Current Affairs – 27 Feb 2024
Current Affairs – 27 Feb 2024
Know Your Customer (KYC)
The government of India has formed an expert committee headed by Finance Secretary T V Somanathan to make its recommendations to bring out uniform Know Your Customer (KYC) norms.

About the Know Your Customer:
- It is a comprehensive process that financial and non-financial institutions follow to verify the authenticity and identity of their customers.
- The KYC process is mandatory for every customer before investing in any instruments or starting a bank account.
- In India at present, separate KYCs are needed for different financial products such as opening a bank account, investing in mutual funds, buying a life cover or investing in retirement-savings funds.
- Multiple KYCs, regular updates and even the exact specifications often prove to be a deterrent for new investors.
- To eliminate the need to do repeated KYC for investing across financial assets, the central government launched the Central KYC Records Registry.
- What is the Central KYC Records Registry?
- It was launched by the central government of India in 2016.
- It has been limited only to the capital markets.
- In fact, while dealing in securities markets, once KYC is done through a Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) registered intermediary such as a broker, depository participant or mutual fund, customers do not have to undergo the same process again for fresh investments.
- The government authorised the Central Registry of Securitisation Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest of India (CERSAI) to perform the functions of the CKYCR.
- This centralised registry receives, stores, safeguards and retrieves the KYC records of a customer in a digitally secure electronic format.
- Customers have to submit their KYC details only once with any of the reporting entities of the Reserve Bank of India, Sebi, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India, Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority at the time of opening an account.
- Once the information is registered, customers will receive a 14-digit KYC Identification Number that can be used at any financial institution registered with CERSAI.
- Financial institutions can access the CKYCR database to retrieve the KYC records of customers while onboarding them.
- In case of any changes in the details of a customer, the reporting entity will initiate a centralised KYC (CKYC) update after taking the latest KYC record of the customer.
Aegis Graham Bell Awards
Recently, the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), the premier Telecom R&D centre of the Government of India, strikes a hat-trick by securing top position in three awards at 14th Annual Aegis Graham Bell Awards.

About Aegis Graham Bell Awards:
- It was initiated in 2010 by the Aegis School of Data Science.
- It is a tribute to the father of telephony and great innovator, Alexander Graham Bell.
- The Aegis School of Business, Data Science and Cyber Security has initiated this award to promote innovations and recognise the outstanding contributions by innovators in various fields including education, Information and Communications Technology (ICT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data science.
- This award in India is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Skill India and the National Informatics Centre.
- Following are the projects of C-DOT which received this award:
- ASTR Project: ASTR (AI & Facial Recognition-powered Solution for Telecom SIM Subscriber Verification) is a game-changer in the fight against cybercrimes.
- Designed to analyse, identify, and eliminate fake/forged mobile connections, it’s a crucial step towards ensuring a secure telecom environment.
- CEIR (Central Equipment Identity Register) solution: CEIR helps revolutionise mobile security by detecting clone IMEIs, restricting the import of counterfeit mobile devices and also enabling the blocking and tracing of lost or stolen phones.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) product: India employs quantum mechanics to create an unbreakable cryptographic protocol even with Quantum computers.
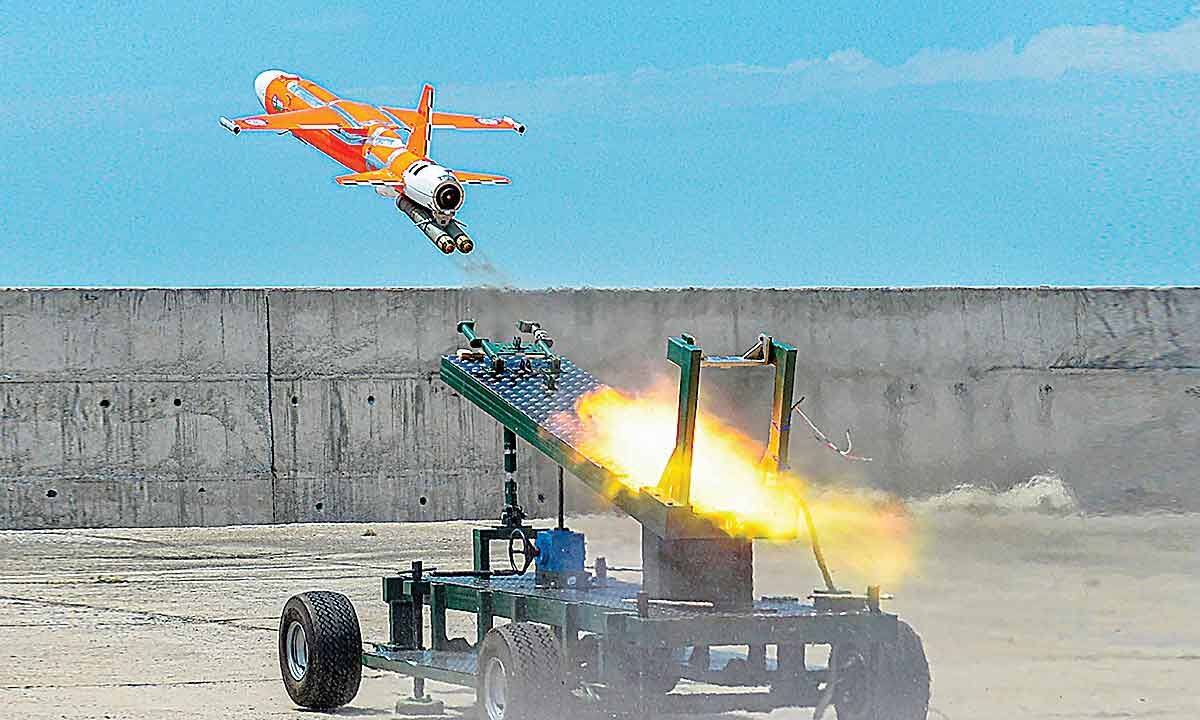
INDRA RV25: 240N
Hyderabad-based Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools Private Limited recently launched its fully indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”.

