenship Act of 1955 to provide a path to Indian citizenship for Hindus, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, Jains, and Parsis who migrated from neighbouring Muslim-majority countries such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan, before December 31, 2014.
- Under the CAA, migrants who entered India till December 31, 2014, and had suffered “religious persecution or fear or religious persecution” in their country of their origin would be made eligible for accelerated citizenship.
- It relaxed the residence requirement for naturalisation of these migrants from twelve years to just six.
- The law exempts the tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Tripura as included in the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution, including the tribal areas of Karbi Anglong in Assam, Garo Hills in Meghalaya, Chakma district in Mizoram, and Tribal areas district in Tripura.
- It also includes a provision for the cancellation of Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration if the OCI cardholder violates any provision of the Citizenship Act or any other applicable law.
INS Tushil
INS Tushil, India’s latest naval asset, initiated its sea trials from Russia’s Baltiysk naval base recently.

About INS Tushil:
- It is the first Krivak-III frigate to be acquired under Project 11356M.
- Project 11356M:
- India in October, 2016 signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) with Russia to purchase/construct four additional Admiral Grigorovich-class (Project 11356M) frigates through a partnership between Russian and Indian shipyards.
- Russia will supply two of the frigates (INS Tushil and INS Tamala), while the other two will be constructed in India.
- The Talwar-class frigates, or Project 11356, are a class of stealth-guided missile frigates.
- The construction of the ships is based on the Indian Navy’s specific requirements to meet the entire spectrum of naval warfare in all three dimensions of air, surface, and sub-surface.
- Features:
- These ships feature “stealth technology” in terms of low radar and underwater noise signatures.
- These ships are being equipped with major Indian-supplied equipment such as surface-to-surface missiles, sonar systems, surface surveillance radar, communication suites, and anti-submarine warfare systems, along with Russian surface-to-air missiles and gun mounts.
- The frigates are designed to fight submarines and warships in brown and blue waters and repel air attacks both independently and within formations.
- The displacement is 3620 tons, the length is 124.8 meters. The full speed is 30 knots, and the cruising range is 4850 miles.
Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme
The Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers has announced the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme.
About Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme:
- The objective is to offer “subsidies based on quality” reimbursement, aiding pharmaceutical companies in achieving revised Schedule M and WHO-GMP certifications.
- The revised guideline aims to support the pharmaceutical industry’s up-gradation to the Revised Schedule-M & WHO-GMP standards, enhancing the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products manufactured in our country.
- Key Features of the Revised Scheme:
- Broadened Eligibility Criteria: Reflecting a more inclusive approach, eligibility for the PTUAS has been expanded beyond Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than 500 crores that requires technology and quality upgradation. Preference remains for MSMEs, supporting smaller players in achieving high-quality manufacturing standards.
- Flexible Financing Options: The scheme introduces more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approach.
- Comprehensive Support for Compliance with New Standards: In alignment with revised Schedule-M and WHO- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, the scheme now supports a broader range of technological upgrades. Eligible activities include improvements such as HVAC systems, water and steam utilities, testing laboratories etc.
- State Government Scheme Integration: The revised scheme allows integration with state government schemes, enabling units to benefit from additional top-up assistance. This collaborative approach aims to maximize support for the pharmaceutical industry in their technology upgradation efforts.
- The new benefit limit is based on turnover of the company. Units with less than Rs 5 crore turnover will get an incentive of 20 percent of investment under eligible activities.
- The units with turnover ranging from Rs 50 crore to less than Rs 250 crore will get an incentive of 15 percent of investment, while for those with turnover ranging from Rs 250 crore to less than Rs 500 crore, it will be 10 percent of investment under eligible expenses.
What is Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme?
- PTUAS has been incorporated as a sub-scheme under the Scheme – Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI), which was launched in July 2022.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
The Government of India recently initiated a scheme through the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) for the upgradation and strengthening of the laboratory network in the country.

About Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS):
- BIS is the National Standard Body of India established under the BIS Act 2016 for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking, and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto. It is the successor of the Indian Standards Institution (ISI), which was created in 1947.
- BIS is functioning under the administrative control of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- BIS has been providing traceability and tangibility benefits to the national economy in a number of ways: providing safe, reliable quality goods; minimizing health hazards to consumers; promoting exports and imports substitute; control over proliferation of varieties through standardization, certification, and testing.
- It operates product certification schemes through which it grants licenses to manufacturers covering practically every industrial discipline, from agriculture and textiles to electronics.
- Certification by the BIS is mandatory for certain classes of products—such as milk powder, X-ray equipment, and gas cylinders—that directly affect public health and safety. In other cases, voluntary, or optional certification or self-certification by the manufacturer may be permitted.
- The BIS employs a large staff of engineers, scientists, and statisticians; testing is carried out in its own laboratories as well as in independent facilities that demonstrate compliance with laboratory guidelines established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Lachit Borphukan
Recently, the Prime Minister of India unveiled a 125-foot bronze statue of Ahom general Lachit Borphukan at his burial site in eastern Assam’s Jorhat district.

About Lachit Borphukan:
- He was a legendary army commander of the Ahom kingdom (1228-1826). He was known for his leadership in the 1671 ‘Battle of Saraighat’.
- He defeated the Mughal forces, led by Raja Ramsingh-I, in this battle, and thwarted a drawn-out attempt by them to take back Assam.
- He was chosen as one of the five Borphukans of the Ahom kingdom by king Charadhwaj Singha and given administrative, judicial, and military responsibilities.
- Borphukan preferred guerrilla tactics which provided an edge to his smaller, but fast moving and capable forces.
- He was buried at the ‘maidam’ — burial grounds for Ahom royals and nobles — at Hollongapar, after passing away a year after the battle at the age of 49 due to illness.
Key points about the AHOM Kingdom
- The Ahom kings ruled large parts of what is now known as Assam for nearly 600 years, from the early 13th century to the early 19th century.
- This was a prosperous, multi-ethnic kingdom which spread across the upper and lower reaches of the Brahmaputra valley, surviving on rice cultivation in its fertile lands.
- The Ahoms engaged in a series of conflicts with the Mughals from 1615-1682, starting from the reign of Jahangir till the reign of Aurangzeb.
Anthropocene Epoch
Scientists have voted against a proposal to declare a new geological epoch called the Anthropocene to reflect how profoundly human activity has altered the planet.

About Anthropocene Epoch:
- It is an unofficial unit of geologic time, used to describe the most recent period in Earth’s history when human activity started to have a significant impact on the planet’s climate and ecosystems.
- The word Anthropocene is derived from the Greek words anthropo, for “man,” and cene, for “new,” coined and made popular by biologist Eugene Stormer and chemist Paul Crutzen in 2000.
- There are numerous phenomena associated with this proposed epoch, such as global warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, mass-scale soil erosion, the advent of deadly heat waves, deterioration of the biosphere, and other detrimental changes in the environment.
- What is the Geological Time Scale?
- Earth’s history is divided into a hierarchical series of smaller chunks of time, referred to as the geologic time scale.
- These divisions, in descending length of time, are called eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
- These units are classified based on Earth’s rock layers, or strata, and the fossils found within them.
- From examining these fossils, scientists know that certain organisms are characteristic of certain parts of the geologic record. The study of this correlation is called stratigraphy.
- Current Epoch: Officially, the current epoch is called the Holocene, which began 11,700 years ago after the last major ice age.
- Debate:
- Scientists still debate whether the Anthropocene is different from the Holocene.
- The term Anthropocene has not been formally adopted by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS),the international organization that names and defines epochs.
- The primary question that the IUGS needs to answer before declaring the Anthropocene an epoch is if humans have changed the Earth system to the point that it is reflected in the rock strata.
Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT)
The Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) recently observed that the assessee was entitled to claim credit for Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) under the Vivad se Vishwas (VSV) Scheme.

About Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT):
- It is a provision in the Income Tax Act of India. It primarily applies to companies and is designed to ensure that companies that report substantial book profits but pay little to no income tax due to various exemptions and deductions are subject to a minimum level of taxation.
- The primary objective behind the MAT tax in India is to curb tax avoidance by companies that manipulate their financial statements to reduce their taxable income artificially. With the introduction of MAT, companies have to pay a fixed percentage of their profits as MAT.
- MAT is applicable to all companies, including foreign companies.
- However, it does not apply to companies that have been granted exemption under Section 10AA of the Income Tax Act, which pertains to Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
- All companies are required to pay corporate tax based on which is higher of the following:
- Normal Tax Liability: Tax computed as per the normal provisions of the Income-tax Law, i.e., by applying the relevant tax rate to the taxable income of the company.
- Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT):Tax computed at 15% (previously 18.5%) on book profit plus cess and surcharge.
- MAT is calculated on the “book profits” of a company, which is different from the taxable profits computed under the regular provisions of the Income Tax Act.
- What is MAT credit? When the amount of MAT for a company is greater than its normal tax liability, the difference between MAT and normal tax liability is called MAT Credit.
Key Facts about Vivad se Vishwas (VSV) Scheme:
- “Vivad se Vishwas Scheme” or “No Dispute but Trust Scheme” is a direct tax scheme introduced by the Government of India in 2020 for settling disputes between taxpayers and the income tax department. It aims to minimize tax-related litigation.
- Under this scheme, the interest and penalty associated with the disputed tax amount is completely waived off on the final settlement of the disputed tax amount.
- There was a time limit set for the payment of taxes under the scheme.
Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2023 Report
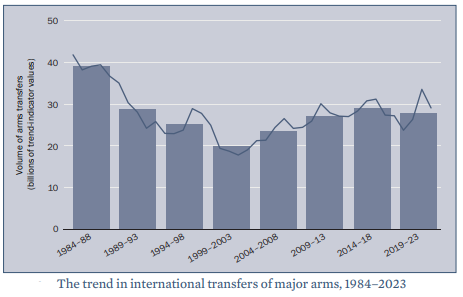
According to a new report ‘Trends in International Arms Transfer 2023, India continues to be the world’s top arms importer.

- Published by – Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
- Study period – 2019-2023
- Export regime – The 5 largest exporters were the United States, France, Russia, China and Germany.
- For the 1st time, France became the 2nd biggest arms exporter after the USA.
- The USA and Western Europe together accounted for 72% of all arms exports in 2019-2023.
- Imports – The 5 largest arms importers were India, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine and Pakistan.
- States in Asia and Oceania accounted for 37% of all arms imports, followed by states in the Middle East, Europe, the Americas and Africa.
- For the 1st time in 25 years, the US has become the largest supplier to Asia and Oceania.
- Pakistan is 5th largest arms importer in 2019-23 where China provides 82% of arms imports.
- India – Its arms imports increased by 4.7% between 2014–2018 and 2019–2023.
- Russia is India’s main-arms-supplier, accounting for 36 % of its arms imports.
The period between 2014 and 2018 was the 1st 5-year stretch in 50 years (since 1960-1964) when deliveries from Russia or the erstwhile Soviet Union (prior to 1991) made up less than half of India’s arms imports.
- India & France – India was the largest single recipient of French arms exports, accounting for nearly 30%.
- The Indian Air Force operates 36 Rafale fighter jets customised in accordance to its needs.
- Furthermore, India is in talks for 26 Rafale Marine jets to be procured for the Navy’s aircraft carrier INS Vikrant from France.
|
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute |
|
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2024 Campaign
Recently, the 5th edition of the ‘Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain’ campaign was launched.

- A transformative movement towards a water-secure and sustainable future.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan, launched by the Ministry of Jal Shakti in 2019 as a “Jan Andolan”, to initiate water conservation at the grass-root level through citizen participation across the country.
- Started in – 2021, as part of Jal Sanchay and has become an annual feature.
- Nodal agency – National Water Mission, Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation in collaboration with Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation.
- Aim – To nudge states and other stakeholders to create rain water harvesting structures suitable to the climatic conditions and sub-soil strata before the monsoon.
- Coverage – All the blocks of all districts (rural as well as urban areas) across the country.
- Focused interventions
- Water conservation and rainwater harvesting.
- Enumerating, geo-tagging & making inventory of all water bodies and preparing scientific plans for water conservation.
- Setting up of Jal Shakti Kendras in all districts
- Intensive afforestation
- Awareness generation.
- JSA: CTR 2024 – It will have a distinctive emphasis on
- De-silting and cleaning of water bodies.
- Revitalizing Abandoned/Defunct Borewells for groundwater recharge and Rejuvenation of Small Rivers.
- Geo-tagging of water bodies, coupled with meticulous mapping and regular updates in the State’s revenue records
- Intensified afforestation efforts in the catchment areas of water bodies.
- Snow harvesting in hilly areas like stupas in Ladakh.
- Implemented period – March to November, 2024, the pre-monsoon and monsoon period in the country.
- 2024 Theme – ‘Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti’, to recognise and appreciate the crucial role played by women in water management, conservation and sustainability.
- It will establish a powerful connection between the ‘Nari Shakti’ and the sustainable management of water resources i.e. Jal Shakti.
Approximately 24 lakh women have been trained for testing water samples using Field Testing Kit (FTK) to ensure quality of piped water supply.
Simdega District Hosts First-Ever Pusa Krishi Vigyan Mela
For the first time, the district of Simdega in Jharkhand is hosting the Pusa Krishi Vigyan Mela, a national-level agricultural science fair. The event, organized by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute, Pusa (New Delhi), is being held at the Albert Ekka Stadium from March 10th to 12th, marking a significant stride towards realizing the vision of a prosperous farmer community.