About the INDRA RV25: 240N
- It is a micro turbojet engine.
- It is designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with support from IIT Hyderabad.
- It has primarily been developed for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- The engine has applications in UAVs, air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and power generation in the future.
What is a turbojet engine?
- A turbojet engine is a jet engine which produces all of its thrust by ejecting a high-energy gas stream from the engine exhaust nozzle.
- In contrast to a turbofan or bypass engine, 100% of the air entering the intake of a turbojet engine goes through the engine core.
- Components: The component parts of a turbojet engine are the inlet, the gas turbine engine, consisting of a compressor, a combustion chamber and a turbine, and the exhaust nozzle.
- Working:
- Air is drawn into the engine through the inlet and compressed and heated by the compressor.
- Fuel is then added to the combustion chamber and ignited.
- The burning fuel adds energy to the exhaust stream by heating and expanding the air.
- Sufficient energy to drive the compressor is extracted from the exhaust stream by the turbine.
- The remainder of the exhaust energy is used to produce thrust, a process which is enhanced by the geometry of the exhaust nozzle.
- As the exhaust gas passes through the nozzle, it is accelerated to high speed as it expands, thus providing propulsion.
- The thrust produced by the engine can be selectively increased by incorporating an afterburner or re-heat into the engine design.
- Turbojet aircraft work on the principle of accelerating a relatively small mass of air to a high speed.
- As optimum efficiency is achieved when the speed of the accelerated air approximates that of the aircraft, turbojet engines do not reach peak efficiency until speeds approach Mach 2.
- Thus, turbojets have relatively poor propulsive efficiency at lower airspeeds, limiting their usefulness to high-speed aircraft.
Flue-Cured Tobacco
The government of India permits the sale of Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco on Tobacco Boards auction platform and waives off penalty on the sale of excess production of registered growers and unauthorised production of unregistered growers in Karnataka.