Promoting Modern Agricultural Techniques
- The mela aims to encourage the adoption of modern agricultural techniques and entrepreneurship among farmers. Union Agriculture Minister Arjun Munda emphasized the government’s focus on increasing farmers’ incomes through these practices.
Participation of Agricultural Experts
- Over 40 agricultural scientists from across India are participating in the event, sharing their insights on improved crop cultivation methods. The fair serves as a crucial platform for farmers to learn about cutting-edge agricultural practices that can significantly uplift their livelihoods.
Initiatives for Farmer Empowerment
- Selected farmers were awarded solar pump sets by the Welfare Department, highlighting efforts to modernize farming in Jharkhand.
- Agricultural universities, institutes, and science centers are showcasing new technologies aimed at promoting agricultural entrepreneurship and prosperity.
- Farmers have the opportunity to learn about advanced agriculture and horticulture techniques to boost productivity, with 1000 farmers receiving training daily.
Showcasing Agricultural Advancements
- The Pusa Agricultural Science Fair features 50 informative stalls, aimed at educating farmers on governmental schemes and agricultural advancements. The fair focuses on vital themes like value addition and crop diversification, designed to enhance agricultural entrepreneurship among farmers.
Cultural Significance
- In a traditional ceremony, dignitaries including Arjun Munda were welcomed, underlining the cultural significance of the event and its role in promoting sustainable agricultural growth in the region.
- The Pusa Krishi Vigyan Mela in Simdega marks a significant milestone in the district’s efforts to empower local farmers and promote agricultural prosperity. By bringing together agricultural experts, showcasing modern techniques, and providing training opportunities, the event aims to equip farmers with the knowledge and skills necessary to enhance their livelihoods and contribute to the broader national agenda of augmenting farmer incomes and ensuring agricultural sustainability.
Important takeaways for all Competitive Exam:
- Jharkhand Chief minister: Champai Soren;
- Jharkhand Capital: Ranchi;
- Jharkhand Founded: 15 November 2000;
- Jharkhand Bird: Koel;
- Jharkhand Flower: Palash.
|
Other Important Topics |
||||||||||
| Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme | ||||||||||
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers announces the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme recently.
|
||||||||||
| Dilli Gramodaya Abhiyan | ||||||||||
Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation inaugurated commencement of PNG facilities in under the ‘Dilli Gramodaya Abhiyan’ recently.
|
||||||||||
| National Speed Breeding Crop Facility | ||||||||||
Union Minister of Science & Technology inaugurated the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility in Punjab.
|
||||||||||
| KIRTI Programme | ||||||||||
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports to inaugurate Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme.
Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS)
Khelo India Scheme
|
||||||||||
| INSAT-3DS | ||||||||||
INSAT-3DS, has initiated Earth imaging operations capturing the first set of images recently.
|
||||||||||
| Vajra Sentinel System | ||||||||||
Big Bang Boom Solutions Private Limited (BBBS) secured an order from the IAF and Indian Army under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative.
|
||||||||||
| Democracy Report 2024 | ||||||||||
India was downgraded on multiple metrics to emerge as one of the worst autocratisers according to the Democracy Report 2024.
Findings
India was downgraded to the status of an electoral autocracy in 2018. |
||||||||||
| Pi (Personal intelligence) | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Miscophus Kaleshi | ||||||||||
Zoological Survey of India discovers new species of Digger Wasp.
|
||||||||||
| Selection rules for district judges | ||||||||||
|