About the Flue-Cured Tobacco:
- Curing is a process by which the harvested tobacco leaf is made ready for the market.
- It is a well-standardised process especially in FCV tobacco to achieve the desirable qualities in the cured leaf along with the removal of moisture.
- There are three types of tobacco curing methods traditionally used: Air-Cured, Fire-Cured, and Flue-Cured.
- Each of the different curing methods results in a tobacco product that is distinguishable by both its nicotine content and its aroma.
- Why is Tobacco cured?
- To create smoking tobacco, the tobacco leaves need to be cured, or dried out.
- The wet, green tobacco leaves of a tobacco plant initially contain too much moisture to catch fire.
- They also have higher chlorophyll content. By releasing a certain amount of chlorophyll from the leaves during the drying-out process, the natural tannins come out giving the smoked tobacco its flavour and scent.
- Key characteristics of Flue-Cured Tobacco:
- Produces primarily cigarette tobacco
- Contains a high sugar content
- Contains medium to high levels of nicotine
- Rich in natural tannins which create its distinct mild and slightly sweet flavour and aroma
- In India Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco is mainly produced in India in 2 states, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI)
A recent study looked at the impact of stratospheric aerosol intervention (SAI) in mitigating global warming effects in West Asia (also known as the Middle East) and North Africa (MENA).

About the Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI):
- Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI), also known as Stratospheric Aerosol Injection, is a geoengineering or climate engineering approach that uses tiny reflective particles or aerosols to reflect sunlight into space in order to cool the planet and reverse or stop global warming.
- It aims to mimic the cooling effects of volcanic eruptions by injecting Sulphur dioxide (SO2) directly into the stratosphere, where it forms sunlight-reflecting sulphate aerosols.
- The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, often cited as the inspiration for this concept, deposited massive amounts of particulate matter and Sulphur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere.
- This aerosol layer was reported to have lowered average temperatures around the world by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) over the following few years.
- It is believed that as more radiation is scattered in the stratosphere by aerosols, less would be absorbed by the troposphere, the lower level of the atmosphere where weather primarily occurs.
- The production of such an artificial aerosol layer could be accomplished by shooting Sulphur particles into the stratosphere with cannons or dispersing them from balloons or other aircraft.
Key Facts about Aerosols:
- They are tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in air or gas.
- Aerosols can be natural, such as fog or gas from volcanic eruptions, or artificial, such as smoke from burning fossil fuels.
- Aerosol particles are either emitted directly into the atmosphere (primary aerosols) or produced in the atmosphere from precursor gases (secondary aerosols).
- Aerosol particles are tiny, but numerous, and often comprise a number of inorganic and organic substances.
- Particles with a diameter of less than 0.1 micrometre are sometimes referred to as Aitken nuclei.
- Visible forms of atmospheric aerosol plumes include smoke, smog, haze, and dust.
Garbhini-GA2
Researchers recently developed Garbhini-GA2, an India-specific artificial intelligence model to precisely determine the gestational age of a foetus.

About Garbhini-GA2:
- It is the first India-specific artificial intelligence (AI) model to precisely determine the age of a foetus in a pregnant woman in the second and third trimesters.
- It has been designed by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad.
- It is part of an interdisciplinary group for advanced research on birth outcomes – the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) India initiative (GARBH-Ini) programme.
- It is the first late-trimester GA estimation model to be developed and validated using Indian population data.
- The Garbhini-GA2 accurately estimates the foetus’ age, reducing error by almost three times.
- Accurate ‘Gestational Age’ (GA) is necessary for the appropriate care of pregnant women and for determining precise delivery dates.
- Once validated in pan-India cohorts, Garbhini-GA2 holds the potential to be widely deployed in clinics across the country, contributing to improved maternal and infant healthcare outcomes and reducing mortality rates.
Key Facts about Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- It is an autonomous institute of Biotechnology under the Ministry of Science and Technology, with the prime ideology of contributing most of its work beyond discovery and research.
- It was established in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana.
- It integrates multidisciplinary teams from the fields of medicine, science, and technology to harness translational knowledge for clinical research.
- It also facilitates social Innovation and entrepreneurship in the field of maternal and child healthcare.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
The ability of Generative AI models to “converse” with humans is due to something known as the Large Language Model, or LLM.
About Large Language Models (LLMs):
- A large language model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) program that can recognize and generate text, among other tasks.
- LLMs are trained on huge sets of data—hence the name “large.”
- LLMs are built on machine learning: specifically, a type of neural network called a transformer model.
- In simpler terms, an LLM is a computer program that has been fed enough examples to be able to recognize and interpret human language or other types of complex data.
- Many LLMs are trained on data that has been gathered from the Internet—thousands or millions of gigabytes’ worth of text.
- However, the quality of the samples impacts how well LLMs will learn natural language, so an LLM’s programmers may use a more curated data set.
- LLMs use a type of machine learning called deep learning in order to understand how characters, words, and sentences function together.
- Deep learning involves the probabilistic analysis of unstructured data, which eventually enables the deep learning model to recognize distinctions between pieces of content without human intervention.
- LLMs are then further trained via tuning: they are fine-tuned or prompt-tuned to the particular task that the programmer wants them to do, such as interpreting questions and generating responses, or translating text from one language to another.
- What are LLMs used for?
- LLMs can be trained to do a number of tasks. One of the most well-known uses is their application as generative AI: when given a prompt or asked a question, they can produce text in reply.
- The publicly available LLM ChatGPT, for instance, can generate essays, poems, and other textual forms in response to user inputs.
Extrajudicial Divorces
The Kerala High Court will reconsider its 2021 ruling on whether Muslim women lost their right to extrajudicial divorce by a way of Khula after the passage of the Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939.

Khula
- Khula refers to the right of a Muslim woman to unilaterally divorce her husband.
- This is similar to the right of talaq conferred upon Muslim men under Sharia law.
- The recognition of khula as a form of divorce stems directly from the Holy Qur’an.
In 1972, the case of K.C. Moyin vs. Nafeesa negated the right of Muslim women to invoke extra-judicial divorce in light of the Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939.
Shariat Act
- The Muslim Personal Law (Shariat) Application Act, 1937, recognizes both judicial and extrajudicial divorce.
- Section 2 – Recognizes all forms of extrajudicial divorce except faskh.
- Section 5 – Allows the dissolution of marriage by court in certain circumstances and allows a district judge to dissolve a marriage based on the woman’s plea.
1939 Act
- The 1939 Act was passed to clarify and consolidate the provisions of the law relating to the dissolution of marriage by Muslim women.
- The 1939 Act recognised the faskh route of extrajudicial divorce.
|
Quick Facts |
| Other forms of extrajudicial divorce available to Muslim women |
Illa
Zihar
Ithna Ashari
Lian
Talaq-e-Bidat
Nikah halala also known as tahleel marriage, is a practice in which a woman, after being divorced by triple talaq, marries another man, consummates the marriage, and gets divorced again in order to be able to remarry her former husband. Talaq-e-Tafwiz
Mubara’at
Faskh
|
Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB)
Union Minster of Jal Shakti has inaugurated the Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB) building at Noida.

- A memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed by Chief Ministers of Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and National Capital Territory of Delhi in 1994 provides for creation of a board called Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB).
Upper Yamuna refers to the stretch of Yamuna from its origin upto and including the Okhla Barrage at Delhi.
- UYRB is a sub-ordinate office under the Department of Water Resources, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Chairman – Union Minister / Minister of State for Water Resources
- Members – Chief Ministers of basin
- Secretary – Chairman, UYRB
- Functions – Regulation and supply of water from all storages and barrages upto and including Okhla barrage.
- Maintenance of minimum flow in Yamuna from ecological considerations.
- Monitoring return flows from the waters withdrawn:
- By Delhi for domestic use.
- By the States of Uttar Pradesh and Haryana for the purpose of silt exclusion.
- For Khara hydel station.
Basin States includes Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan and Delhi.
- Barrages – Tajewala/Hathnikund; Wazirabad; Okhla.
- Canal Networks – Western Yamuna Canal; Eastern Yamuna Canal; Agra Canal/Gurgaon Canal.
|
Yamuna River |
|
















/newsdrum-in/media/media_files/sBLMdZQDrrEakWKp163a.jpg)
























































)











/bnn/media/media_files/b4d93356a374de7b5db34e6f58eb38bde71e2eeea7ad6d36f481df3bba404a48.jpg)
































)

.jpg)